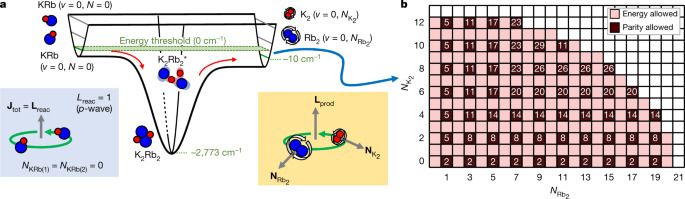
In a major breakthrough, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have discovered how amyloid beta—the neurotoxin believed to be at the root of Alzheimer’s disease (AD)—forms in axons and related structures that connect neurons in the brain, where it causes the most damage. Their findings, published in Cell Reports, could serve as a guidepost for developing new therapies to prevent the onset of this devastating neurological disease.
Among his many contributions to research on AD, Rudolph Tanzi, Ph.D., vice chair of Neurology and co-director of the McCance Center for Brain Health at MGH, led a team in 1986 that discovered the first Alzheimer’s disease gene, known as APP, which provides instructions for making amyloid protein precursor (APP). When this protein is cut (or cleaved) by enzymes—first, beta secretase, followed by gamma secretase—the byproduct is amyloid beta (sometimes shortened to Abeta). Large deposits of amyloid beta are believed to cause neurological destruction that results in AD. Amyloid beta formed in the brain’s axons and nerve endings causes the worst damage in AD by impairing communication between nerve cells (or neurons) in the brain. Researchers around the world have worked intensely to find ways to block the formation of amyloid beta by preventing cleavage by beta secretase and gamma secretase. However, these approaches have been hampered by safety issues.
Despite years of research, a major mystery has remained. “We knew that Abeta is made in the axons of the brain’s nerve cells, but we didn’t know how,” says Tanzi. He and his colleagues probed the question by studying the brains of mice, as well as with a research tool known as Alzheimer’s in a dish, a three-dimensional cell culture model of the disease created in 2014 by Tanzi and a colleague, Doo Yeon Kim, Ph.D. Earlier, in 2013, several other MGH researchers, including neurobiologist Dora Kovacs, Ph.D. (who is married to Tanzi), and Raja Bhattacharyya, Ph.D., a member of Tanzi’s lab, showed that a form of APP that has undergone a process called palmitoylation (palAPP) gives rise to amyloid beta. That study indicated that, within the neuron, palAPP is transported in a fatty vesicle (or sac) known as a lipid raft. But there are many forms of lipid rafts.