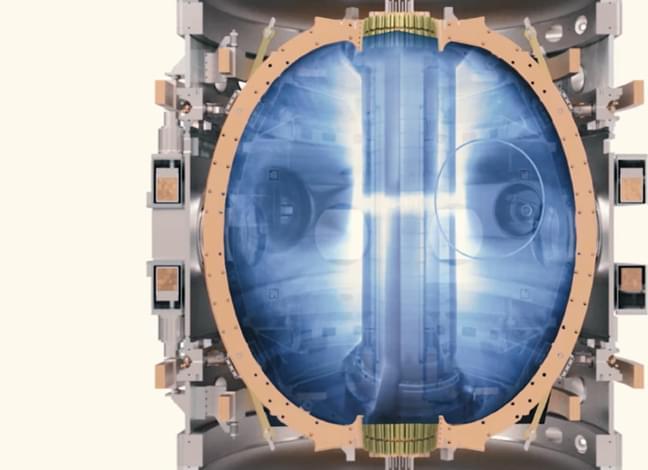
Tokamak Energy, based near Oxford, UK, has demonstrated a world-first with its privately-funded ST40 spherical tokamak. The reactor achieved a plasma temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius, the threshold required for commercial fusion energy.
At nearly seven times hotter than the centre of the Sun, this is by far the highest temperature ever generated within a spherical tokamak and also by any privately-funded tokamak. The ST40 had previously achieved a temperature of 15 million degrees in June 2018. While several government laboratories have reported plasma temperatures above 100 million degrees in conventional tokamaks, this milestone has been achieved in just five years, for a cost of less than £50m ($70m) and in a much more compact fusion device. This provides further proof that spherical tokamaks are a viable route to the delivery of clean, secure, low cost, scalable fusion energy.