Circa 2017 o.o
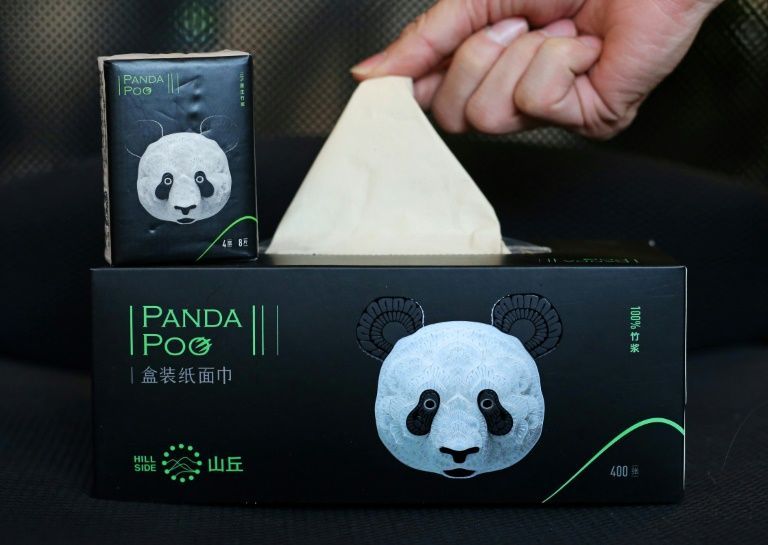
When life gave one Chinese company giant panda poop, it decided to make paper — and profits. The Qianwei Fengsheng Paper Company in southwest Sichuan province has teamed up with the China Conservation and Research Center for the Giant Panda to recycle the animal’s faeces and food debris into toilet paper, napkins and other household products, state media reported Wednesday. The goods, soon to be released on the Chinese market, will be marketed as part of a “panda poo” product line decorated with a picture of the bamboo-eating, black-and-white bear. “They’re taking care of our garbage for us,” Huang Yan, a researcher at the giant panda centre, told the Chengdu Business Daily. Huang told Xinhua state news agency that the 10 kilograms (22 pounds) of bamboo poo that adult pandas unleash daily are rich in fibre after absorbing the fructose from the shoots. In addition to their valuable dung, pandas also produce 50 kilograms of food waste every day from the bamboo husks they spit out after chewing. While the process of turning bamboo into paper generally involves the breaking down of fructose to extract fibre, this step naturally occurs in the pandas’ digestive tract, the paper company’s president, Yang Chaolin, told Xinhua. Fengsheng will collect the faeces from three panda bases in Sichuan a couple of times a week. After it is boiled, pasteurised and turned into paper, it will be tested for bacteria before going on sale. Boxes of “panda poo” tissues will be sold at 43 yuan ($6.5) a pop. “Pandas get what they want and we do too,” Yang said. “It’s a win-win.”