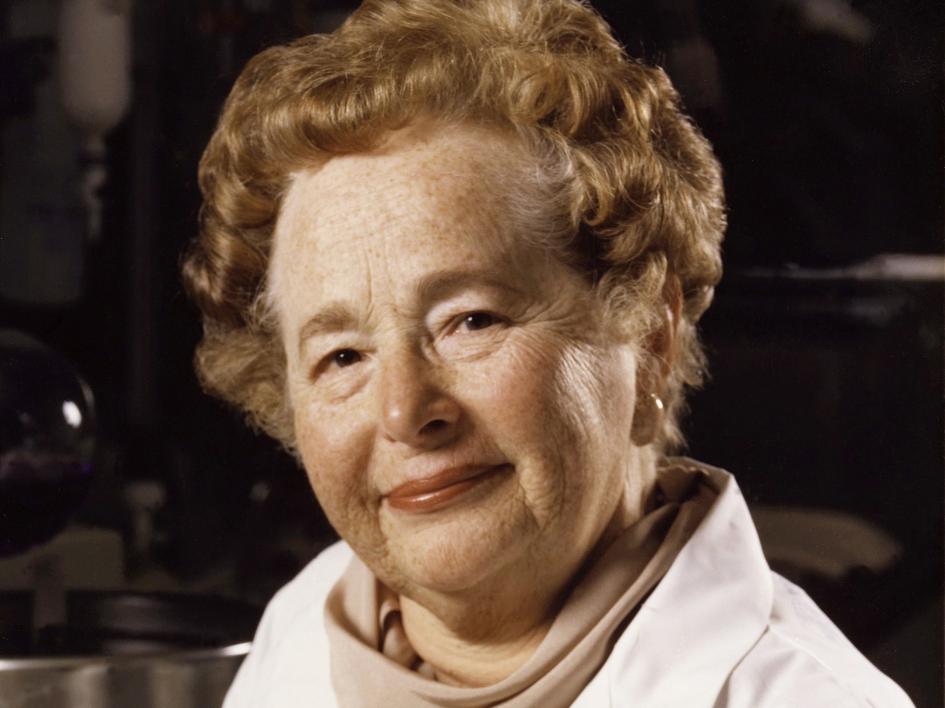
Fifty years ago, few scientists believed a drug could fight viruses with low side effects. Then Gertrude Elion showed the doubters “what I could do on my own.”
Brad Porter, who recently defended working conditions at Amazon warehouses, leaves to run Scale’s tech division.
Adapting the Intelligence Community
As machines become the primary collectors, analysts, consumers, and targets of intelligence, the entire U.S. intelligence community will need to evolve. This evolution must start with enormous investments in AI and autonomization technology as well as changes to concepts of operations that enable agencies to both process huge volumes of data and channel the resulting intelligence directly to autonomous machines. As practically everything becomes connected via networks that produce some form of electromagnetic signature or data, signals intelligence in particular will need to be a locus of AI evolution. So will geospatial intelligence. As satellites and other sensors proliferate, everything on earth will soon be visible at all times from above, a state that the federal research and development center Aerospace has called the “GEOINT Singularity.” To keep up with all this data, geospatial intelligence, like signals intelligence, will need to radically enhance its AI capabilities.
The U.S. intelligence community is currently split up into different functions that collect and analyze discrete types of intelligence, such as signals or geospatial intelligence. The RIA may force the intelligence community to reassess whether these divisions still make sense. Electromagnetic information is electromagnetic information, whether it comes from a satellite or an Internet of Things device. The distinction in origin matters little if no human ever looks at the raw data, and an AI system can recognize patterns in all of the data at once. The division between civilian and military intelligence will be similarly eroded, since civilian infrastructure, such as telecommunications systems, will be just as valuable to military objectives as military communications systems. Given these realities, separating intelligence functions may impede rather than aid intelligence operations.
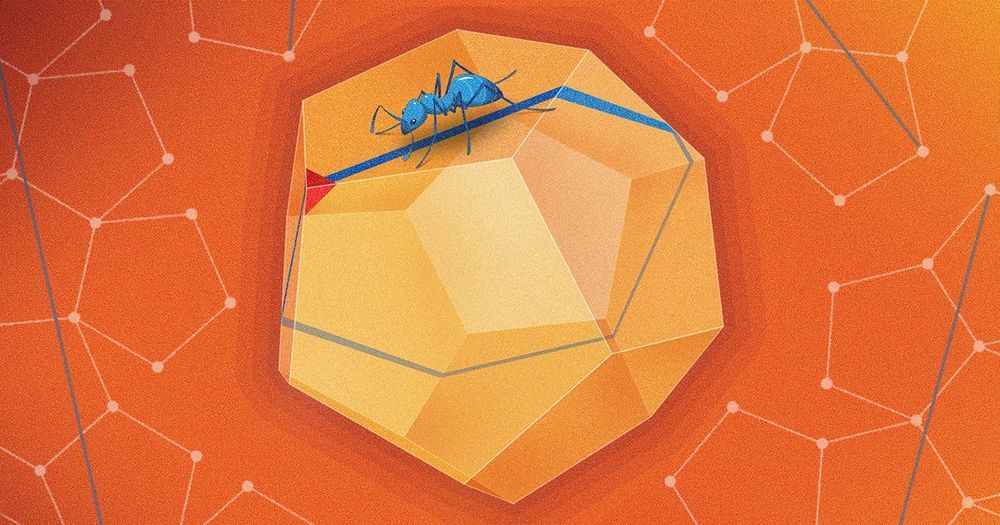
Three mathematicians have resolved a fundamental question about straight paths on the 12-sided Platonic solid.
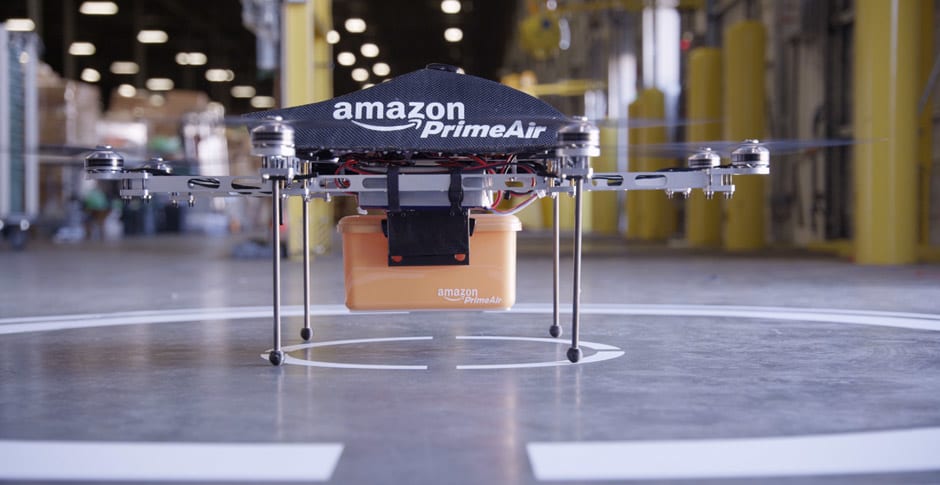
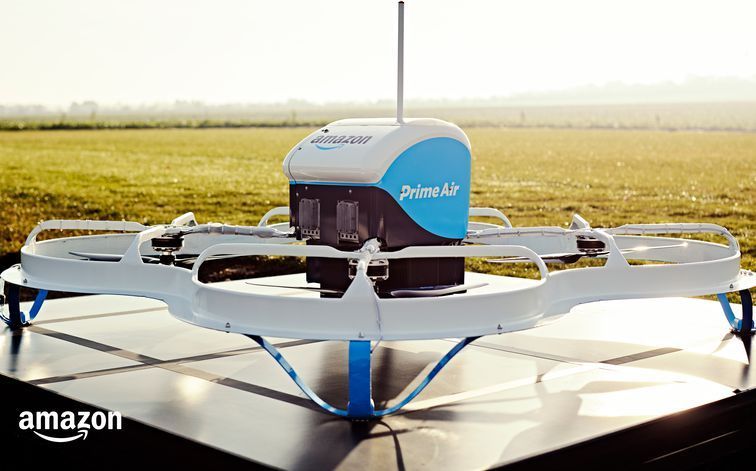
Amazon received federal approval to operate its fleet of Prime Air delivery drones, the Federal Aviation Administration said Monday, a milestone that allows the company to expand unmanned package delivery.
The approval will give Amazon broad privileges to “safely and efficiently deliver packages to customers,” the agency said. The certification comes under Part 135 of FAA regulations, which gives Amazon the ability to carry property on small drones “beyond the visual line of sight” of the operator.
Amazon said it will use the FAA’s certification to begin testing customer deliveries. The company said it went through rigorous training and submitted detailed evidence that its drone delivery operations are safe, including demonstrating the technology for FAA inspectors.
Amazon Prime Air has cleared a regulatory hurdle, moving the online retail giant one step closer to dropping packages off at your doorstep with drones. The US Federal Aviation Administration on Saturday issued Amazon Prime Air a “a Part 135 air carrier certificate,” allowing it to begin commercial drone deliveries in the US.
“Amazon Prime Air’s concept uses autonomous [unmanned aircraft systems] to safely and efficiently deliver packages to customers,” said a spokesperson for the FAA on Monday. “The FAA supports innovation that is beneficial to the public, especially during a health or weather-related crisis.”
Amazon and other companies are trying to make drones the future of deliveries.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
The evolving understanding of cancer genetics is allowing for clinicians to look at how to move rare cancer treatments, and identifications, forward.
Live coverage: Rocket Lab launches Capella’s first commercial radar satellite – Spaceflight Now.
Live coverage of the countdown and launch of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket from Launch Complex 1 on Mahia Peninsula in New Zealand carrying Capella Space’s Sequoia radar remote sensing satellite. Text updates will appear automatically below. Follow us on Twitter.
Rocket Lab’s live video webcast begins approximately 15 minutes prior to launch, and will be available on this page.
Elon musk’s spacex vs jeff bezos’s blue origin: which space project will dominate the cosmos?