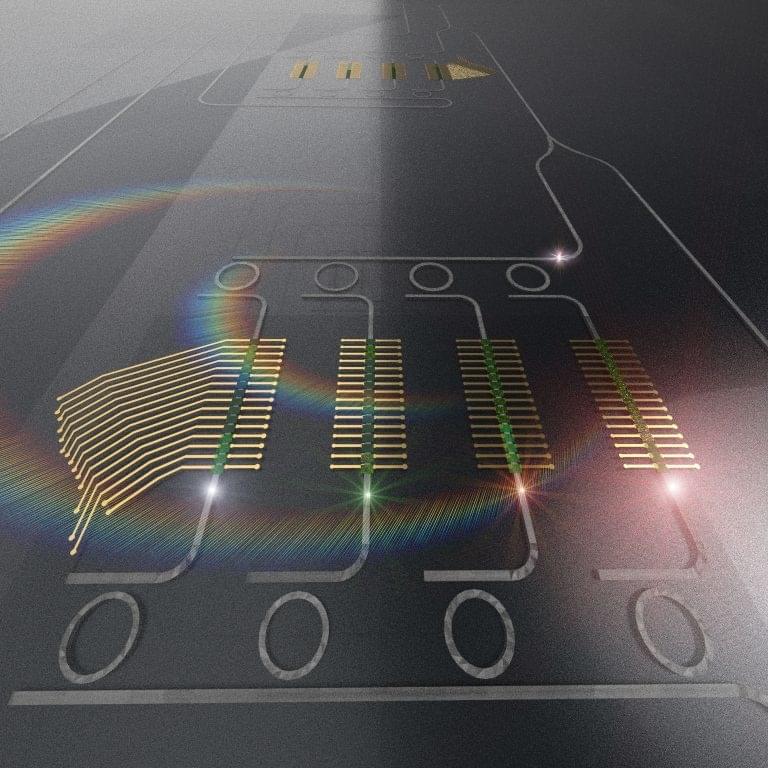
Researchers discover how to use light instead of electricity to advance artificial intelligence.


In celebration of Pride Month, Inara, one of our moderators, is fundraising to pay for her transition surgery. I donated.
Gender dysphoria is the term used to describe a sense of discomfort or distress that a person may experience because of a mismatch between their gender identity and their sex assigned at birth. Methods of relieving gender dysphoria include transitioning socially (pronoun usage, name change, etc.) and physically (surgery).
I have medical insurance but it does not cover trans healthcare. Yes, we are still fighting for trans rights! I need allies willing to take action on my behalf.

In this bold new future, we have discovered the best possible use for artificial intelligence: making more pigs.

Osaka University researchers discovered that adjusting lifestyle behaviors can have a significant impact on lifespan, even in those with chronic health issues.
Ever since the beginning of civilization, humans have wanted to live longer. Whether it be the Fountain of Youth, Gilgamesh’s secret plant of immortality, or the elixir of life, the idea of immortality is incredibly prevalent in humanity’s oldest and most well-known stories.
Unfortunately, immortality is only a myth. The average lifespan in the United States is nearly 79 years and it is unlikely to increase dramatically in the next few years. Still, scientists have been researching how to increase our longevity and have found promising results.


It rarely makes the news that SpaceX has to fix stuff because they generally fix it within a few weeks and that is not considered newsworthy.
Anyway, at the moment the next Cargo Dragon flight is being delayed due to a thruster propellant leak and the next Crew Dragon capsule has a defective heatshield that is going to have to be replaced before launch. (The heatshield is less of an issue as the flight isn’t until September anyway.)
This Cargo Dragon has flown twice before so it is interesting that it suddenly decided to leak. Its thruster fuel is extra explosive, so SpaceX will need to figure this out. (3 years ago, a Crew Dragon was destroyed by such a leak during testing.)
Misplaced hypergols are not something one messes around with.

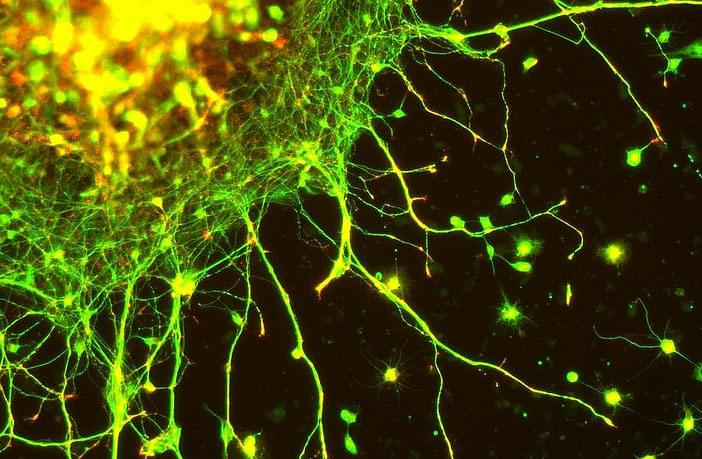
To assess whether a compound holds promise for treating a disease, researchers usually begin by studying its use in animals. This allows us to see if the compound has a chance of curing the disease.
Animal models, however, rarely reproduce all aspects of a disease. The alternative is to represent the disease in cell cultures. While at first glance, Petri dishes look quite different from a person with a disease, the reality could be quite different when you look at them more closely.
Alzheimer’s has been cured more than 400 times in laboratories. How then can we still consider Alzheimer’s to be incurable? The reason is that it has only been cured in animals.