Elisabeth Schirmer, Stefan Schuster and Peter Machnik investigated the effects of bisphenols A and S on neuronal functioning. Using in vivo recordings in goldfish they demonstrate that basic neuronal properties such as action potentials and synaptic transmission are perturbed after chronic exposure to bisphenols.
Recent work has shown that human auditory cortex contains neural populations anterior and posterior to primary auditory cortex that respond selectively to music. However, it is unknown how this selectivity for music arises. To test whether musical training is necessary, we measured fMRI responses to 192 natural sounds in 10 people with almost no musical training. When voxel responses were decomposed into underlying components, this group exhibited a music-selective component that was very similar in response profile and anatomical distribution to that previously seen in individuals with moderate musical training. We also found that musical genres that were less familiar to our participants (e.g., Balinese gamelan) produced strong responses within the music component, as did drum clips with rhythm but little melody, suggesting that these neural populations are broadly responsive to music as a whole. Our findings demonstrate that the signature properties of neural music selectivity do not require musical training to develop, showing that the music-selective neural populations are a fundamental and widespread property of the human brain.
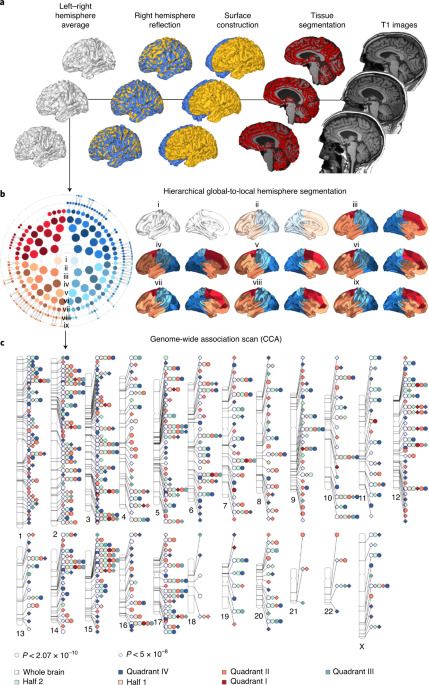
A multivariate genome-wide association study highlighting loci that influence both face and brain shape suggesting shared developmental axes during early embryogenesis. These loci did not overlap with those governing behavioral–cognitive traits or neuropsychiatric risk indicating divergence between early brain development and cognitive function.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=yPtL1rM6GF0&feature=share
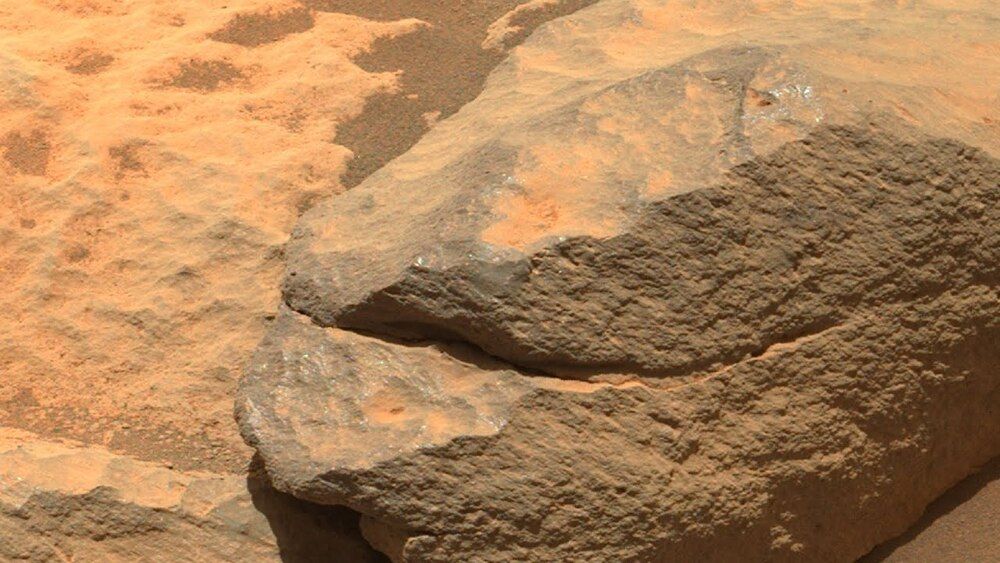
On April 14, 2021 NASA’s Perseverance Rover sent amazing images of Mars’s rocks captured by Mastcam-Z. Several rocks has interesting erosion component to be analyzed. There are also diverse aeolian processes that, in addition to dune forms, result in small abrasion forms on exposed rocks. Rover strongly uses Mastcam-Z. That is a pair of cameras that takes color images and video, three-dimensional stereo images, and has a powerful zoom lens. Like the Mastcam cameras on the Curiosity rover, Mastcam-Z on Mars 2020 consists of two duplicate camera systems mounted on the mast that stands up from the rover deck. The cameras are next to each other and point in the same direction, providing a 3D view similar to what human eyes would see, only better. They also have a zoom function to see details of faraway targets.
Credit: nasa.gov, NASA/JPL-Caltech, NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU
Source for NASA’s Perseverance Mars mission: https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/spacecraft/rover/
#mars #perseverance #news
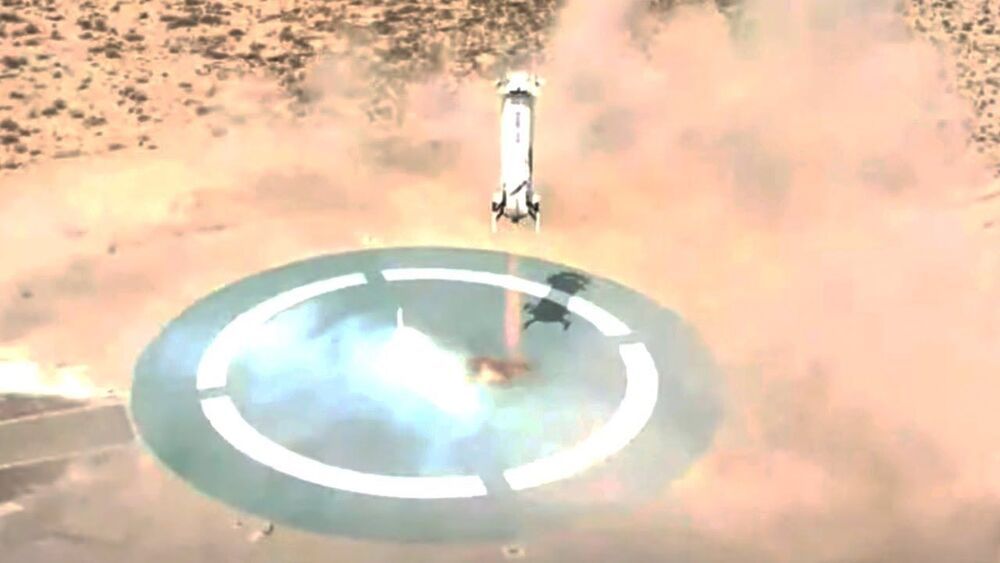
Blue Origin launched an uncrewed test flight of its New Shepard suborbital vehicle on April 14, 2021 from their West Texas facility. The capsule and rocket both landed several minutes after launch. The private spaceflight company complete an ‘astronaut rehearsal’ prior to the flight with future crew members boarding the capsule temporarily. Full Story: https://www.space.com/blue-origin-new-shepard-ns-15-launch-landing-success.
Credit: Blue Origin
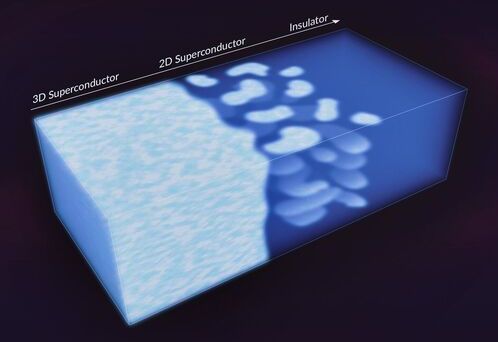
Creating a two-dimensional material, just a few atoms thick, is often an arduous process requiring sophisticated equipment. So scientists were surprised to see 2D puddles emerge inside a three-dimensional superconductor—a material that allows electrons to travel with 100% efficiency and zero resistance—with no prompting.
Within those puddles, superconducting electrons acted as if they were confined inside an incredibly thin, sheet-like plane, a situation that requires them to somehow cross over to another dimension, where different rules of quantum physics apply.
“This is a tantalizing example of emergent behavior, which is often difficult or impossible to replicate by trying to engineer it from scratch,” said Hari Manoharan, a professor at Stanford University and investigator with the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, who led the research.
Physix World – What is Physix?
Posted in climatology, government
In a Universal-nutshell, Physix assists the World (People, Government, Corporations, Non-Profits, Climate, Nature, Technology) in Making it Better!
Quality Vote or Q-vote.
Is an anonymous feedback voting and posting metric, via the scale as shown. It will display wave length patterns in how people feel on various topics after a user has voted on it. Eventually the team plans to allow commenting, that will also enable you to take a color rating feedback (timestamps) based on your comment, and others as well. This will give weighted value to these timestamped ratings comments when in competition with many on one post. It is currently in working alpha prototype testing mode now.
In an attempt to better track users and predict their search habits, Google Chrome has developed FLoC (Federated Learning of Cohorts). FLoC provides visibility into user data to any website that desires this information.
In fact, FLoC places each user in an ID group to help websites recognize and target individuals. In response, the alternative search engine DuckDuckGo has come out with an extension for Chrome that can block FLoC tracking. Furthermore, users now have the option of using either the DuckDuckGo application or extension to entirely opt out of FLoC monitoring.
Google first implemented FLoC in order to offer all users advertisements based on their demographic and search trends, but without including third-party cookies. However, the company waited only a short time before deciding the tracking method would apply to all Google Chrome users regardless of whether the user chose to opt in or not. Understandably concerned about privacy, many users have expressed wanting to learn more about alternative search engine options.
The fortunes of the founders and senior management of carmakers listing in Shanghai rest on investors’ continuing love of NEV stocks as they cannot sell their shares during a lock-up period on the Star Market for several years. The 500-per cent surge in Tesla’s share price has propelled chief executive Elon Musk to become the world’s wealthiest man last month, beating fellow centibillionaire Jeff Bezos of Amazon.com. Here are some of the biggest upcoming fundraising drives and new entrants to watch in the industry in the coming months:
We flag the biggest upcoming fundraising drives by Chinese electric car companies in 2021 and point out the new entrants to watch in the booming industry.
To make some of the most precise measurements we can of the world around us, scientists tend to go small — right down to the atomic scale, using a technique called atom interferometry.
Now, for the first time, scientists have performed this kind of measurement in space, using a sounding rocket specially designed to carry science payloads into low-Earth space.
It’s a significant step towards being able to perform matter-wave interferometry in space, for science applications that range from fundamental physics to navigation.