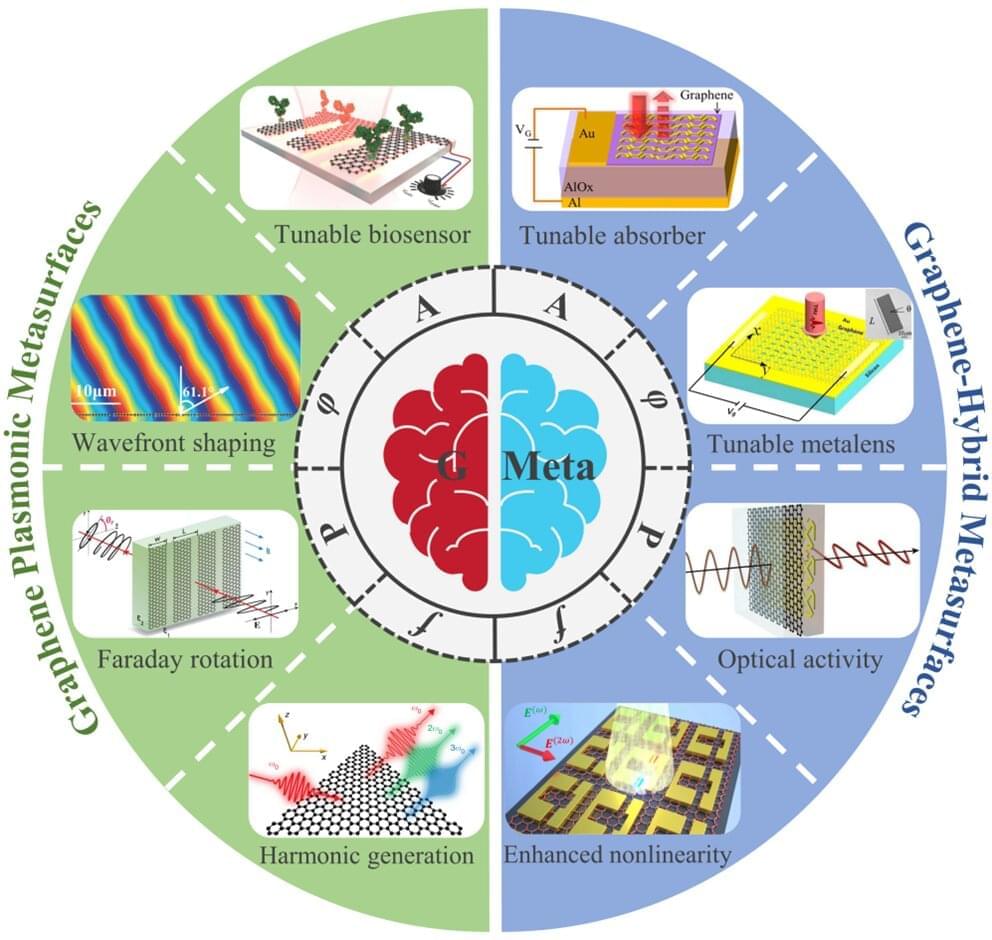
A new publication in Opto-Electronic Advances overviews dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene.
Metasurfaces, artificial subwavelength structured interfaces, exhibit unprecedented capabilities to manipulate electromagnetic (EM) waves ranging from visible to terahertz and microwave frequencies.
In the past decade, static metasurfaces and metadevices have been researched extensively. Due to the passive nature of building blocks in general made of metals and/or dielectrics, however, their functionalities cannot be actively tuned in situ after fabrication, which seriously impedes their application scenarios such as varifocal lens, dynamic holography, and beam steering in LiDAR. Motivated by those significant requirements, scientists have struggled for years to improve the dynamical tunability of metasurfaces, and introducing active materials or components into the passive metasurfaces has been proposed as the first thought strategy.