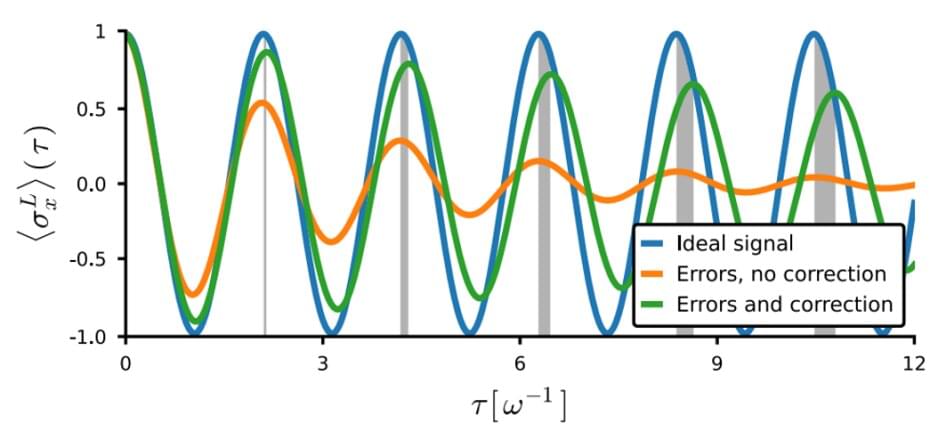
Whether a computer could ever pass for a living thing is one of the key challenges for researchers in the field of Artificial Intelligence. There have been vast advancements in AI since Alan Turing first created what is now called the Turing Test—whether a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. However, machines still struggle with one of the fundamental skills that is second nature for humans and other life forms: lifelong learning. That is, learning and adapting while we’re doing a task without forgetting previous tasks, or intuitively transferring knowledge gleaned from one task to a different area.
Now, with the support of the DARPA Lifelong Learning Machines (L2M) program, USC Viterbi researchers have collaborated with colleagues at institutions from around the U.S. and the world on a new resource for the future of AI learning, defining how artificial systems can successfully think, act and adapt in the real world, in the same way that living creatures do.
The paper, co-authored by Dean’s Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Alice Parker and Professor of Biomedical Engineering, and of Biokinesiology and Physical Therapy, Francisco Valero-Cuevas and their research teams, was published in Nature Machine Intelligence, in collaboration with Professor Dhireesha Kudithipudi at the University of Texas at San Antonio, along with 22 other universities.