The design could someday enable a fully decarbonized power grid, researchers say.
Engineers at MIT and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have designed a heat engine with no moving parts. Their new demonstrations show that it converts heat to electricity with over 40 percent efficiency — a performance better than that of traditional steam turbines.
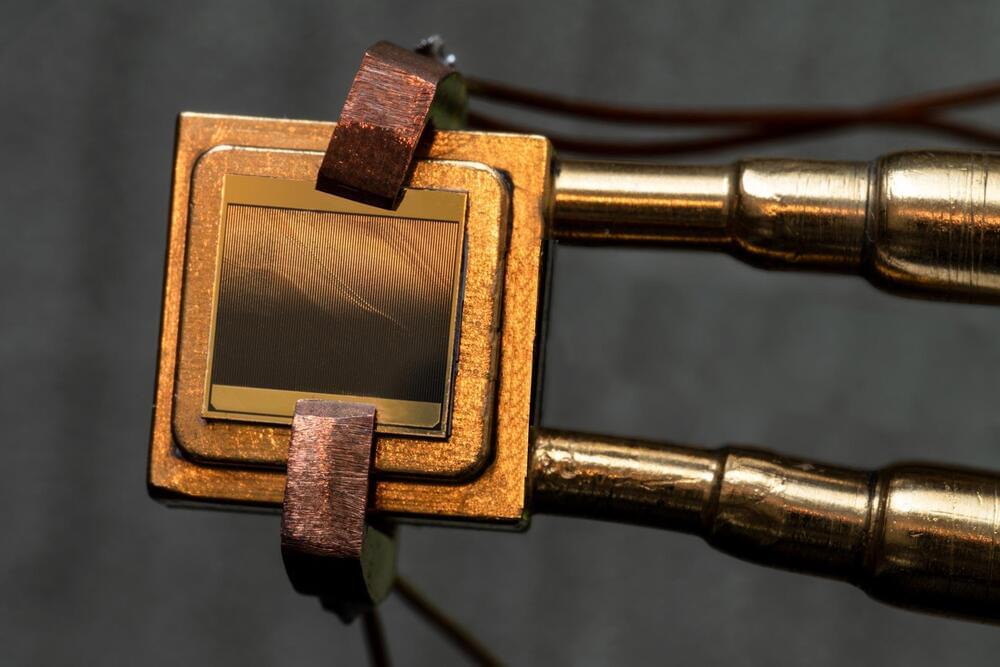
The heat engine is a thermophotovoltaic (TPV) cell, similar to a solar panel’s photovoltaic cells, that passively captures high-energy photons from a white-hot heat source and converts them into electricity. The team’s design can generate electricity from a heat source of between 1,900 to 2,400 degrees Celsius 0, or up to about 4,300 degrees Fahrenheit.