Current methods for cancer diagnosis are based on identifying biomarkers — molecules that reveal a particular state or process in the body – produced by the tumor or associated proteins. Not surprisingly, these markers are more abundant once the tumor has already developed significantly. And the more advanced the tumor, the more difficult it is to find effective treatment options.
Now, a research team has developed a test that can detect early-stage solid tumors with just a blood sample. In addition, the test also provides information relevant to the choice of treatment.
To achieve this early detection, the team focused the test not on the markers produced by the tumor, but on the body’s defensive reaction to the cancer. Since the 19th century it has been known that the emergence of cancer cells causes changes in the immune system, and it was also known that these changes are more intense in cancer’s earliest stages. But they had never been used for diagnosis. The new study focuses on them, specifically on the changes in blood proteins derived from cancer’s disruption of the immune system.
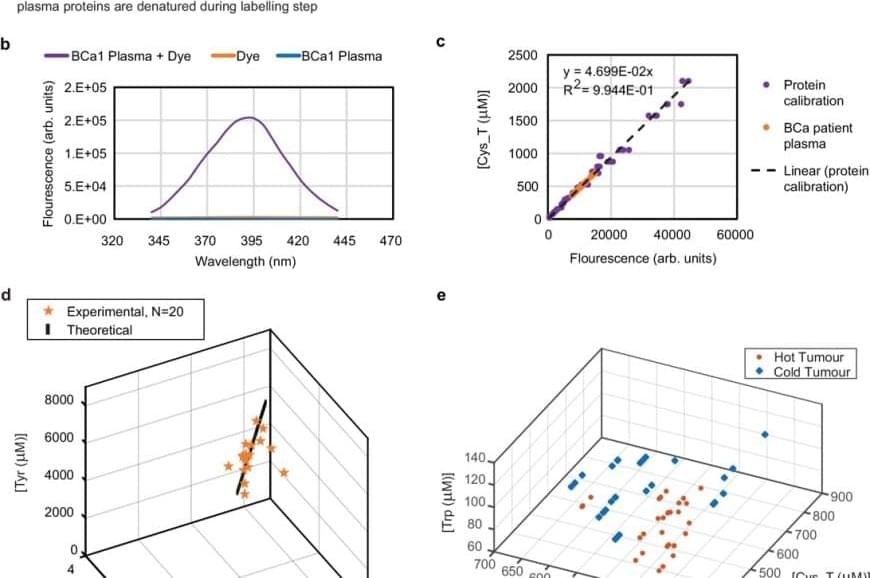
But this approach posed a problem to the team: human blood contains more than 5,000 proteins, which makes it extremely difficult to analyze. So they used bioinformatics analysis and narrowed the scope of the study to five amino acids: lysine, tryptophan, tyrosine, cysteine and cysteine not bound to disulphide bonds.
They then subjected the sample to reactions that emit fluorescence when light is applied to them — fluorogenic reactions — and revealed the exact concentration of each of these amino acids in the plasma. Using the artificial intelligence tool machine learning, they identified patterns in these concentrations that could be translated into diagnostic signals.
As they explain in the published article, they applied this technique to samples from 170 patients and were able to identify 78% of cancers with a 0% false positive rate.