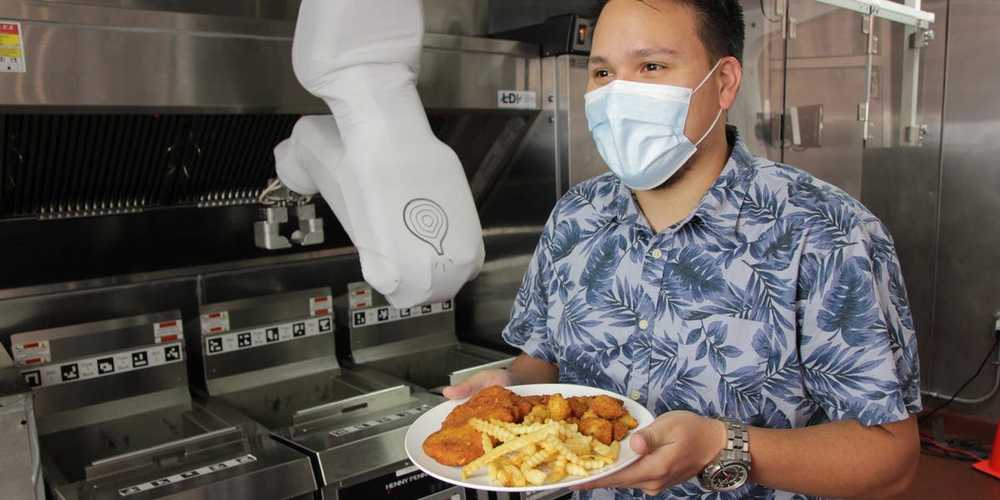
Flippy can cook 19 items, including Impossible Burgers, chicken wings, and hash browns, replacing the need for staff to do so.
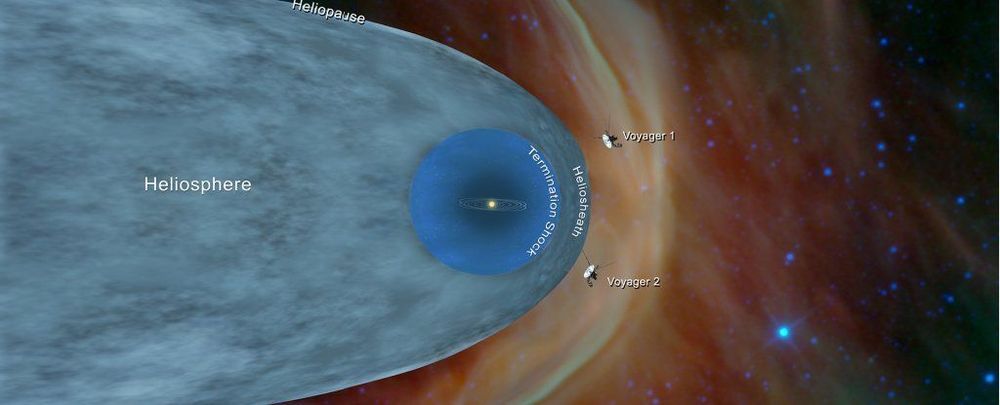
In November 2018, after an epic, 41-year voyage, Voyager 2 finally crossed the boundary that marked the limit of the Sun’s influence and entered interstellar space. But the little probe’s mission isn’t done yet — it’s now sending home information about the space beyond the Solar System.
And it’s revealing something surprising. As Voyager 2 moves farther and farther from the Sun, the density of space is increasing.
It’s not the first time this density increase has been detected. Voyager 1, which entered interstellar space in 2012, detected a similar density gradient at a separate location.
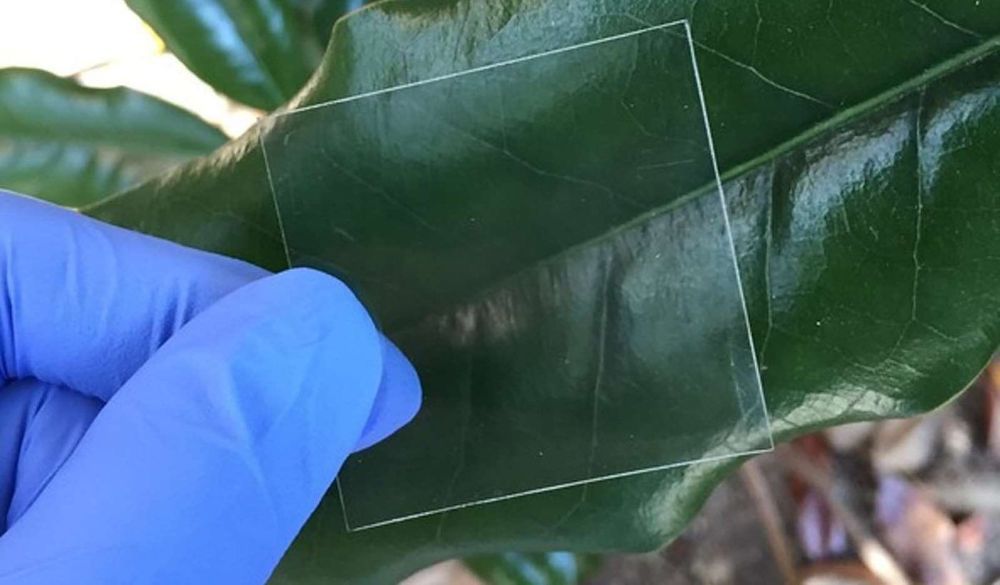
Looks like we will have wooden glass in the future. 😃
University of Maryland scientists made a transparent wood nearly as clear as glass to make stronger, better insulating windows.
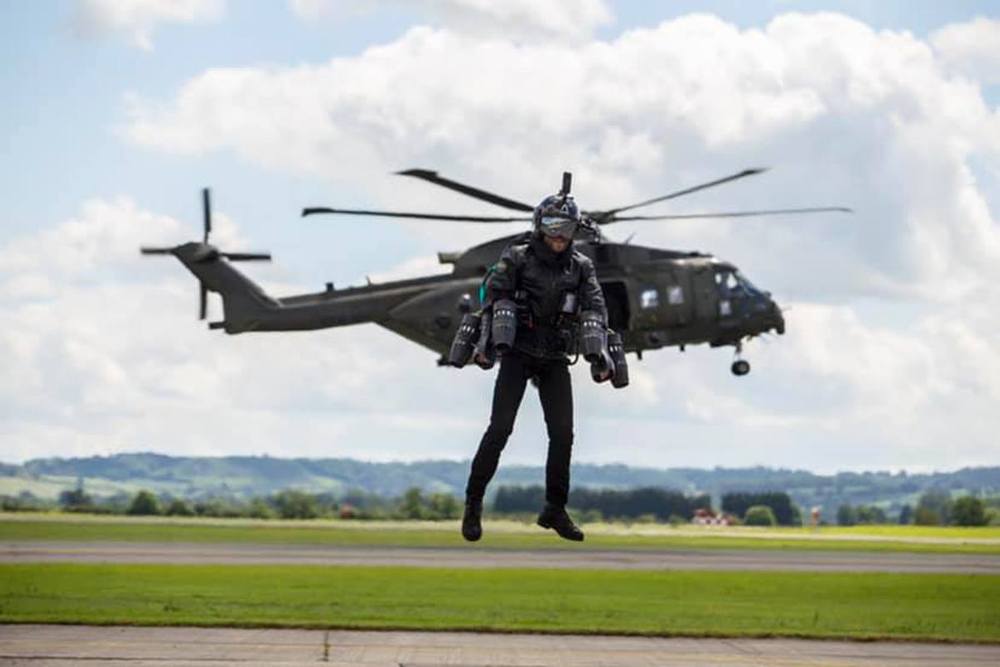
Cops are now hunting down the “jetpack dude” who has been flying around near LAX. Some people are calling it an accident waiting to happen.
The FBI is on the case as well.
Scientists in China have created a nanogenerator that can generate wind energy created by a person on a brisk walk.
Article. The research/article indicates that childhood trauma can not only impact the current generation, but future generations. Biochemical signals are sent to the germ cells, modifying the expression of some genes and/or the DNA structure.
Traumatic experiences can have a lasting impact, so children that suffer through them can feel their effects for a lifetime. Work has also shown that trauma can change the way genes are expressed, through epigenetics. Epigenetic changes do not alter the sequence of genes but they alter the biochemistry of DNA, and these changes are sometimes passed down to future generations through germ cells. Scientists have been working to learn more about how traumatic events get embedded in the genetic code of germ cells.

“In a world first, a “cold-shock” protein has been found in the blood of regular winter swimmers at London’s Parliament Hill Lido.”
“The protein has been shown to slow the onset of dementia and even repair some of the damage it causes in mice.”
“Prof Giovanna Mallucci, who runs the UK Dementia Research Institute’s Centre at the University of Cambridge, says the discovery could point researchers towards new drug treatments which may help hold dementia at bay.”
Swimmers at a London lido aid understanding of what cold does to the body.