Huge “foundation models” are turbo — charging AI progress.
They can have abilities their creators did not foresee.


Machine learning can get a boost from quantum physics.
On certain types of machine learning tasks, quantum computers have an exponential advantage over standard computation, scientists report in the June 10 Science. The researchers proved that, according to quantum math, the advantage applies when using machine learning to understand quantum systems. And the team showed that the advantage holds up in real-world tests.
“People are very excited about the potential of using quantum technology to improve our learning ability,” says theoretical physicist and computer scientist Hsin-Yuan Huang of Caltech. But it wasn’t entirely clear if machine learning could benefit from quantum physics in practice.

Solving the 3D structure at near atomic level resolution, one of the world’s hardest, giant jigsaw puzzles—the nuclear pore complex—the largest molecular machine in human cells, with structure-based AI prediction @ScienceMagazine
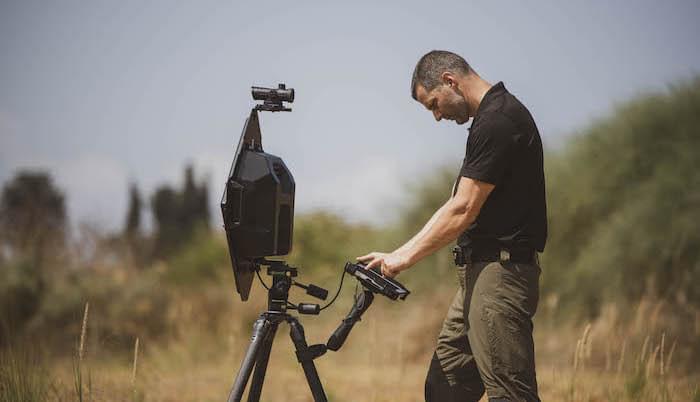

According the company, this innovative system enables the detection of live objects behind walls at a distance of more than 50 meters.
Camero-Tech, a member of the SK Group and an Israeli developer, producer, and marketer of pulse-based UWB micro-power radar ‘Through Wall Imaging’ systems, announced the launching of its groundbreaking XaverTM LR40 (XLR40) system, which detects live objects behind walls at distances of over 50 meters.
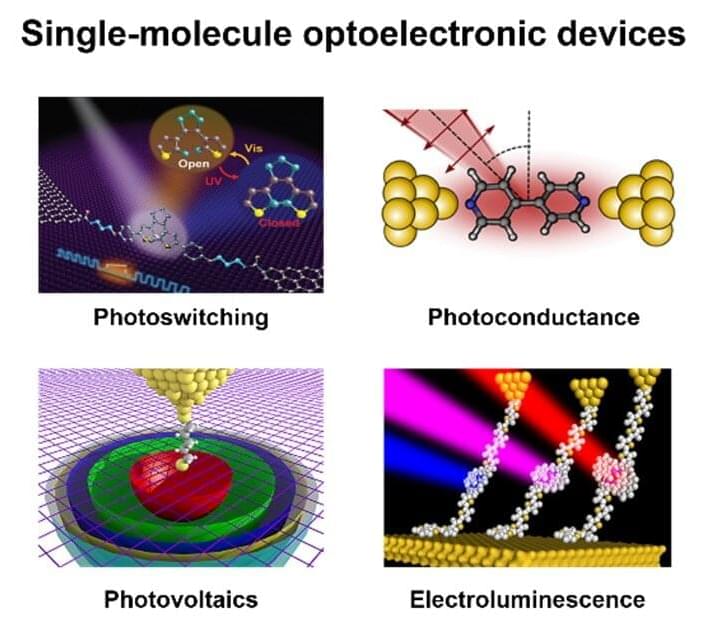
Single-molecule electronic devices, which use single molecules or molecular monolayers as their conductive channels, offer a new strategy to resolve the miniaturization and functionalization bottlenecks encountered by traditional semiconductor electronic devices. These devices have many inherent advantages, including adjustable electronic characteristics, ease of availability, functional diversity and so on.
To date, single-molecule devices with a variety of functions have been realized, including diodes, field-effect devices and optoelectronic devices. In addition to their important applications in the field of functional devices, single-molecule devices also provide a unique platform to explore the intrinsic properties of matters at the single-molecule level.
Regulating the electrical properties of single-molecule devices is still a key step to further advance the development of molecular electronics. To effectively adjust the molecular properties of the device, it is necessary to clarify the interactions between electron transport in single-molecule devices and external fields, such as external temperature, magnetic field, electric field, and light field. Among these fields, the use of light to adjust the electronic properties of single-molecule devices is one of the most important fields, known as “single-molecule optoelectronics.”
A new science fiction novel does a masterful job of crafting a narrative from an idea long discussed in philosophy: Is the mind needed?
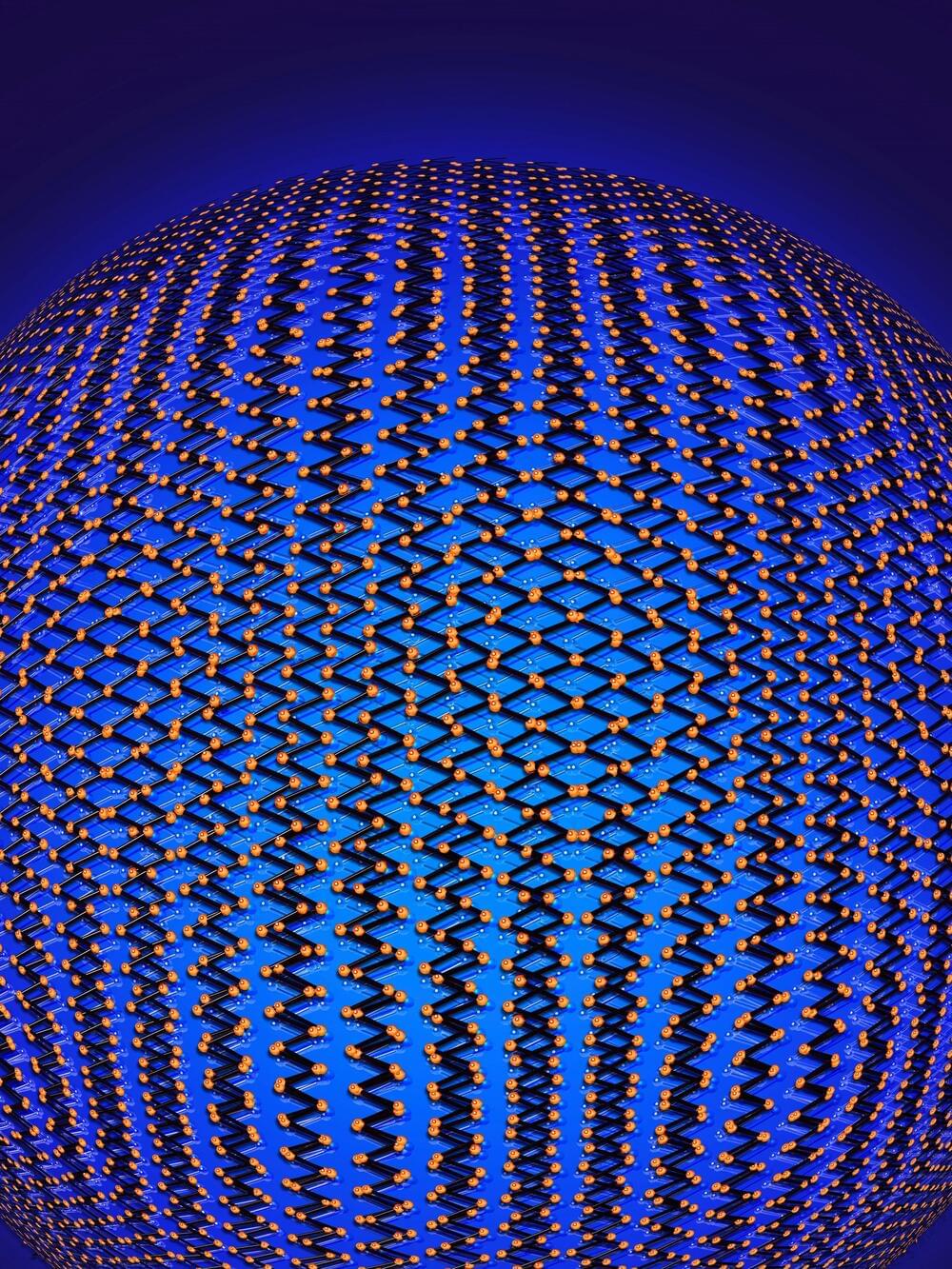
A recent experiment detailed in the journal Nature is challenging our picture of how electrons behave in quantum materials. Using stacked layers of a material called tungsten ditelluride, researchers have observed electrons in two-dimensions behaving as if they were in a single dimension—and in the process have created what the researchers assert is a new electronic state of matter.
“This is really a whole new horizon,” said Sanfeng Wu, assistant professor of physics at Princeton University and the senior author of the paper. “We were able to create a new electronic phase with this experiment—basically, a new type of metallic state.”
Our current understanding of the behavior of interacting electrons in metals can be described by a theory that works well with two-and three-dimensional systems, but breaks down when describing the interaction of electrons in a single dimension.
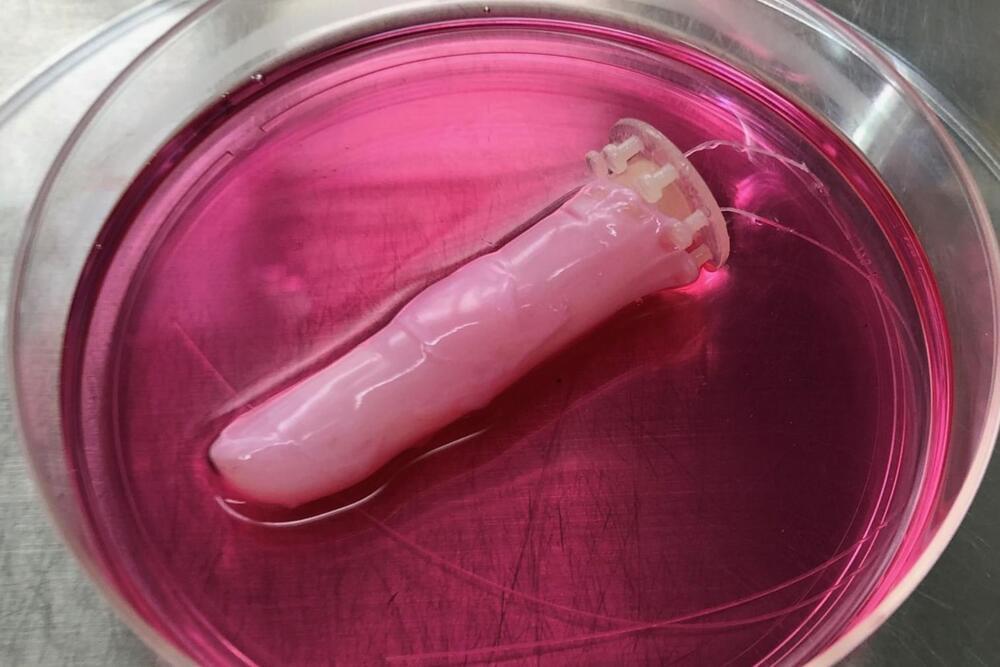
We’ve been hearing a lot about synthetic skins designed for robotic hands, which would give the devices more human-like qualities. Well, scientists in Japan have gone a step further, by covering a robotic finger in a self-healing skin made from live human cells.
Led by Prof. Shoji Takeuchi, a team at the University of Tokyo started by building an articulated motor-driven robotic finger, capable of bending and straightening like its human counterpart. That finger was then submerged in a cylinder filled with a solution made up of collagen and human dermal fibroblast cells – these are the main components of our skin’s connective tissues.
Due to its natural properties, that solution shrank and conformed to the contours of the finger, forming a seamless hydrogel coating. Next, the scientists added a layer of human epidermal keratinocyte cells, which constitute 90 percent of our epidermis (the outermost layer of skin). These formed a moisture-retaining/water-resistant barrier on top of the gel, and gave the finger a more natural texture.
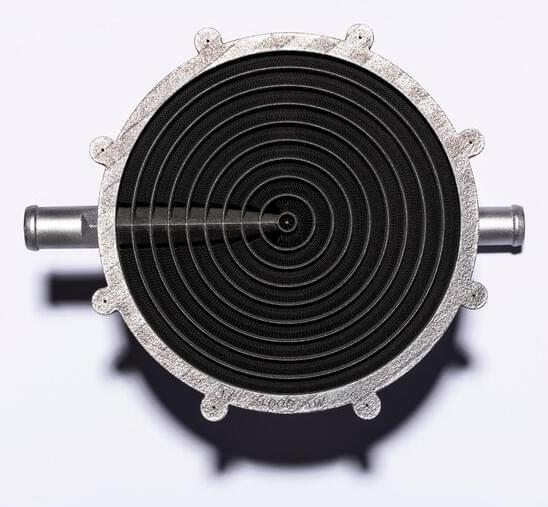

Conflux has specialized in making heat exchangers since its inception. Previously, the company collaborated with GKN to make its technology available in Europe. We interviewed CEO Michael Fuller, including on the 3DPOD. We also saw how the startup obtainined a series A round. The next step in Conflux’s development is the mass customization of its heat exchange products.
So far, Conflux offers individually designed heat exchangers to order. Usually for F1 teams and high-end industrial applications, these high-value heat sinks have all been unique and made specifically for their applications. That’s all well and dandy, of course, but it won’t really scale.
Now. the company has developed an annular water charge air cooler (WCAC) heat exchanger. WCAC heat exchangers are all the rage in automobiles now because they can potentially be more efficient in engine cooling than plate or other heat exchangers. WCACs could potentially improve mileage, top speed, and reduce A/C consumption in passenger cars. In racing, they probably won’t focus too much on the A/C consumption, but would be very pleased with the other potential advantages.
Numerous activities, including construction and demolition, mining and industrial activities, cooking and gardening, and others, generate a substantial amount of garbage. The amount of waste generated is directly proportional to consumption and production patterns.
In most cases, waste formation is the result of inefficient material utilization. Trends in the number, composition and impacts of these materials provide insight into the nation’s efficiency in using (and reusing) materials and resources. It also provides a better understanding of the effects of waste on human health and the environment.
According to surveys, 92 million tonnes of cloth are dumped as garbage each year worldwide. Estimates predict that this figure will likely exceed 130 million tonnes by 2030. When 200 tonnes of water used to make a single tonne of fabric is considered, it becomes clear that the end-to-end processes of the garment industry are severe threats to environmental initiatives.