Scientists have identified a previously unknown group of inhibitory neurons defined by the adhesion molecule Kirrel3.



Apple’s prioritization of shareholder value through massive share buybacks over investing in innovation and R&D may be a strategic misstep that could hinder its future success and allow competitors to gain an edge, particularly in emerging markets like AI
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Innovation and Investment.
🔬 Q: How could Apple’s buyback program have been used differently? A: A: Apple’s $700 billion share buyback over the past decade could have been invested in R&D to develop innovative products like a car, potentially yielding greater long-term value.
🤖 Q: What is Apple’s current stance on AI development? A: Apple’s inaction in AI is notable, with Siri’s performance declining over time, indicating a lack of focus on this crucial technology sector.
Product Development and Market Strategy.
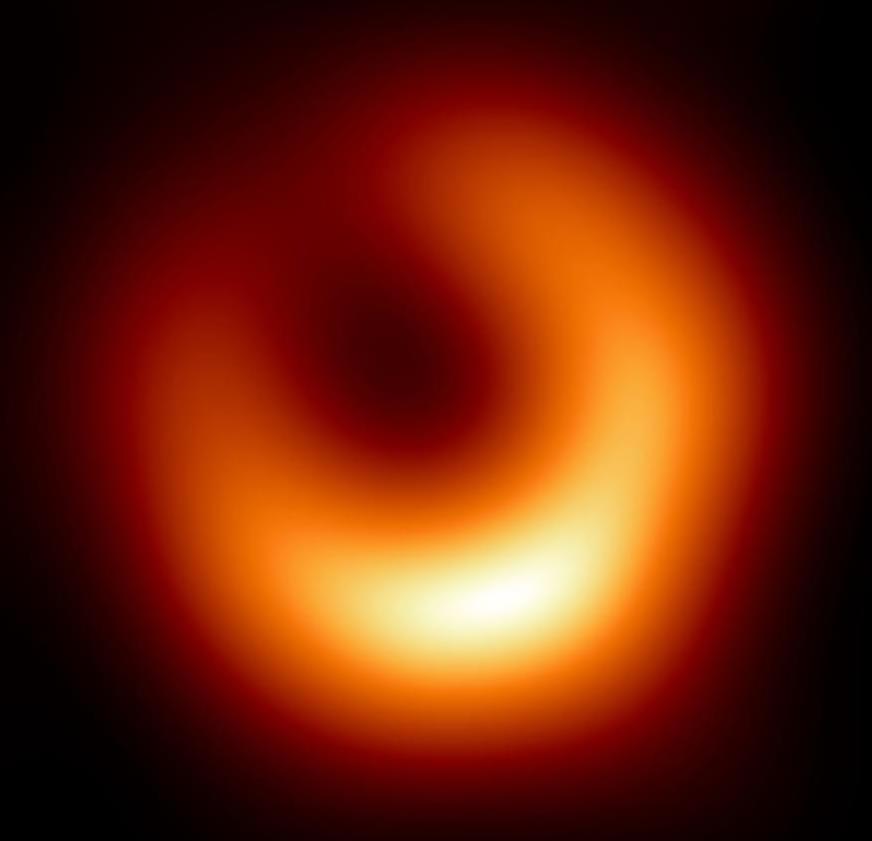

“I think it’s reasonable to expect we could find a nearby one within the next decade,” Bambi said in the statement.
Today, building the necessary laser array would cost around $1.1 trillion, far beyond the reach of current science budgets. But if trends in technology continue, Bambi estimates that cost could fall to around one billion euros within 30 years, putting it on par with current flagship space missions.
“We don’t have the technology now,” Bambi said in the statement. “But in 20 or 30 years, we might.”
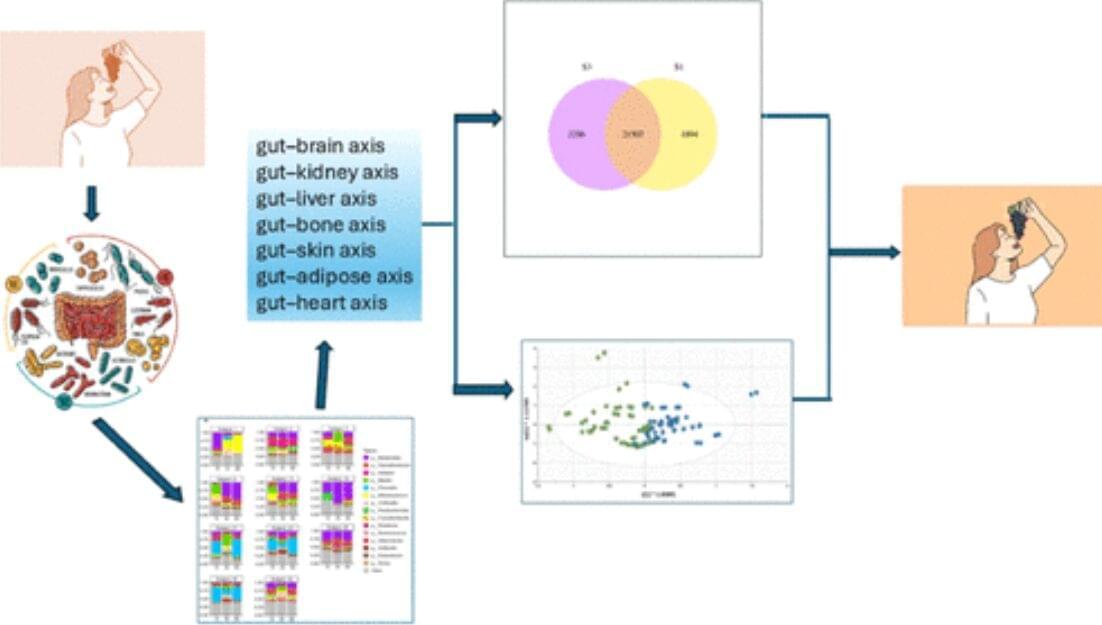
Fresh grapes contain a potent mix of over 1,600 compounds that benefit heart, brain, skin, and gut health. New evidence suggests they deserve official superfood recognition, with benefits even at the genetic level.
A new article appearing in the current issue of the peer-reviewed Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry explores the concept of “superfoods” and makes a case that fresh grapes have earned what should be a prominent position in the superfood family. The author, leading resveratrol and cancer researcher John M. Pezzuto, Ph.D., D.Sc., Dean of the College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences at Western New England University, brings forth an array of evidence to support his perspective on this issue.
As noted in the article, the term “superfood” is a common word without an official definition or established criteria. Mainstream superfoods are typically part of the Mediterranean Diet and generally rich in natural plant compounds that are beneficial to a person’s health. Pezzuto addresses the broader topic of superfoods in detail, then makes the scientific case for grapes, noting that fresh grapes are underplayed in this arena and often not included with mention of other similar foods, such as berries.

Berzerkers.
Get a free trial TODAY with Hostinger Horizons! Use code ISAACARTHUR to get 10% off your first month here: http://hostinger.com/isaacarthur.
The silence of the stars might be hiding more than an absence of life — it might conceal ancient machines, monuments, and traps from civilizations long vanished. Today, we explore these eerie cosmic echoes and the risks of unearthing them.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Group: / 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Ancient Alien Artifacts — Cosmic Relics Of A Dangerous Past Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Script Editor: Lukas Konecny Graphics: Sergio Botero, Udo Schroeter Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator Chapters 0:00 Intro 1:42 The Cosmic Junkyard 3:56 What Survives When Civilizations Don’t 9:31 Dangerous by Design 12:04 False Gifts and Poisoned Knowledge 15:37 We Might Already Be Inside One 19:21 Detecting the Undetectable 21:34 The Human Reaction 23:31 The Million-Year Message 24:55 Galactic Cemeteries 26:53 The Ghosts We Might Meet 28:43 The Next Artifacts.
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Ancient Alien Artifacts — Cosmic Relics Of A Dangerous Past.
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Script Editor: Lukas Konecny.
Graphics: Sergio Botero, Udo Schroeter.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Chapters.
0:00 Intro.
1:42 The Cosmic Junkyard.
3:56 What Survives When Civilizations Don’t.
9:31 Dangerous by Design.
12:04 False Gifts and Poisoned Knowledge.
15:37 We Might Already Be Inside One.
19:21 Detecting the Undetectable.
21:34 The Human Reaction.
23:31 The Million-Year Message.
24:55 Galactic Cemeteries.
26:53 The Ghosts We Might Meet.
28:43 The Next Artifacts
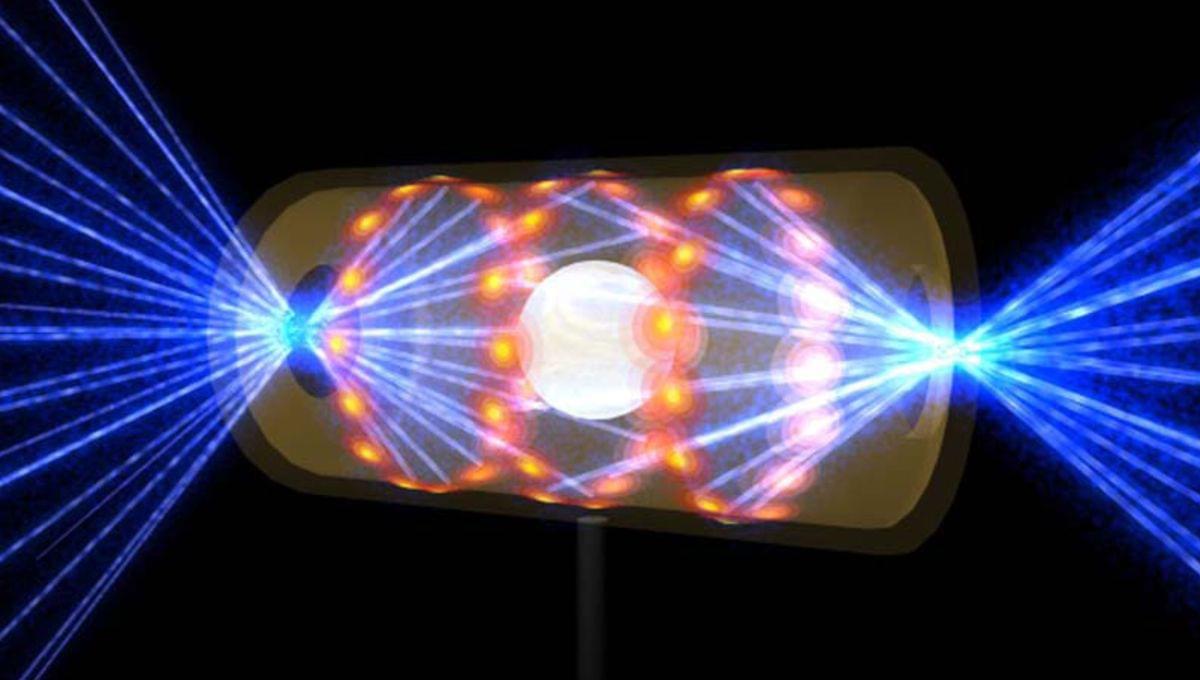
What this means in real time is that researchers using these maps do not know if there are any errors or issues ahead of them, nor do they know if these errors are part of the research design. Nevertheless, this is all they have to work with, so they have to make a decision based on this limited information, and doing so will always have high costs in terms of the ignition attempt, which is expensive.
To overcome this, the team at the NIF created a new way to create these “maps” by merging past data with high-fidelity physics simulations and the knowledge of experts. This was then fed into a supercomputer that ran statistical assessments in the course of over 30 million CPU hours. Effectively, this allows the researchers to see all the ways that things can go wrong and to pre-emptively assess their experimental designs. This saves a lot of time and, more importantly, money.
The team tested this approach on an experiment they ran in 2022, and, after a few changes to the model’s physics, was able to predict the outcome with an accuracy above 70 percent.