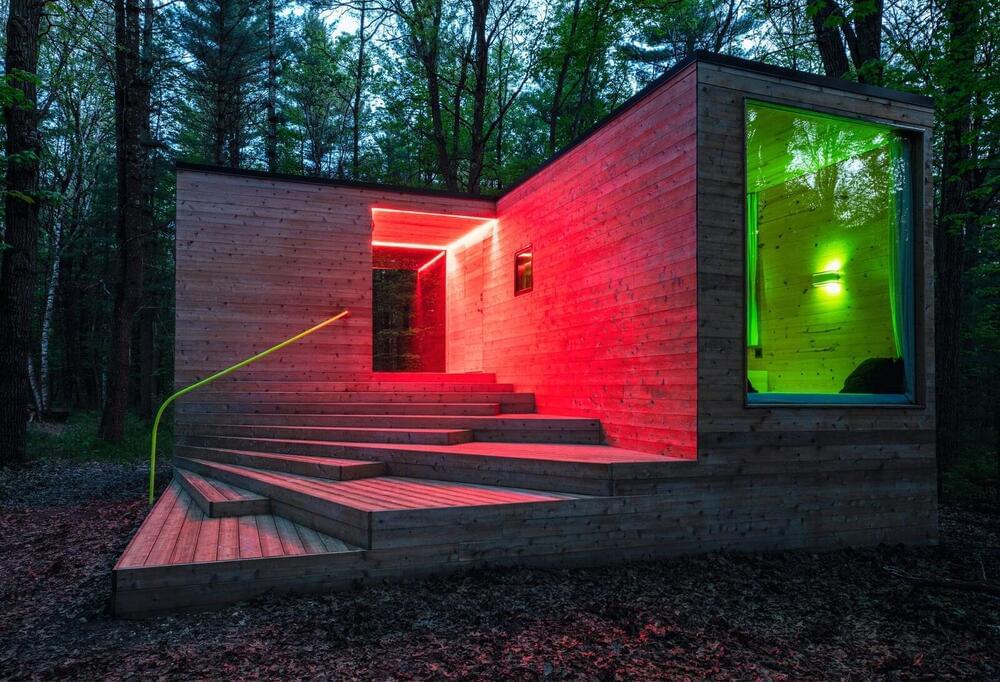
With inspiration pulled straight from movies, Carhartt, and even Kanye West, the Airbnb—designed and built by two friends—went viral on TikTok for being anything but your typical weekend away.


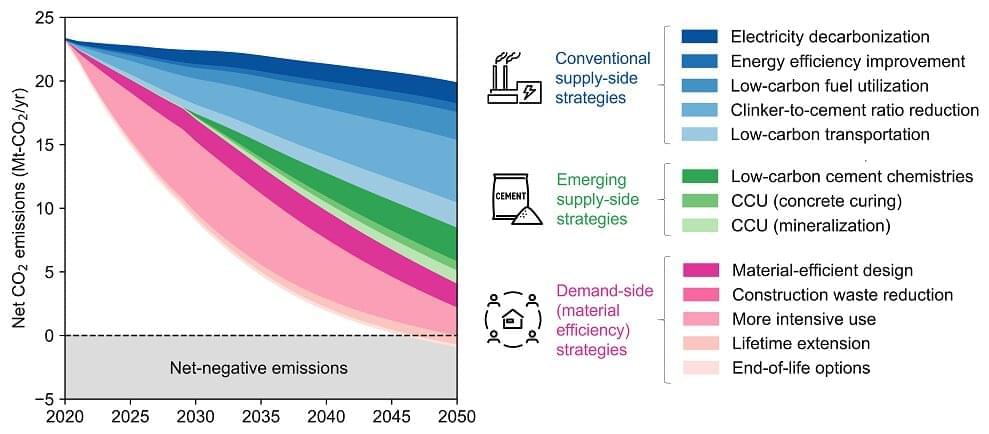
The concrete industry is just one of many looking at new manufacturing methods to reduce its carbon footprint. These efforts are essential to fulfilling the Paris Agreement, which asks each of its signees to achieve a net-zero carbon economy by 2050. However, a new study from researchers in Japan and Belgium and focusing exclusively on Japan concludes that improved manufacturing technologies will only get the industry within 80% of its goal. Using a dynamic material flows analysis model, the study claim that the other 20% will have to come from changes in how concrete is consumed and managed, putting expectations on the buyer as well as the seller.
Electric cars, fluorescent lights, water-saving shower heads, these are all examples of efforts to lower our carbon footprint. However, the energy savings are made from the supply side, with companies developing new technologies that reduce the amount of energy consumed for the same amount of use. Notably, they put little demand on the user, who can use the product no differently than before.
The same holds true for concrete, the most consumed human-made material in the world. Many studies have shown the potential for making the concrete industry more energy efficient through esoteric efforts like “clinker-to-cement ratio reduction,” “cement substitution with alternative binders,” and “carbon capture and utilization.” The problem, explains Dr. Takuma Watari, a researcher at the Japan National Institute for Environmental Studies and lead of the new study, is that supply-side efforts are not enough if nations are serious about achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
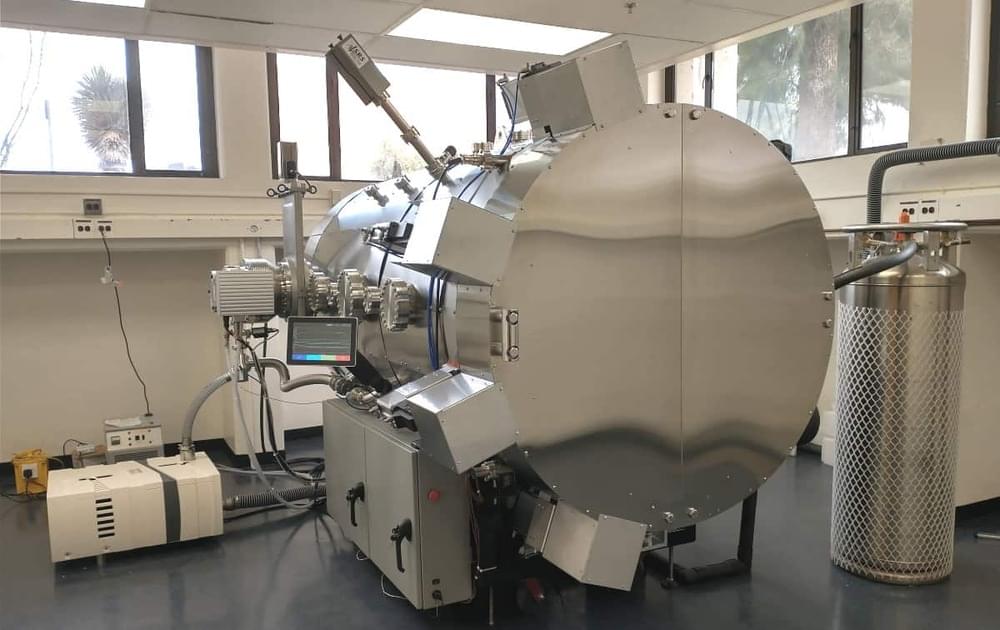
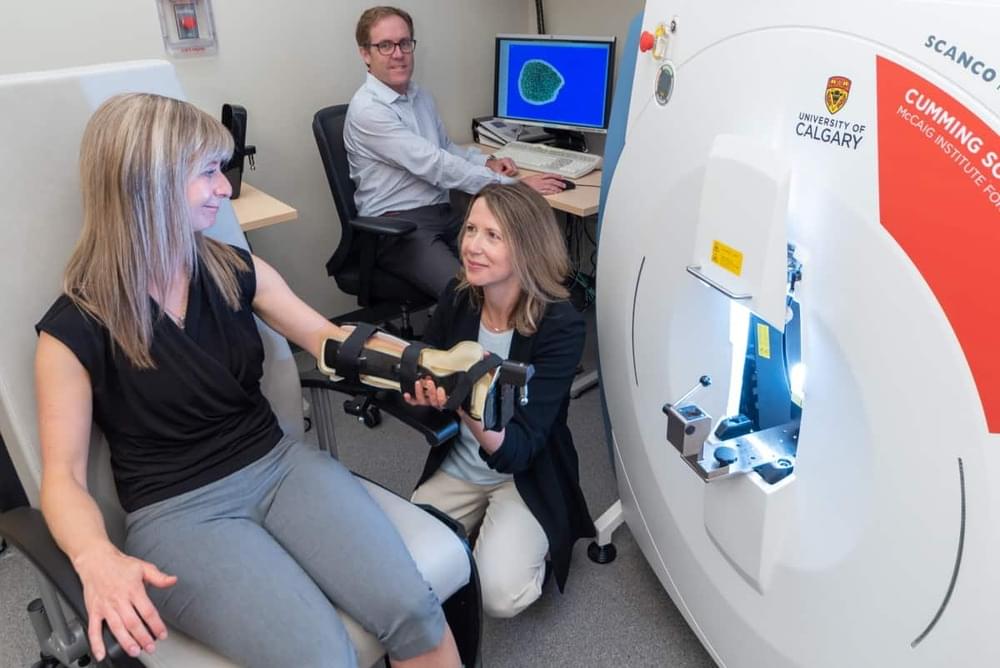
Equally important is the emphasis that RVS puts on its own off-the-shelf thermal vacuum systems. Put another way, that means thermal testing at a palatable price-point while also ensuring that ease-of-use is paramount. “In responding to our call for proposals, RVS was competitive on price and delivered versus desired functionality,” notes Manny Montoya, CAAO technical manager, who heads up a diverse team of engineers, technicians and machinists supporting the research of Douglas and other astronomers at Steward Observatory.
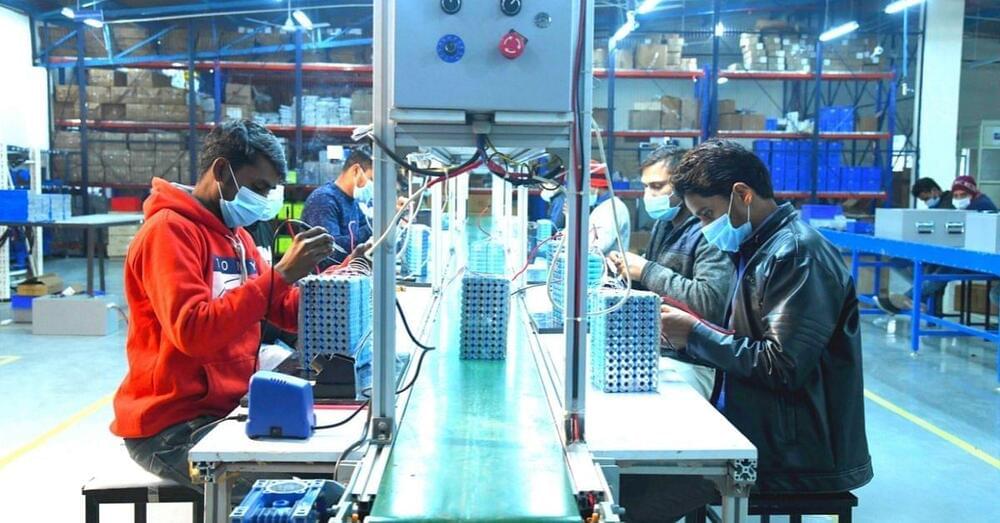

T he introduction of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has revolutionised transport technology. We wouldn’t be witnessing the current electric vehicle (EV) revolution without them. However, with the production of these batteries, which contain lithium and cobalt, comes associated with environmental and social costs. In the Democratic Republic of Congo, which accounts for 60% of the world’s supply of cobalt, a large number of unregulated mines use children as miners.
Children as young as 7 “breathe in cobalt-laden dust that can cause fatal lung ailments while working tunnels that are liable to collapse,” notes this report in The Guardian. Meanwhile, lithium mining has resulted in significant loss of groundwater in South America, while toxic leaks resulting from the process have poisoned water bodies in Tibet.
To lessen the burden on the environment, while meeting the growing demand for EVs, one possible solution could be recycling these Li-ion batteries.
Following the successful launch of NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Oct. 16, 2021, a group of engineers huddled around a long conference table in Titusville, Florida. Lucy was mere hours into its 12-year flight, but an unexpected challenge had surfaced for the first-ever Trojan asteroids mission.
Data indicated that one of Lucy’s solar arrays powering the spacecraft’s systems—designed to unfurl like a hand fan—hadn’t fully opened and latched, and the team was figuring out what to do next.
Teams from NASA and Lucy mission partners quickly came together to troubleshoot. On the phone were team members at Lockheed Martin’s Mission Support Area outside of Denver, who were in direct contact with the spacecraft.
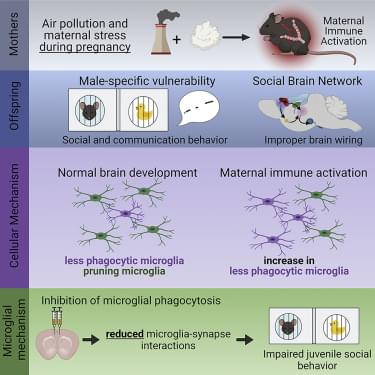
Block et al. show that combined exposure to air pollution and maternal stress during pregnancy activates the maternal immune system and induces male-specific impairments in social behavior and circuit connectivity in offspring. Cellularly, prenatal stressors diminish microglia phagocytic function,…
The serotonin hypothesis of depression is still influential. We aimed to synthesise and evaluate evidence on whether depression is associated with lowered serotonin concentration or activity in a systematic umbrella review of the principal relevant areas of research. PubMed, EMBASE and PsycINFO were searched using terms appropriate to each area of research, from their inception until December 2020. Systematic reviews, meta-analyses and large data-set analyses in the following areas were identified: serotonin and serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, concentrations in body fluids; serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding; serotonin transporter (SERT) levels measured by imaging or at post-mortem; tryptophan depletion studies; SERT gene associations and SERT gene-environment interactions. Studies of depression associated with physical conditions and specific subtypes of depression (e.g.