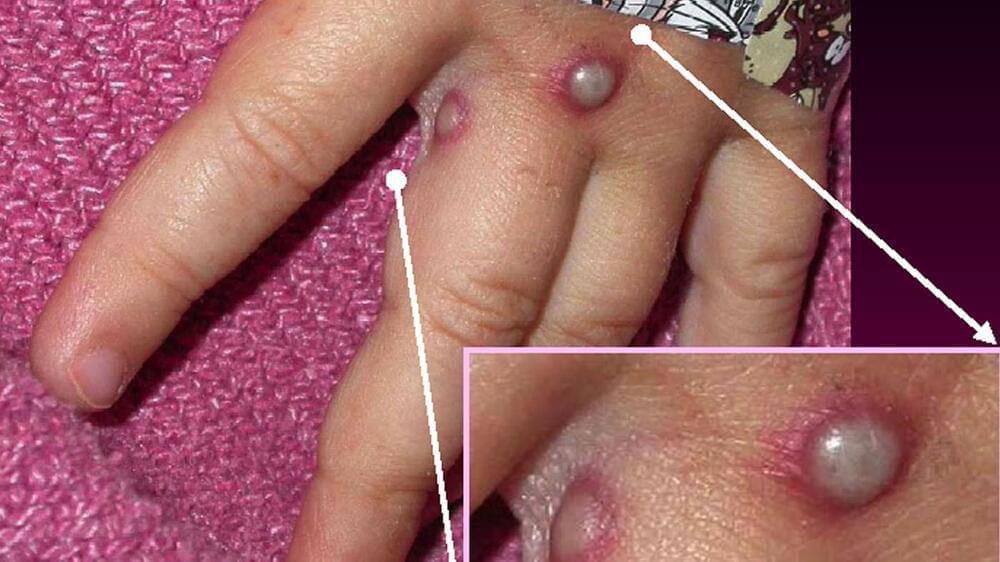
When excited by lasers, a tiny glass container filled with rubidium atoms can act as a receiver for streamed video signals.
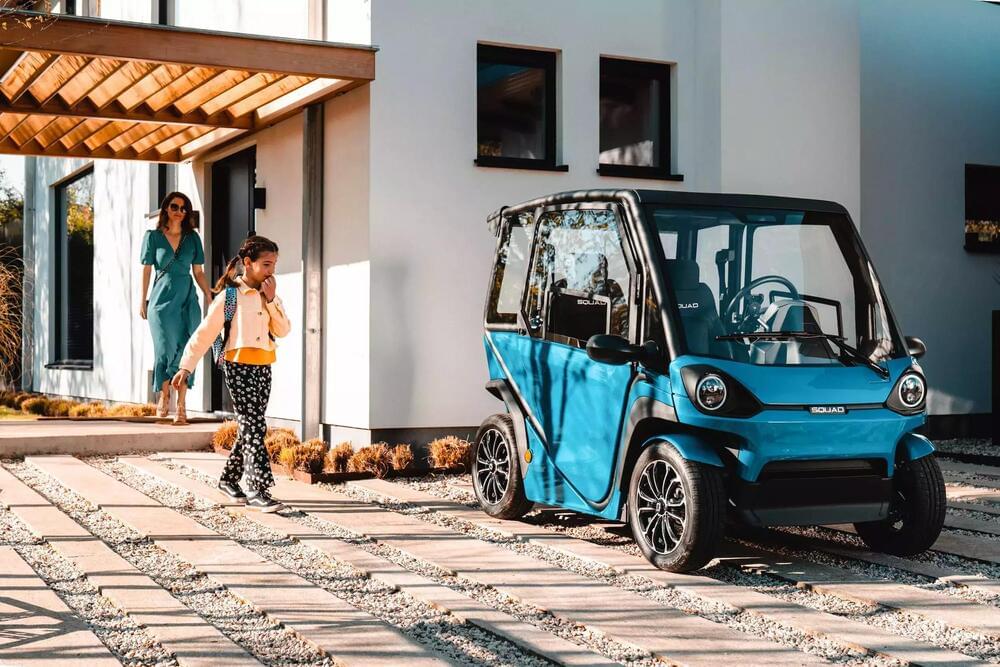






Probs just an exterrestial’s ear ring or something 🤔
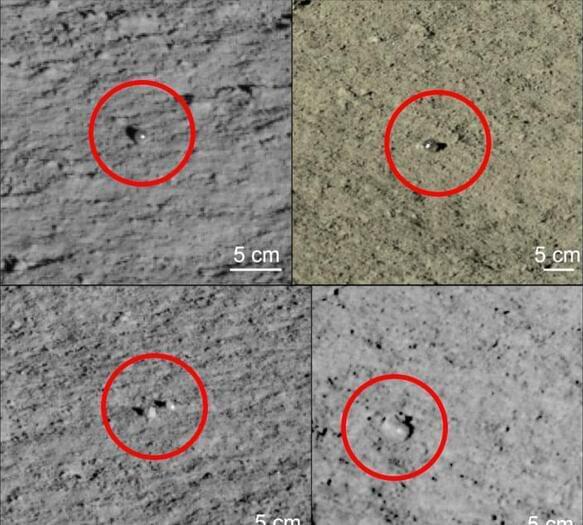
China’s Yutu-2 rover just won’t stop making — or at least claiming – weird discoveries on the Moon. Case in point, Chinese space authorities now say it’s found several mysterious glass spheres found on the far side of the lunar surface.
The team behind the discovery published a paper about the findings in the journal Science Bulletin, in which they describe the objects as “translucent glass globules.”
The spheres are roughly a centimeter in diameter, they say, and were spotted in images taken by the panorama camera on the Yutu-2 rover on the dark side of the Moon.
Researchers at Trend Micro identified a set of mobile apps available on the Google Play Store performing malicious tasks in the background, including stealing user credentials and banking details from Android users. Some of these apps have nearly 100,000 downloads, so the scope of the problem is considerable.
In total, the analysis revealed the detection of 200 malicious applications that hide code from dangerous malware variants, capable of putting users of the affected devices in serious trouble.
One of the main threats identified is Facestealer, a spyware variant capable of stealing Facebook access credentials, allowing subsequent phishing campaigns, social engineering, and invasive advertising. Facestealer is constantly updated and there are multiple versions, making it easy for them to get into the Play Store.
A group of researchers developed a tool capable of detecting errors in the way applications such as Adobe Acrobat or Microsoft Word process JavaScript code, which has allowed finding a total of 134 security flaws, of which 33 have already received a CVE tracking key.
The tool is called “Cooper”, in reference to the technique known as “Cooperative Mutation” it employees. Xu Peng, a software development specialist and co-author of the tool, explains that tools like the ones mentioned accept information from scripting languages; for example, Acrobat allows JavaScript to manipulate PDF files.
This requires the PDF to define native PDF objects and parse the JavaScript code. Native objects are processed by Acrobat modules and a built-in JavaScript engine handles the scripts, while a “binding layer” does the translation.