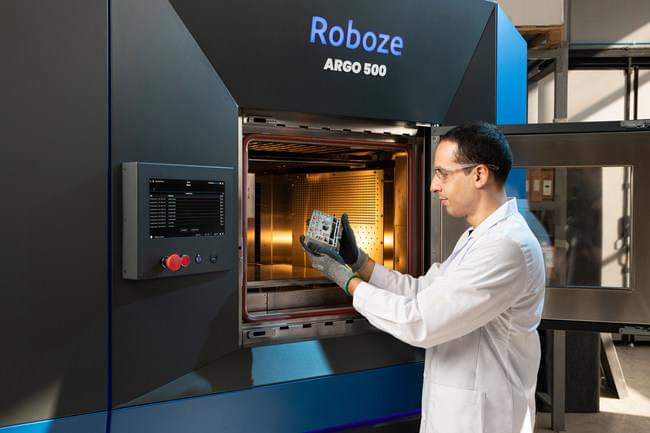
Siemens and Roboze have announced that they are collaborating to develop workflows dedicated to the industrialization of 3D printing. This includes an emphasis on expanding the use of the technology in energy, mobility, and aerospace. Though the exact nature of the agreement isn’t fully elucidated, it marks a significant shift for both firms.
Siemens is the largest industrial manufacturer in Europe, with a storied history spanning nearly two centuries and annual revenues totaling €62.3 billion, as of 2021. In contrast, Roboze is a comparatively new firm, established in Italy in 2013. The company has since built itself up into a leader in industrial-grade material extrusion 3D printers, earning such customers as Ducati, GE, and the U.S. Army.
The partners do not exactly clarify their intent except to say that they will work together to “increase the productivity, competitiveness and efficiency of manufacturers that have embarked on the path to the future of industry.” They do mention focusing on “digitalization and automation projects”.