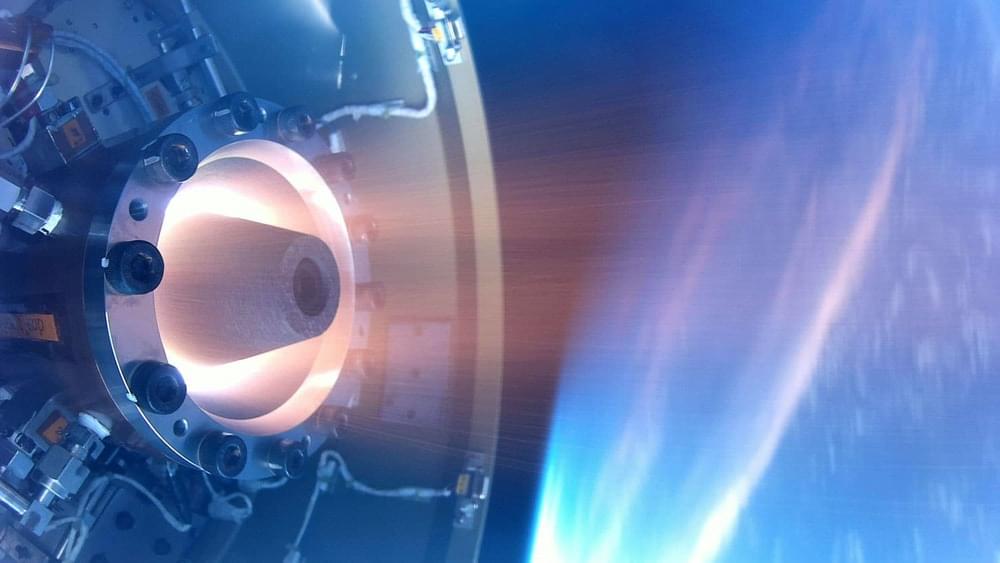
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has announced that it has successfully demonstrated the operation of a “rotating detonation engine” for the first time in space. The novelty of the technologies in question is that such systems obtain a large amount of thrust by using much less fuel compared to conventional rocket engines, which is quite advantageous for space exploration.
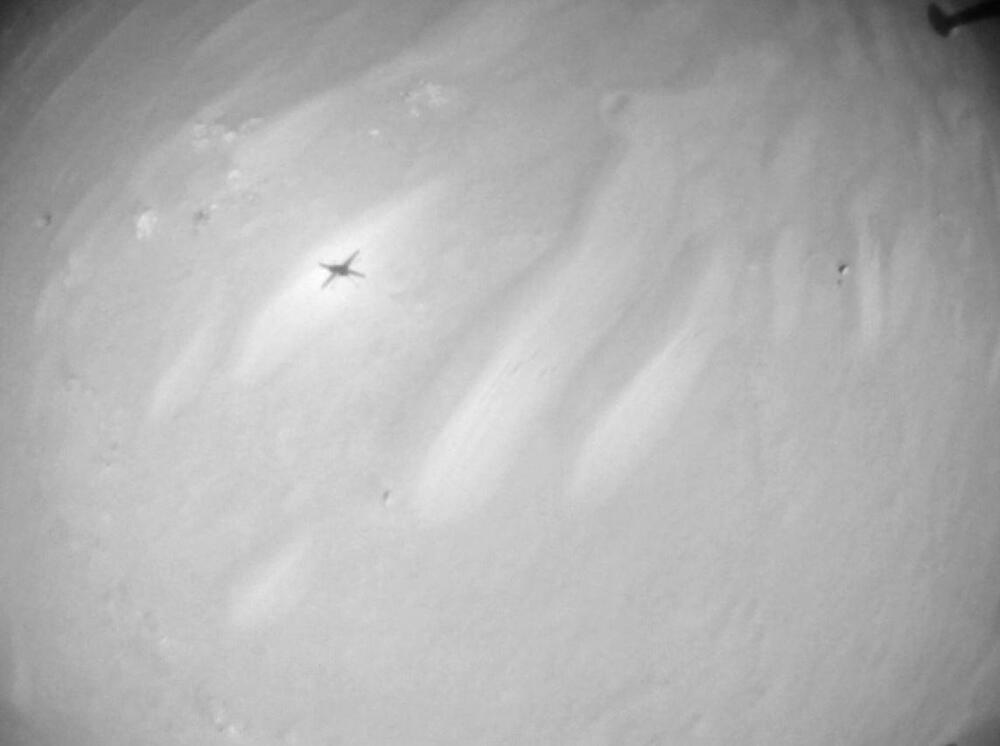
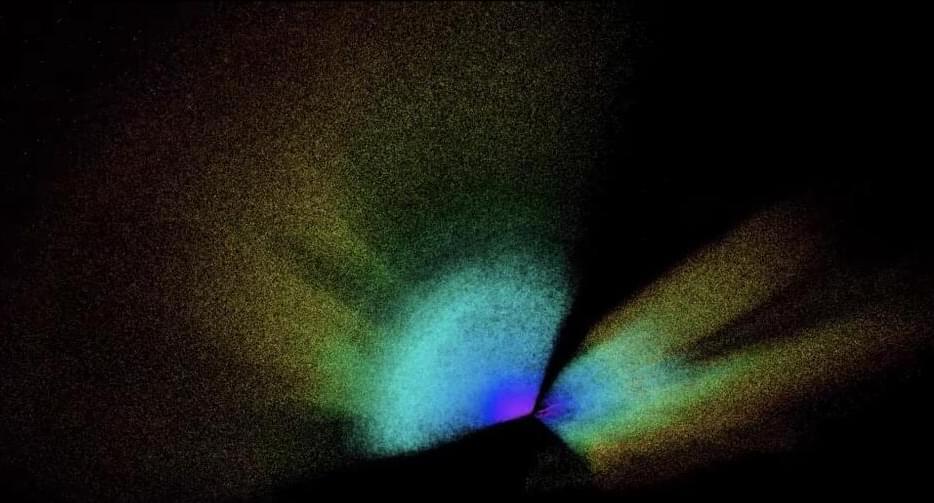
On July 27 the Japanese agency launched a pair of futuristic propulsion systems into space to carry out the first tests. They were launched from the Uchinoura Space Center aboard the S-520–31, a single-stage rocket capable of lofting a 220 lbs (100 kg) payload well above 186 miles (300 km). After recovering the rocket from the ocean, the JAXA team of engineers analyzed the data and confirmed the success of the mission, which put the new system at an estimated altitude of (146 miles) 234.9 km.
The rotating detonation engine uses a series of controlled explosions that travel around an annular channel in a continuous loop. This process generates a large amount of super-efficient thrust coming from a much smaller engine using significantly less fuel – which also means sending less weight on a space launch. According to JAXA, it has the potential to be a game-changer for deep space exploration.