A team of materials scientists at Rice University has developed a new way to grow ultrathin semiconductors directly onto electronic components.
The method, described in a study published in ACS Applied Electronic Materials, could help streamline the integration of two-dimensional materials into next-generation electronics, neuromorphic computing and other technologies demanding ultrathin high-speed semiconductors.
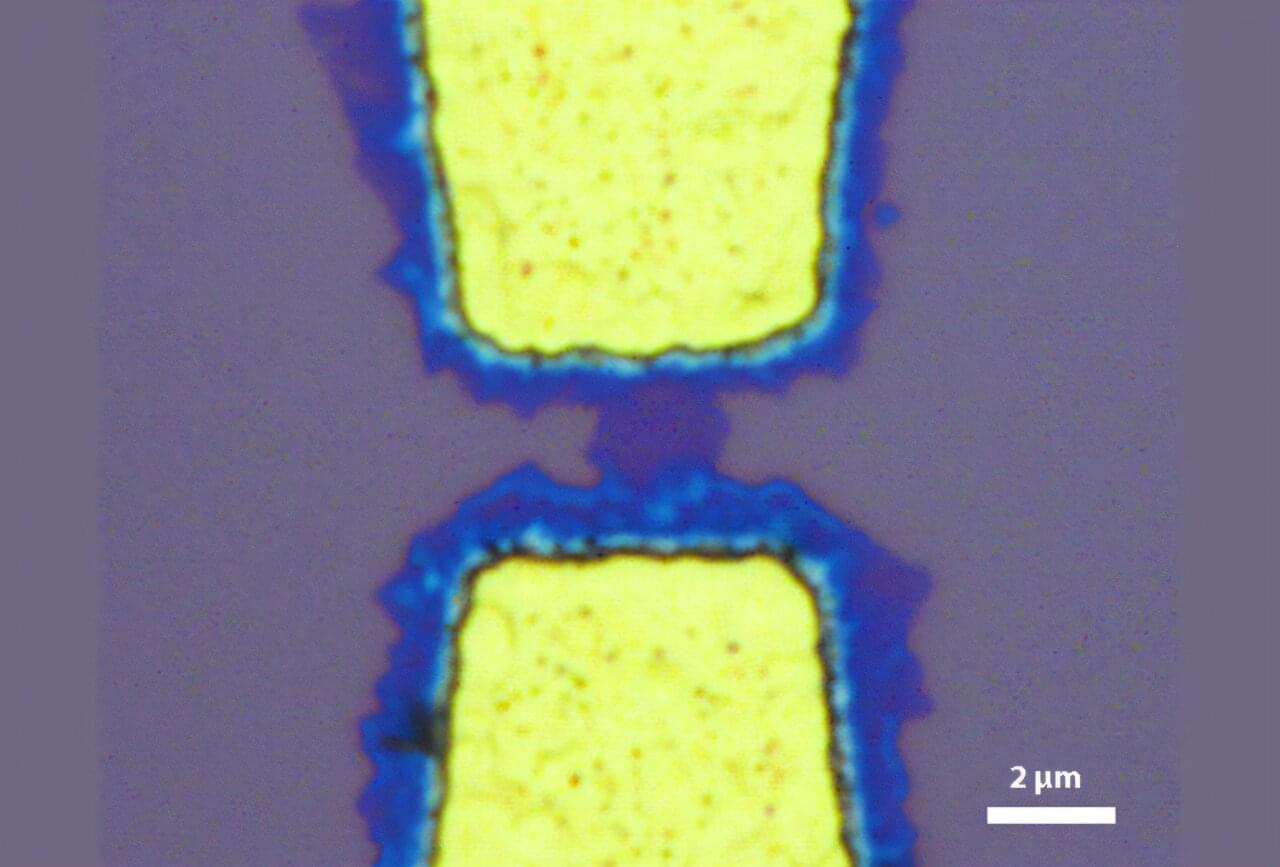
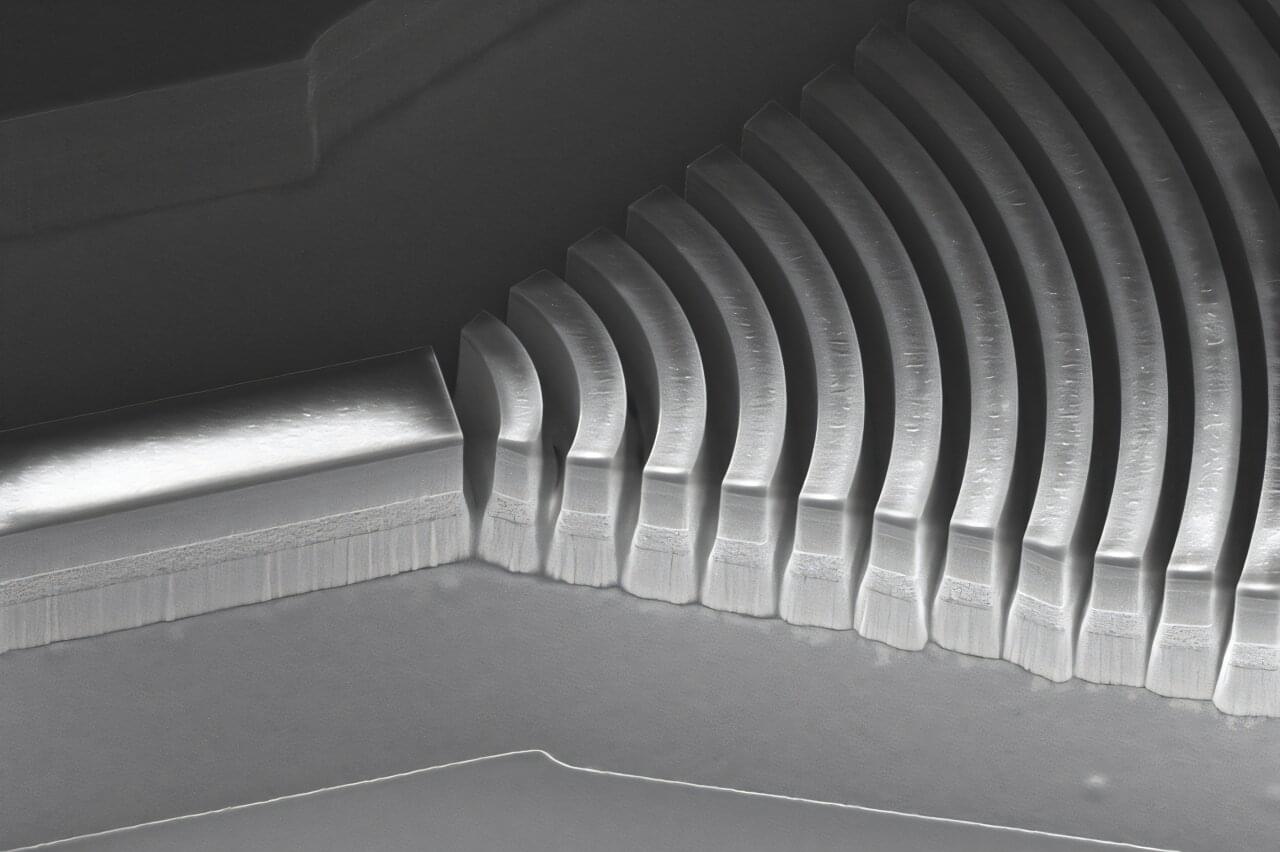
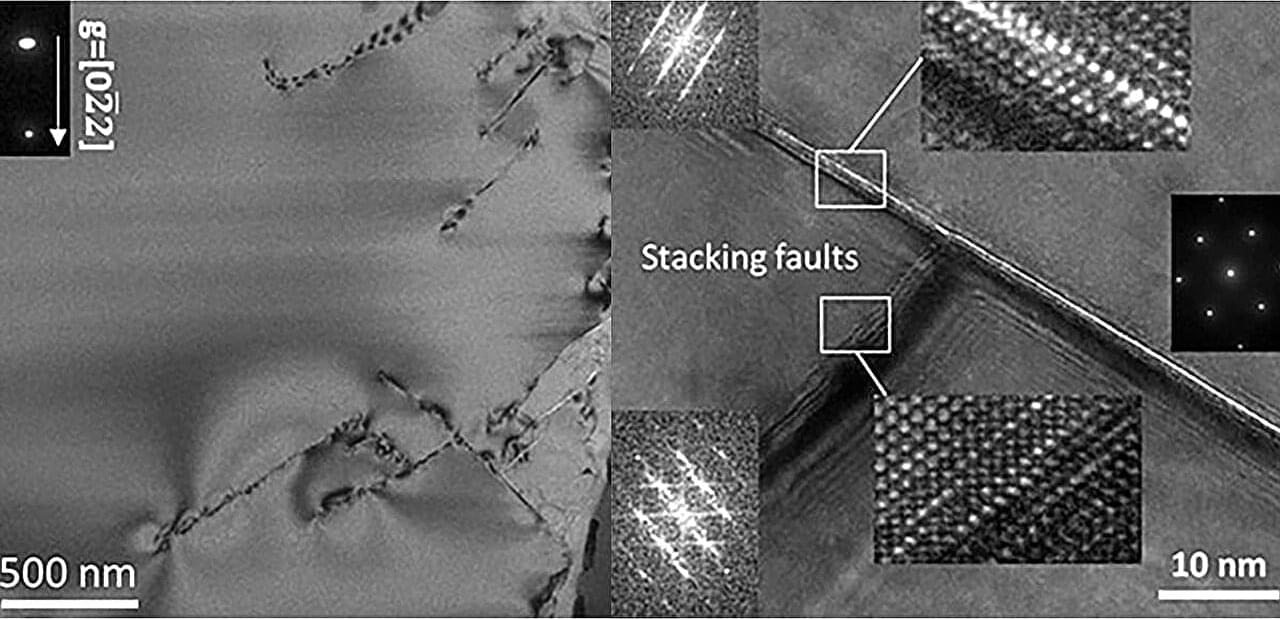
The researchers used chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to grow tungsten diselenide, a 2D semiconductor, directly onto patterned gold electrodes. They next demonstrated the approach by building a functional, proof-of-concept transistor. Unlike conventional techniques that require transferring fragile 2D films from one surface to another, the Rice team’s method eliminates the transfer process entirely.