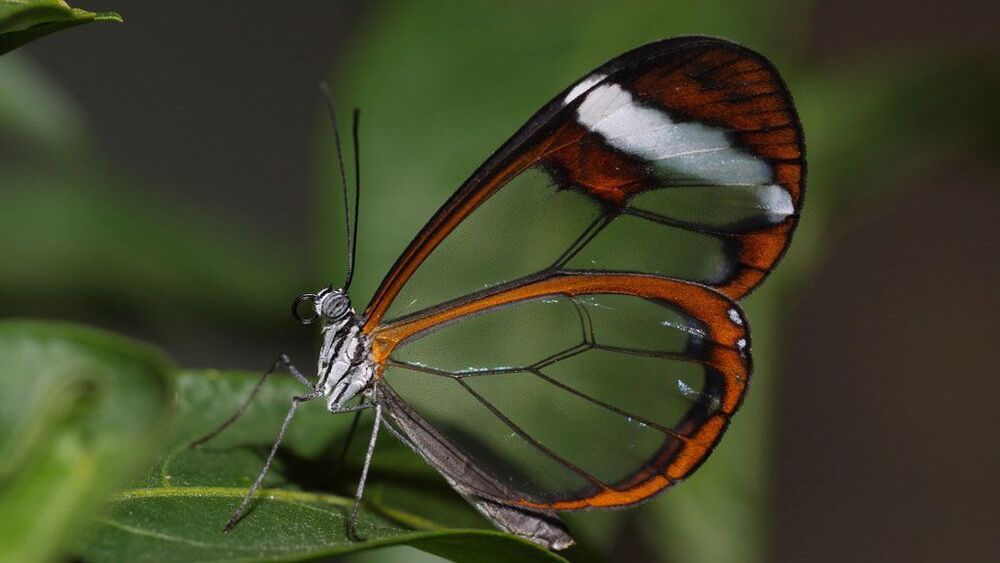
Close-up views of glasswing butterflies reveal the secrets behind the insect’s see-through wings: sparse, spindly scales and a waxy coating.




Most cases of Parkinson’s disease are considered idiopathic – they lack a clear cause. Yet researchers increasingly believe that one factor is environmental exposure to trichloroethylene (TCE), a chemical compound used in industrial degreasing, dry-cleaning and household products such as some shoe polishes and carpet cleaners.
To date, the clearest evidence around the risk of TCE to human health is derived from workers who are exposed to the chemical in the work-place. A 2008 peer-reviewed study in the Annals of Neurology, for example, found that TCE is “a risk factor for parkinsonism.” And a 2011 study echoed those results, finding “a six-fold increase in the risk of developing Parkinson’s in individuals exposed in the workplace to trichloroethylene (TCE).”
Dr Samuel Goldman of The Parkinson’s Institute in Sunnyvale, California, who co-led the study, which appeared in the Annals of Neurology journal, wrote: “Our study confirms that common environmental contaminants may increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s, which has considerable public health implications.” It was off the back of studies like these that the US Department of Labor issued a guidance on TCE, saying: “The Board recommends […] exposures to carbon disulfide (CS2) and trichloroethylene (TCE) be presumed to cause, contribute, or aggravate Parkinsonism.”


At some point in the next few months, Microsoft will start encouraging people to upgrade to Windows 11. If we’re lucky, the company will have learned from its “Get Windows 10” debacle and will not launch a glorified malware application. Regardless of how the company approaches the topic, however, you can bet we’re all going to get blitzed with advertising one way or another.
But that lovely event/hostage-taking is still in the future. For now, Microsoft would appreciate it if everyone stopped downloading the leaked version of Windows 11 that popped up last week. In the process, the OS developer has confirmed what everybody already knew — Windows 11 is, in fact, an official thing that’s happening.
There are now several monoclonal antibodies, identical copies of a therapeutic antibody produced in large numbers, that are authorized for the treatment of COVID-19. But in the ongoing effort to beat this terrible pandemic, there’s plenty of room for continued improvements in treating infections with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
With this in mind, I’m pleased to share progress in the development of a specially engineered therapeutic antibody that could be delivered through a nasal spray. Preclinical studies also suggest it may work even better than existing antibody treatments to fight COVID-19, especially now that new SARS-CoV-2 “variants of concern” have become increasingly prevalent.
These findings come from Zhiqiang An, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and Pei-Yong Shi, The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, and their colleagues. The NIH-supported team recognized that the monoclonal antibodies currently in use all require time-consuming, intravenous infusion at high doses, which has limited their use. Furthermore, because they are delivered through the bloodstream, they aren’t able to reach directly the primary sites of viral infection in the nasal passages and lungs. With the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, there’s also growing evidence that some of those therapeutic antibodies are becoming less effective in targeting the virus.-Dr Francis Collins.

The EU’s data protection agencies on Monday called for an outright ban on using artificial intelligence to identify people in public places, pointing to the “extremely high” risks to privacy.
In a non-binding opinion, the two bodies called for a “general ban” on the practice that would include “recognition of faces, gait, fingerprints, DNA, voice, keystrokes and other biometric or behavioural signals, in any context”.
Such practices “interfere with fundamental rights and freedoms to such an extent that they may call into question the essence of these rights and freedoms,” the heads of the European Data Protection Board and the European Data Protection Supervisor said.
In 2013, François Englert and Peter Higgs won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, which was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle by the A Toroidal LHC Apparatus (ATLAS) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiments at The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)’s Large Hadron Collider in 2012. The Higgs mode or the Anderson-Higgs mechanism (named after another Nobel Laureate Philip W Anderson), has widespread influence in our current understanding of the physical law for mass ranging from particle physics—the elusive “God particle” Higgs boson discovered in 2012 to the more familiar and important phenomena of superconductors and magnets in condensed matter physics and quantum material research.
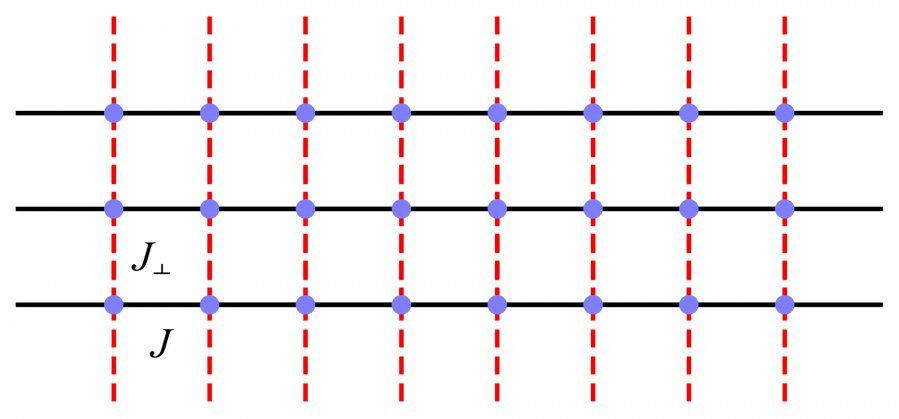
The Higgs mode, together with the Goldstone mode, is caused by the spontaneous breaking of continuous symmetries in the various quantum material systems. However, different from the Goldstone mode, which has been widely observed via neutron scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies in quantum magnets or superconductors, the observation of the Higgs mode in the material is much more challenging due to its usual overdamping, which is also the property in its particle physics cousin—the elusive Higgs boson. In order to weaken these damping, two paths have been suggested from the theoretical side, through quantum critical points and dimensional crossover from high dimensions to lower ones. For , people have achieved several remarkable results, whereas there are few successes in.
To fulfill this knowledge gap, from 2020, Mr Chengkang Zhou, then a first-year Ph.D. student, Dr. Zheng Yan and Dr. Zi Yang Meng from the Research Division for Physics and Astronomy of the University of Hong Kong (HKU), designed a dimensional crossover setting via coupled spin chains. They applied the quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) simulation to investigate the excitation spectra of the problem. Teaming up with Dr. Hanqing Wu from the Sun Yat-Sen University, Professor Kai Sun from the University of Michigan, and Professor Oleg A Starykh from the University of Utah, they observed three different kinds of collective excitation in the quasi-1D limit, including the Goldstone mode, the Higgs mode and the scalar mode. By combining numerical and analytic analyses, they successfully explained these excitations, and in particular, revealed the clear presence of the Higgs mode in the quasi-1D quantum magnetic systems.


In case you need the information.
The CDC designated the delta variant of the coronavirus — first identified in India — as a “variant of concern” June 15, reigniting attention on the race between vaccines and coronavirus variants.
The new classification comes amid mounting evidence that the variant spreads more easily than existing strains and causes more severe infections, the CDC said in a June 15 statement to Becker’s. People infected by the delta variant may have twice the risk of hospitalization of people infected with the alpha variant first identified in the U.K., according to research released this week from Scotland. In May, the U.K.’s Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies also said the delta variant could be up to 50 percent more transmissible than alpha, which is currently the dominant strain in the U.S., though research is still preliminary.
The delta variant now accounts for about 10 percent of COVID-19 cases in the U.S. and could become the nation’s dominant strain by this fall, according to Scott Gottlieb, MD, a former FDA commissioner who now serves on Pfizer’s board of directors.