RACER to focus on new autonomy algorithm technologies.
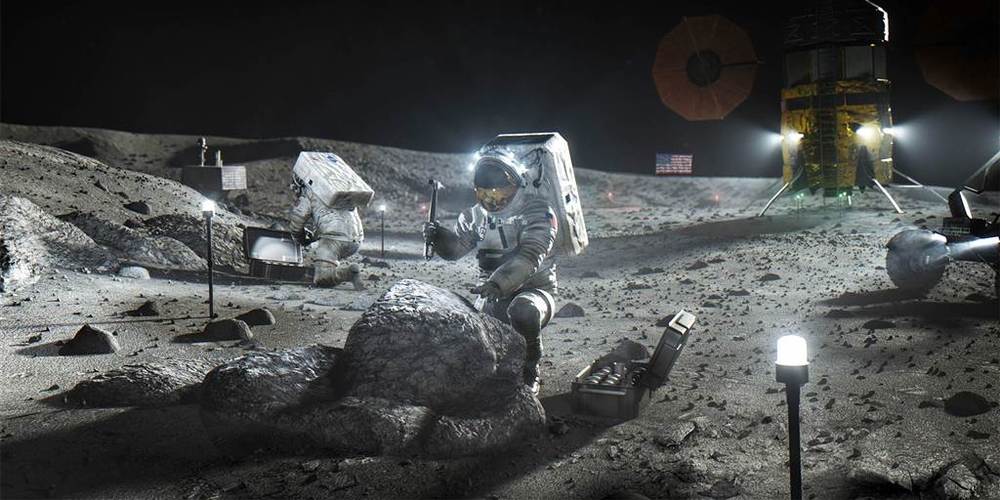
NASA developed the Artemis Accords to partner with other nations to set basic principles to guide robotic and crewed lunar exploration.
Eight nations have signed on to become founding members of NASA’s Artemis Accords, an international agreement that establishes how countries can cooperate to peacefully and responsibly conduct exploration of the moon.
NASA announced Tuesday that the United States signed the accords, together with Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, the United Arab Emirates and the United Kingdom. NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine said the agreement would establish a “singular global coalition” to guide future expeditions to the moon.
“With today’s signing, we are uniting with our partners to explore the moon and are establishing vital principles that will create a safe, peaceful and prosperous future in space for all of humanity to enjoy,” Bridenstine said in a statement released Tuesday.
Hugely informative and surprisingly candid new Cosmic Controversy episode on why the Moon is so crucial to our collective space future with Notre Dame Planetary Geologist Clive Neal. Well worth a listen.
Notre Dame Planetary Geologist Clive Neal stops by the podcast for a terrifically candid discussion of why the Moon has to be the first stop en route to Mars. We talk about why the Moon holds the key to the new Space Economy; the prospects for NASA making its 2024 Artemis mission deadline; and, why lunar samples are still being analyzed 50 years hence. Why more lunar samples and lunar seismometers are keys to understanding our inner solar system. And why it’s imperative that we revisit the Moon in a permanent way if we are ever to make Mars our own. We also mull over the politics of all of this three weeks away from a pivotal presidential election.
Ogba Educational Clinic championing STEM Education and Artificial Intelligence in Africa.
Officials said SpaceX is working on rocket-based delivery of military supplies around the globe just days after the news that it’s developing missile-tracking satellites.
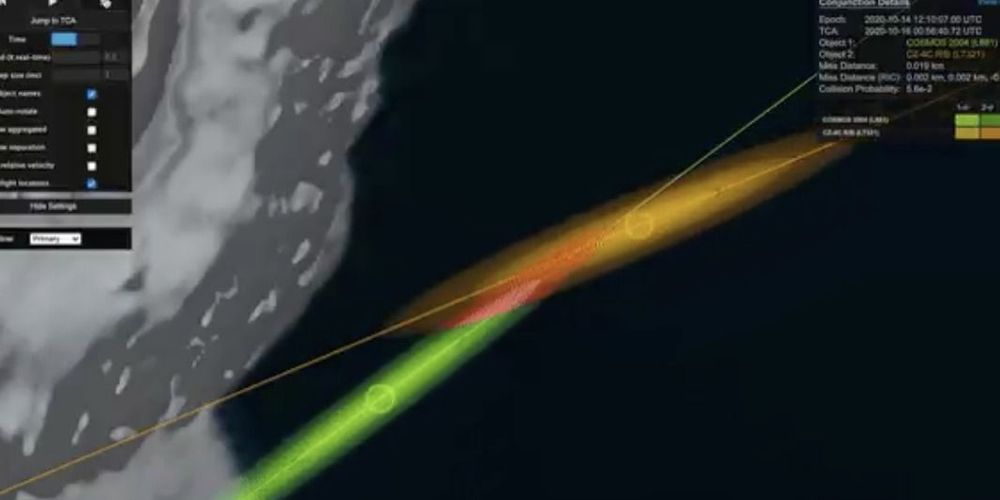
Experts are worried about what could happen up in low-Earth orbit.
On Tuesday, LeoLabs, a company that monitors the paths of space junk in low-Earth orbit, announced on Twitter it was tracking a potential conjunction—that’s space-speak for a mid-orbit crash—tonight between a defunct Soviet satellite and a discarded Chinese rocket stage.
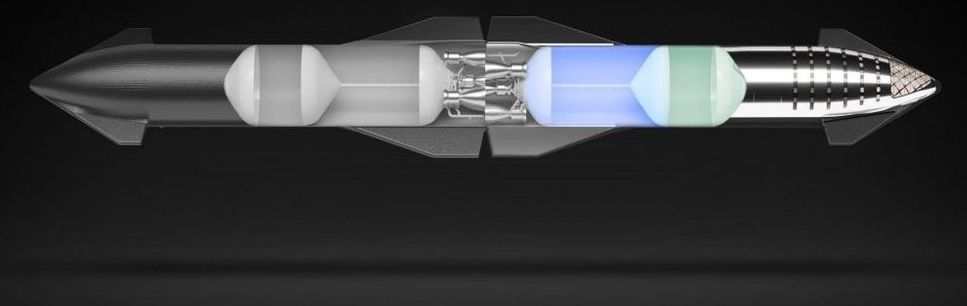
SpaceX’s Starship program has won $53 million from NASA to perform a full-scale test of orbital propellant transfer, taking the company and space agency’s relationship on the crucial technology to the next level.
NASA revealed the results of its fifth round of “Tipping Point” solicitations on October 14th, announcing awards of more than $370 million total to 14 separate companies. This year’s investments focused on three main categories: “cryogenic fluid management, lunar surface [operations], and closed-loop [i.e. autonomous] descent and landing capability demonstrations.”
In a fairly predictable outcome, the bulk (~$176 million) went to Lockheed Martin and the United Launch Alliance (ULA), while the other half (~$189 million) was split among the twelve remaining companies. In an upset, however, SpaceX was awarded a substantial contract for a crucial aspect of Starship development.
In episode two of Hacking the Apocalypse, Claire Reilly looks at the risk of an all-out nuclear war and tours a Cold-War era missile silo that’s now a luxury escape bunker.
CNET playlists: https://www.youtube.com/user/CNETTV/playlists
Download the new CNET app: https://cnet.app.link/GWuXq8ExzG
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cnet
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/cnet
Follow us on Instagram: http://bit.ly/2icCYYm
A three-person crew successfully reached the International Space Station on Wednesday aboard a Russian rocket after the fastest ever journey from Earth of just over three hours.
The mission of the Soyuz space craft carrying two Russian cosmonauts and one NASA astronaut was of immense importance to Russia’s space agency Roscosmos, coming as the SpaceX programme relaunches crewed spaceflight from the United States and ignites fresh talk of a space race between the two countries.
Roscosmos said “a new record for flights to the International Space Station was set – the total time from launch to docking of the Soyuz MS-17 was three hours and three minutes.”
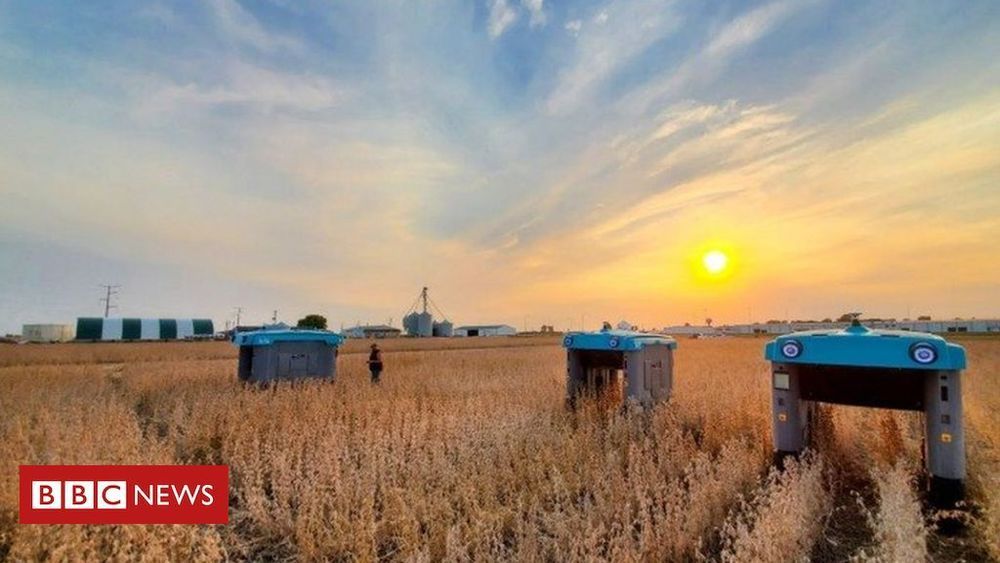
Robots will help farmers analyze crops to determine how to get better yields. Re-sharing from BBC.
The project will analyse every leaf on every crop, helping farmers tend the fields.
New images taken by BepiColombo come at a time when interest in the second planet from the sun is at an all time high.