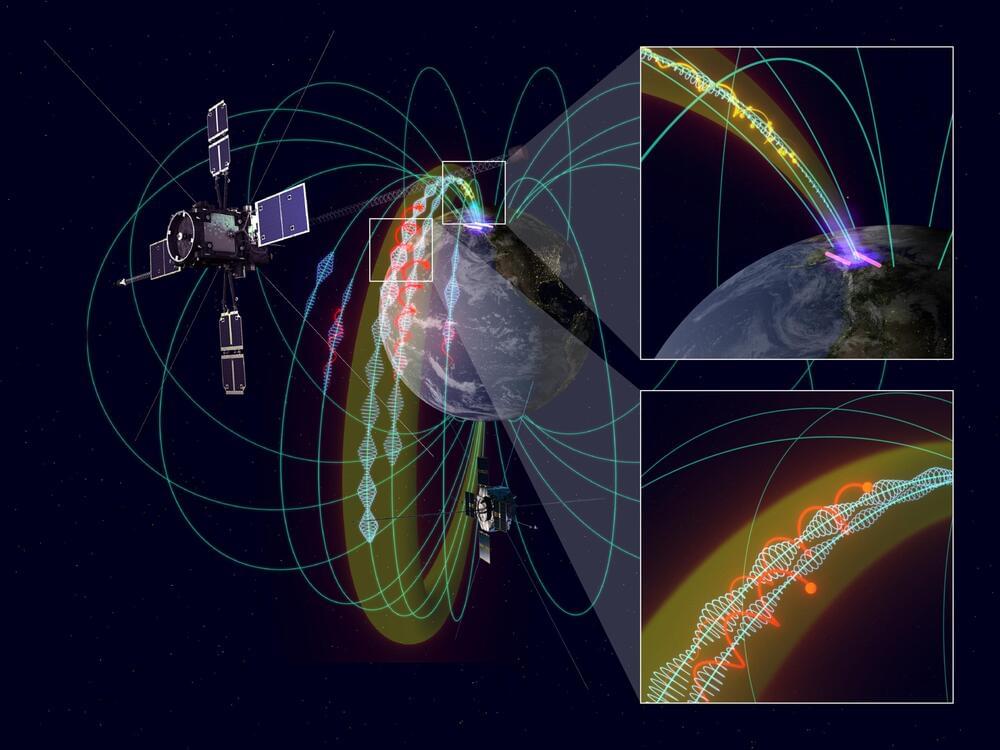
Using data on electromagnetic (EM) waves and plasma particles measured simultaneously via multiple satellites, an international collaborative research group has discovered the existence of invisible “propagation path” of EM waves and elucidated the mechanism by which EM waves propagate to the ground.
It is known that various kinds of EM waves occur naturally in geospace and cause variations in the plasma environment that surrounds the Earth via a physical process known as wave–particle interaction. In particular, when geospace storms occur due to disturbances of sun and solar wind, EM waves become more active, and variations of geospace environment sometimes, may cause damage to spacecrafts, expose astronauts to radiation, and cause terrestrial power grid failures. To understand variation in the plasma environment caused by EM waves in space, in-situ measurement has been performed in space using spacecrafts, such as the Japanese geospace satellite Arase.
As EM waves in space propagate far away from their origin, to correctly understand the effects of EM waves, it is crucial to understand where in space the EM waves are generated and how they are propagated. However, it has been difficult to unravel the origin of EM waves and the mysteries of how EM waves spread spatially using only single-point observation. “Electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves (EMIC waves),” which are the focus of this study, are an important class of EM wave in geospace that control variations in the geospace plasma environment. The source region of ion mode waves has a finite spatial extent, and generated EMIC waves are considered to propagate north to south along the geomagnetic field lines. The specific spatial size of the EMIC wave source region and the 3D aspect of how the propagation path is formed from space to ground are yet to be elucidated.