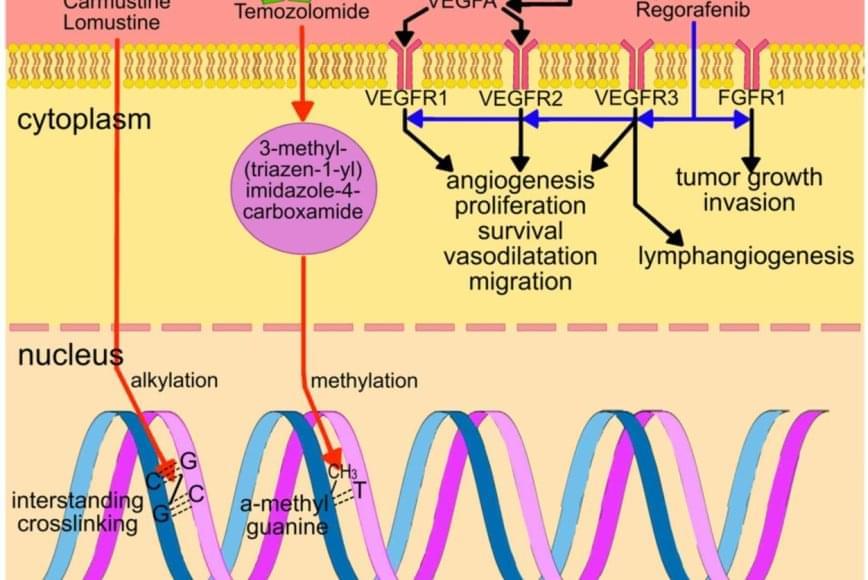
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a highly aggressive and malignant brain tumor with a poor prognosis. Treatment options are limited, and the development of effective therapeutics is a major challenge. Here are some current and emerging therapeutic strategies for GBM:
Current Therapies 1. Surgery: Surgical resection is the primary treatment for GBM, aiming to remove as much of the tumor as possible. 2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is used to kill remaining tumor cells after surgery. 3. Temozolomide (TMZ): TMZ is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat GBM, often in combination with radiation therapy. 4. Bevacizumab (Avastin): Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to inhibit angiogenesis.
Emerging Therapies 1. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors) and cancer vaccines, aim to stimulate the immune system to attack GBM cells. 2. Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular pathways involved in GBM, such as the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. 3. Gene Therapy: Gene therapies aim to introduce genes that can help kill GBM cells or inhibit tumor growth. 4. Oncolytic Viruses: Oncolytic viruses are engineered to selectively infect and kill GBM cells. 5. CAR-T Cell Therapy: CAR-T cell therapy involves genetically modifying T cells to recognize and attack GBM cells. 6. Small Molecule Inhibitors: Small molecule inhibitors target specific proteins involved in GBM, such as EGFR, PDGFR, and BRAF.