We derive a wealth of benefits from teetering between calmness and mayhem.



Just as electromagnetic energy is quantized into propagating photons, acoustic energy propagates in quanta called phonons. The science of photon behaviour – called quantum electrodynamics – is an important branch of modern physics because it provides a relativistic description of the interaction of light with matter. Scientists have used the theory in a variety of applications such as atomic clocks and quantum computation. In recent years, scientists have begun applying some of the same concepts to phonons in a field called quantum acoustodynamics. Last year, for example, two groups independently used laser-based measurements to entangle the oscillations of membranes in cavities.
Like other young researchers, I began my investigation of the brain without worrying much whether this perception-action theoretical framework was right or wrong. I was happy for many years with my own progress and the spectacular discoveries that gradually evolved into what became known in the 1960s as the field of “neuroscience.” Yet my inability to give satisfactory answers to the legitimate questions of my smartest students has haunted me ever since. I had to wrestle with the difficulty of trying to explain something that I didn’t really understand.
Over the years I realized that this frustration was not uniquely my own. Many of my colleagues, whether they admitted it or not, felt the same way. There was a bright side, though, because these frustrations energized my career. They nudged me over the years to develop a perspective that provides an alternative description of how the brain interacts with the outside world.
The challenge for me and other neuroscientists involves the weighty question of what, exactly, is the mind. Ever since the time of Aristotle, thinkers have assumed that the soul or the mind is initially a blank slate, a tabula rasa on which experiences are painted. This view has influenced thinking in Christian and Persian philosophies, British empiricism and Marxist doctrine. In the past century it has also permeated psychology and cognitive science. This “outside-in” view portrays the mind as a tool for learning about the true nature of the world. The alternative view—one that has defined my research—asserts that the primary preoccupation of brain networks is to maintain their own internal dynamics and perpetually generate myriad nonsensical patterns of neural activity. When a seemingly random action offers a benefit to the organism’s survival, the neuronal pattern leading to that action gains meaning. When an infant utters “te-te,” the parent happily offers the baby “Teddy,” so the sound “te-te” acquires the meaning of the Teddy bear. Recent progress in neuroscience has lent support to this framework.
Track 4 from the split digital album between Triangular Ascension & Abiotha.

In this episode of Longevity by Design, our hosts, Dr. Gil Blander and Ashley Reaver, MS, RD, CSSD, are joined by Dr. George Church, Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School. Tune in as Dr. George Church discusses the many roles of gene therapy, including its ability to reverse age-related diseases.
For science-backed ways to live a healthier, longer life, download InsideTracker’s InnerAge eBook at insidetracker.com/podcast.
Social:
Instagram — https://www.instagram.com/insidetracker.
Twitter — https://twitter.com/InsideTracker.
Facebook — https://www.facebook.com/InsideTracker.
Website — https://www.insidetracker.com/
In the Press — https://www.insidetracker.com/press-page/
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is “fully deployed,” according to the agency’s science administrator Thomas Zurbuchen — and that’s certainly a reason to celebrate after decades of hard work and a ten billion dollar price tag.
But the massive space observatory isn’t out of the woods just yet. As it spins around the Sun in a chaotic orbit, it will likely encounter plenty of space debris along the way — and an impact, its team says, is likely inevitable.
“Some small impacts from micrometeorites will happen,” NASA Goddard Space Flight Center scientist Michelle Thaller said during a livestream over the weekend. “You know, over the lifetime of the mission there will be some damage to the mirrors of the telescope.”

Astronomers are flummoxed by a mysterious celestial object that appears to be releasing massive bursts of energy at regular 18 minute intervals.
Like a lighthouse, the beacon is sending out radiation three times an hour at such an intensity that it’s one of the brightest points in the sky — and, researchers say, it could turn out to be an entirely new class of celestial object.
A team, led by astrophysicist Natasha Hurley-Walker from the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, had a closer look at the object after it was discovered by Curtin University student Tyrone O’Doherty, who used the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) telescope in outback Western Australia.

Round Rock-based motor company Infinitum Electric is expanding as it steps up production and breaks into the electric vehicle business.
The company is growing its footprint and workforce on the back of an $80 million funding round, which it announced this week. The financial infusion brings the company’s funding to date to $135 million.
Infinitum Electric was founded in 2016 in Austin by CEO Ben Schuler and moved to Round Rock in 2019. The motors include circuit boards that cut down on some of the costly equipment required in traditional motors, making Infinitum’s motors more efficient, smaller and quieter than traditional motors, according to the company.
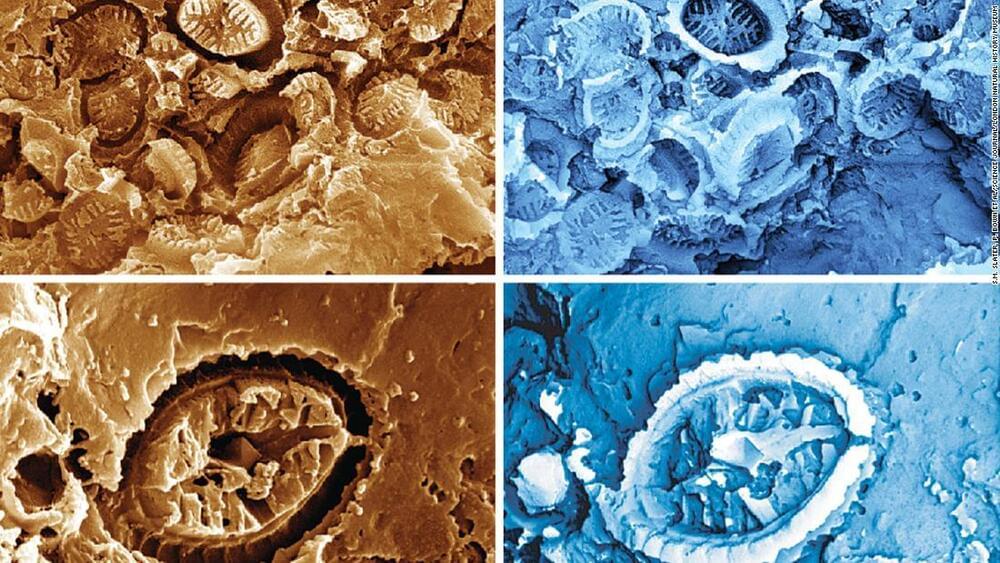
The unexpected discovery of “ghost” fossils belonging to tiny, ancient organisms could provide insights about how life reacts to climate change in Earth’s oceans.
Looking through a powerful microscope, researchers were stunned to see the impressions left by single-celled plankton, or fossilized nannoplankton, that lived millions of years ago – especially since they were analyzing something else.
A study detailing the findings published Thursday in the journal Science.