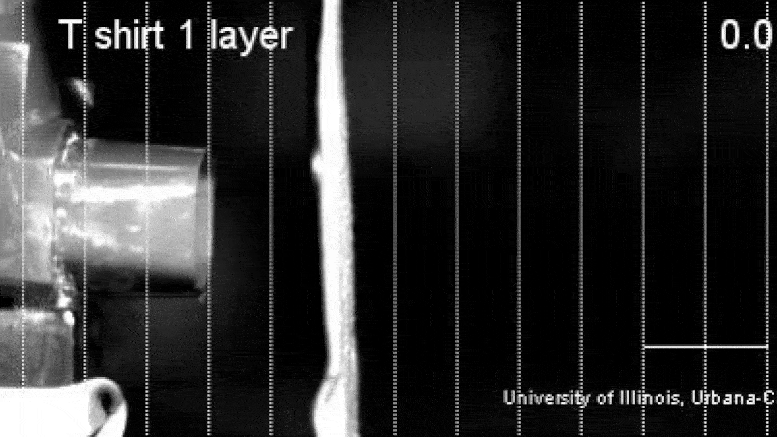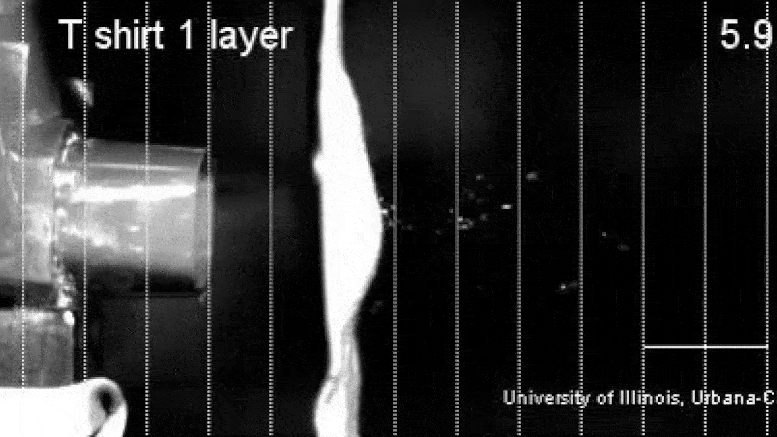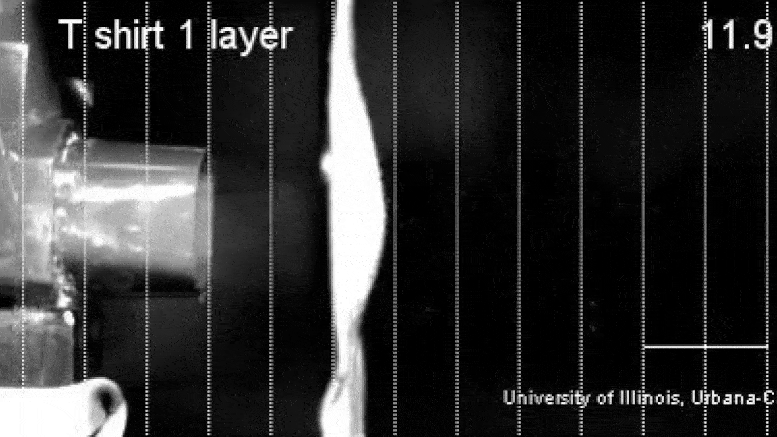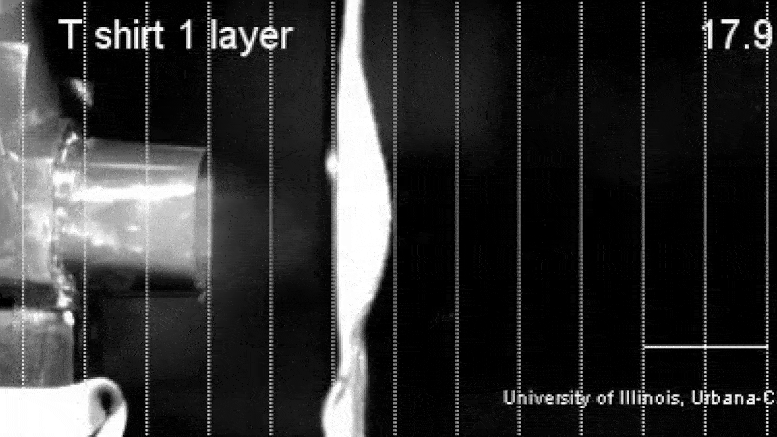
UIUC Editor’s note: Health authorities believe COVID-19 spreads by the transmission of respiratory droplets, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends homemade cloth face coverings for use in public spaces. Starting today, Illinois joins many other states in requiring people to wear masks while out. However, initial uncertainty regarding the masks’ effectiveness in reducing exhaled droplets leaves some people unsure or skeptical of their usefulness during the current COVID-19 pandemic. Mechanical science and engineering professor Taher Saif spoke with News Bureau physical sciences editor Lois Yoksoulian about a study that he and his graduate students, Onur Aydin and Bashar Emon, performed on the effectiveness of common household fabrics for use in homemade masks.
Physically speaking, are the respiratory droplets produced by talking and breathing the same as those that come from a cough or a sneeze?
The droplets released during sneezing and coughing are larger than those released while speaking and breathing, and any of these droplets may carry many virus particles. The larger droplets tend to fall nearby due to gravity, but the smaller ones can go far, with the majority of them remaining within six feet of the infected individual. Unfortunately, because symptomatic, presymptomatic and asymptomatic carriers can shed the coronavirus, we cannot tell without testing which individuals are the sources of infection. Hence, a physical barrier, such as a mask, can prevent the spreading.