Biologists have used CRISPR gene editing to store information inside DNA in living bacterial cells, which could become a storage medium of the future.
Largest spider
Posted in futurism
Computer-based artificial intelligence can function more like human intelligence when programmed to use a much faster technique for learning new objects, say two neuroscientists who designed such a model that was designed to mirror human visual learning.
New program aims to build and demonstrate ruggedized device for tactical applications.
Like.
Comment.
Linear accelerators, LINACs for short, are devices that accelerate electrons or other sub-atomic particles along a straight line to generate a beam of high energy. LINACs have a variety of commercial uses such as generating X-rays for cargo inspection, medical diagnostics, food sterilization, and even enabling precise external radiation treatments to destroy cancer cells without damaging surrounding tissue. To generate more powerful electron beams using current technology, however, requires building larger LINACs that can grow to dozens of meters or longer depending on the application. Unfortunately, powerful LINACs are too large and heavy to be practical for military use in the field.
DARPA has announced its Advanced Concept Compact Electron Linear-accelerator (ACCEL) program whose goal is to develop a powerful, deployable electron LINAC. A webinar Proposers Day for potential proposers is scheduled for January 282021.
“A high-power compact, rugged accelerator that could be transported by truck or aircraft to austere locations would provide multiple defense and homeland security benefits,” said Col. Dan “Animal” Javorsek, ACCEL program manager. “It could be used for medical treatments in locales without advanced hospitals, remote detonation of Improvised Explosive Devices, and mobile imaging or inspection of shipping containers’ contents to counter chem-bio and radiological threats. A deployable LINAC could also enable portable sterilization for foods and surfaces to prevent contamination and infection in deployed environments.”
Leveraging new tech, DARPA aims for night-vision goggles the size and weight of regular eyeglasses.
Like.
Comment.
For decades U.S. warfighters have benefitted from advanced night-vision technology, allowing pilots to fly low-level missions on pitch-black nights and ground forces to conduct operations against adversaries in the dark. But current night-vision goggle (NVG) technology requires cumbersome binocular-like optics mounted on a helmet, offering limited field of view (FOV) and putting unhealthy strain on the wearer’s neck. Building on recent scientific advances in photonics and optical materials pioneered in DARPA’s Defense Sciences Office (DSO), a new effort seeks to develop next-generation NVGs that are as lightweight and compact as a pair of regular eyeglasses or sunglasses.
DARPA today announced its Enhanced Night Vision in eyeglass form (ENVision) program. ENVision aims to create lightweight NVGs that offer a wide FOV across multiple infrared (IR) spectrum bands without needing separate optics for each IR band. The goal is to enable night vision through fog, dust, and other obscurants as well as provide thermal vision – all via a single flat lens. A Proposers Day for interested participants is being held via webinar on January 212021.
“Our warfighters experience significant neck strain from current NVGs caused by the weight of the optics extending 4–5 inches in front of their helmets,” said Rohith Chandrasekar, program manager in DARPA’s Defense Sciences Office. “If you’ve never worn NVGs for hours at a time imagine wearing a baseball cap all day with a two-pound weight attached to the front of the bill – that gives you a small sense of the stress experienced. Extended use of such systems leads to a condition where the neck no longer has energy to keep the head upright requiring warfighters to use their hands to lift and point their heads. NVG wearers also have to swivel their heads frequently for peripheral vision since current optics only provide a 40-degree field of view compared to the 120-degree wide view we have with our eyes, which only makes use of NVG systems more painful.”
Atmospheric Water Extraction (AWE) performers aim to meet clean water needs of deployed troops, even in austere environments.
Like.
Comment.
DARPA recently awarded five contracts and selected one Government partner to develop technology to capture potable water from the air in quantities sufficient to meet critical DoD needs, even in extremely dry climates. GE Research, Physical Sciences Inc., Honeywell International Inc., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Texas at Austin, and U.S. Naval Research Laboratory were chosen to develop next-generation, scalable sorbent materials and prototypes under DARPA’s Atmospheric Water Extraction (AWE) program.
The goal of the AWE program is to provide fresh water for a range of military, stabilization, and humanitarian needs through the development of small, lightweight, low-powered, distributable systems that extract moisture from the atmosphere. DARPA is open to various approaches, with an emphasis on advanced sorbents that can rapidly extract water from ambient air and release it quickly with minimal energy inputs. These sorbent materials offer potential solutions to the AWE challenge, provided they can be produced at the necessary scale and remain stable over thousands of extraction cycles. In addition to developing new sorbents, AWE researchers will need to engineer systems to optimize their suitability for highly mobile forces by substantially reducing the size, weight, and power requirements compared to existing technologies.
“Access to clean water is of critical importance to the warfighter, and current water distribution operations incur numerous financial, maintenance, and logistical challenges,” noted Dr. Seth Cohen, AWE program manager. “The selected AWE program performers are being asked to leverage advanced modeling, innovative engineering, and additive manufacturing methods to support the program, which in turn will help maintain combat readiness, reduce casualties and cost due to water transportation, and enhance humanitarian and disaster relief efforts.”
Field tests validate tech that automatically links diverse radio waveforms in contested environments.
Like.
Comment.
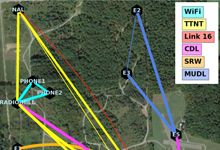
A DARPA network technology program recently concluded field tests demonstrating novel software that bridges multiple disparate radio networks to enable communication between incompatible tactical radio data links – even in the presence of hostile jamming. The technology is transitioning to Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) and the Marine Corps, which plans to put the software on a software reprogrammable multi-channel radio platform for use on aircraft and ground vehicles.
Started in 2016, the Dynamic Network Adaptation for Mission Optimization program, or DyNAMO, has developed technologies that enable automated, real-time dynamic configuration of tactical networks to ensure that heterogeneous radio nodes – whether on ground, air, or sea – can interoperate in a contested battlespace.
As a capstone event to conclude the program, DARPA recently demonstrated DyNAMO capabilities in over-the-air field tests at the Air Force Research Lab’s experimentation and test facility near Rome, New York. Diverse military tactical data links, including LINK 16, Tactical Targeting Networking Technology (TTNT), Common Data Link (CDL), and Wi-Fi networks were deployed to the test site. DyNAMO successfully provided uninterrupted network connectivity between all the data links under varying conditions in a simulated contested environment.
New initiative aims to lower high barrier to entry for resource-constrained organizations, increasing access to participate in forward-looking research.
Like.
Comment.
As the world continues to change and advance at a rapid pace, the need for continuous innovation has never been greater. DARPA’s open innovation model leverages the expertise and novel ideation found in large and small businesses, government organizations, and academic institutions. However, resource constraints across these organizations can limit their participation in cutting-edge research opportunities. Within the microelectronics arena in particular, skyrocketing costs for designing integrated circuits are stifling participation in the innovation process.
To help remove potential roadblocks to further increasing the speed of innovation, the agency today announced DARPA Toolbox – a new, agency-wide effort to provide open licensing opportunities with commercial technology vendors to the researchers behind DARPA programs. Through DARPA Toolbox, successful proposers will receive greater access to commercial vendors’ technologies and tools via pre-negotiated, low-cost, non-production access frameworks and simplified legal terms. For commercial vendors, DARPA Toolbox will provide an opportunity to leverage the agency’s forward-looking research and a chance to develop new revenue streams based on programmatic achievements developed with their technologies.
“DARPA performers are frequently encumbered by having to negotiate access to tools, IP, and services, and execute complex legal agreements that take the time away from what they do best – advancing science to benefit the nation,” said Serge Leef, the Microsystems Technology Office (MTO) program manager spearheading this effort. “Through DARPA Toolbox, we are working to effectively lower the high barrier to entry with the goal of encouraging more proposals from non-traditional and resource-constrained organizations that can bring innovative insights and ideas to bear on DARPA programs.”
Next capture attempts scheduled to occur in spring of 2021
Like.
Comment.
Attempts at airborne retrieval of three unmanned air vehicles, nicknamed Gremlins, were just inches from success in DARPA’s latest flight test series that started on October 28. Each X-61A Gremlins Air Vehicle (GAV) flew for more than two hours, successfully validating all autonomous formation flying positions and safety features. Nine attempts were made at mechanical engagement of the GAVs to the docking bullet extended from a C-130 aircraft, but relative movement was more dynamic than expected and each GAV ultimately, safely parachuted to the ground.
“All of our systems looked good during the ground tests, but the flight test is where you truly find how things work,” said Scott Wierzbanowski, program manager for Gremlins in DARPA’s Tactical Technology Office. “We came within inches of connection on each attempt but, ultimately, it just wasn’t close enough to engage the recovery system.”
Hours of data were collected over three flights, including aerodynamic interactions between the docking bullet and GAV. Efforts are already underway to analyze that data, update models and designs, and conduct additional flights and retrieval attempts in a fourth deployment this spring.
DARPA Looks to Light up Integrated Photonics with Chip-Scale Laser DevelopmentAgency announces performer teams selected for LUMOS program.
Like.
Comment.
First demonstrated sixty years ago, the laser has become an essential technology in today’s world. It has transformed diverse fields including communications, sensing, manufacturing, and medicine. More recently, innovations in integrated photonics have allowed the miniaturization of key optical components and the ability to arrange several elements on a single silicon chip. When combined with lasers, these photonic integrated circuits (PICs) have the potential to replace large and costly optical systems with chip-scale solutions. However, due to differences in the properties of the materials that compose them, lasers and PICs are difficult to combine onto the same platform, limiting the benefits of integration and preventing broad technology impact.
To address this challenge, DARPA developed the Lasers for Universal Microscale Optical Systems (LUMOS) program, which aims to bring high-performance lasers to advanced photonics platforms. As highlighted in the recent program kick-off meeting, LUMOS will address several commercial and defense applications by directing efforts across three distinct Technical Areas.
The first LUMOS Technical Area brings high-performance lasers and optical amplifiers into advanced domestic photonics manufacturing foundries. Two research teams were selected in this area: Tower Semiconductor and SUNY Polytechnic Institute. These performers will work to demonstrate flexible, efficient on-chip optical gain in their photonics processes to enable next-generation optical microsystems for communications, computing, and sensing. LUMOS technologies will be made available to future design teams through DARPA-sponsored multi-project wafer runs.