A new paper documents the first-ever known case of a congenitally blind person who has synesthesia.
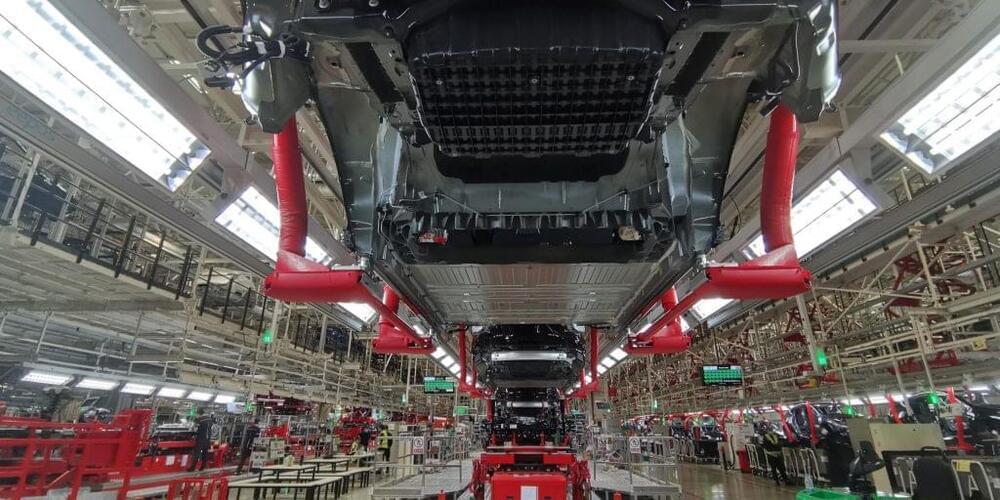


Tesla Giga Shanghai has resumed over 80% production along with several other companies, according to Chinese official Zhang Hongtao — the chief engineer of the Shanghai Economics and Information Technology Commission.
China created a “whitelist” to support companies resuming production and minimize the impact of Covid along the supply chain. As of Saturday, April 30, approximately 1,854 companies have made it onto the whitelist, including Tesla, and are authorized to resume work.
During a press conference, Zhang stated that Shanghai created a second list of 1,188 companies that can resume work. According to the Global Times, the companies fall into the automobile manufacturing, equipment manufacturing, and biomedicine sector.

I am going another route, and think Lifeboat, and others to may want to think about accounts with Mastodon, and others. We often empower what we don’t like and complain about. How does Mastodon work? Well for starters you can get a dedicated server, you moderate yourself, 🙄…and:
“Mastodon is a social media network comprised of nodes (called ”servers” or ”instances”), each running special software. Anyone can run their own Mastodon instance (if they have the proper dedicated server), which can then link to others in a federation or remain private. Individuals or companies can have complete control over individual Mastodon servers, so there are still centralized points of administration, but it’s not as concentrated as in the case of Twitter, Tumblr, or Facebook.
The Mastodon software is open source. It is based on an open-source social networking protocol called ActivityPub, which is developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (the same organization that maintains standards for the web.)
https://www.howtogeek.com/801927/a-twitter-alternative-how-does-mastodon-work/
Mastodon is an open source decentralized social network — by the people for the people. Join the federation and take back control of your social media!
Neil deGrasse Tyson gives his opinion on Elon Musk buying Twitter. Should Elon Musk be spending his time on Twitter or getting us to Mars? What does Neil deGrasse Tyson think of Mars as a backup plan for humanity? Is Neil deGrasse Tyson concerned about Elon Musk’s new policies?
#neildegrassetyson #elonmusk #twitter.
Join the Modern Wisdom Community on Locals — https://modernwisdom.locals.com/
Listen to all episodes on audio:
Apple Podcasts: https://apple.co/2MNqIgw.
Spotify: https://spoti.fi/2LSimPn.
Get in touch in the comments below or head to…
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/chriswillx.
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/chriswillx.
Email: https://chriswillx.com/contact/
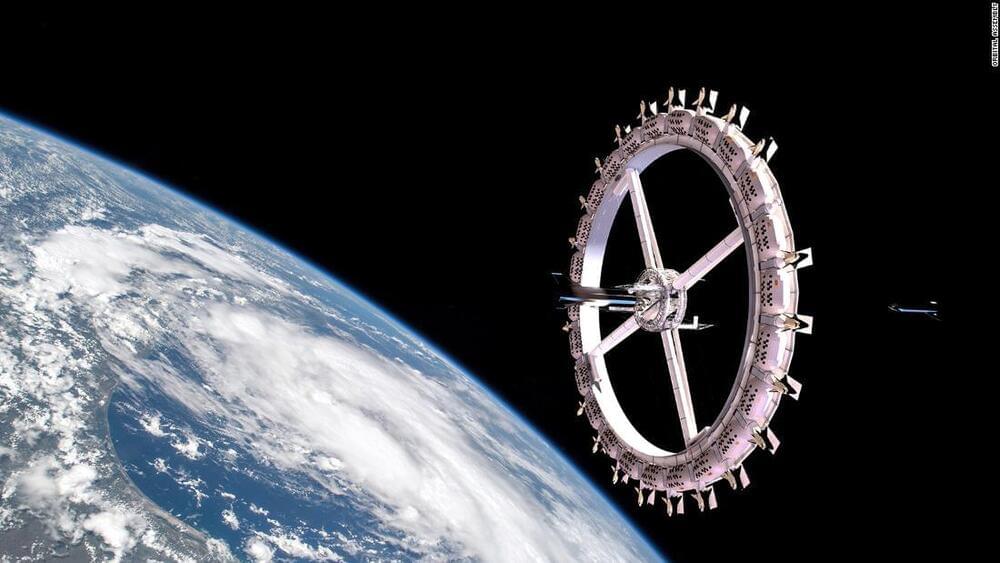

Orbital Assembly is now aiming to launch not one but two space stations with tourist accommodation: Voyager Station, the renamed original design, is now scheduled to accommodate 400 people and to open in 2027, while new concept Pioneer Station, housing 28 people, could be operational in just three years.
The goal, says Orbital Assembly, is to run a space “business park” home to offices as well as tourists.
Space tourism seems closer than ever before — over the past year, billionaire Virgin founder Richard Branson blasted into suborbital space with his company Virgin Galactic, while Star Trek actor William Shatner became the oldest person in space thanks to a jaunt with Blue Origin.

You don’t even have to cover your mouth. Virtual reality has come a long way in recent years, creating unreal environments and unprecedented tactile experiences. However, researchers have struggled to recreate an adequate simulation of our most precious senses of touch, like kissing.
You would be forgiven if you thought that the current wave of virtual reality headsets was a modern phenomenon. There were obviously some awkward—and failed—attempts to capitalize on the virtual reality craze of the early 1990s and for most people, this is as far back as virtual reality goes. The truth is that virtual reality is much, much older.
The science behind virtual reality was first explored in a practical sense as far back as the 1800s, but some could argue that it goes all the way back to Leonardo Da Vinci and the first explorations of perspective in paintings of the era. So how do virtual reality headsets work, and how come it took so long for them to become, well, a reality?
A virtual reality headset works because of a physiological concept known as stereopsis. You may not have heard the proper name, but you know about it; this refers to our ability to perceive depth because of the subtle horizontal differences in the image that each eye receives when we look at something.
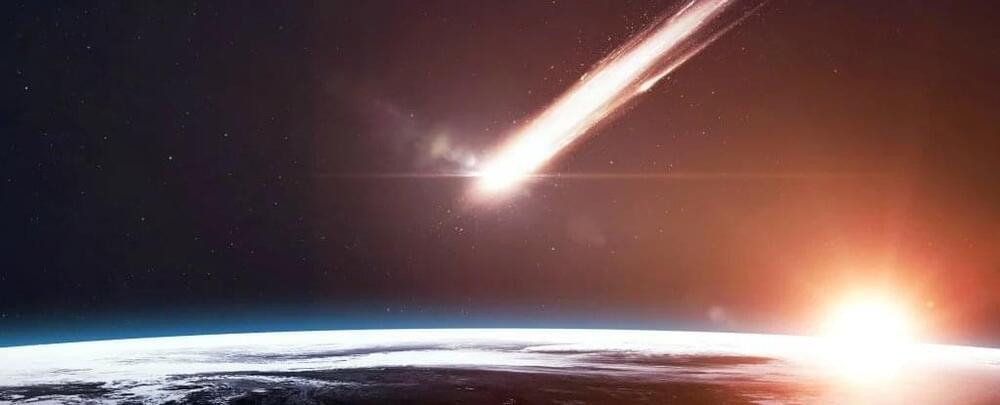

We still don’t know just how the first life emerged on Earth. One suggestion is that the building blocks arrived here from space; now, a new study of several carbon-rich meteorites has added weight to this idea.
Using new, extremely sensitive analysis techniques for these meteorites, a team led by scientists from Hokkaido University in Japan detected organic compounds that form the very backbone of the nucleic acid molecules common to all life as we know it – DNA and RNA.
The researchers analyzed three carbon-rich meteorites: the Murchison meteorite which landed in Australia in 1969, the Murray meteorite which landed in Kentucky in 1950, and the Tagish Lake meteorite which fell to Earth in 2000, landing in British Columbia.