A new APT hacker group, known as “Praying Mantis” is targeting high-profile public and private organizations in the United States.
The company that makes SG was testing it mainly against other cancers, but Dr. Tagawa, who is also a professor of urology and a member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine, and his colleagues showed in a 2015 pilot trial that it shrank tumors in three of six patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma that had not responded to platinum-based chemotherapy. That trial led to the enrollment of a group of 45 patients with treatment-refractory urothelial carcinoma (amongst many others with various advanced cancers) with encouraging results.
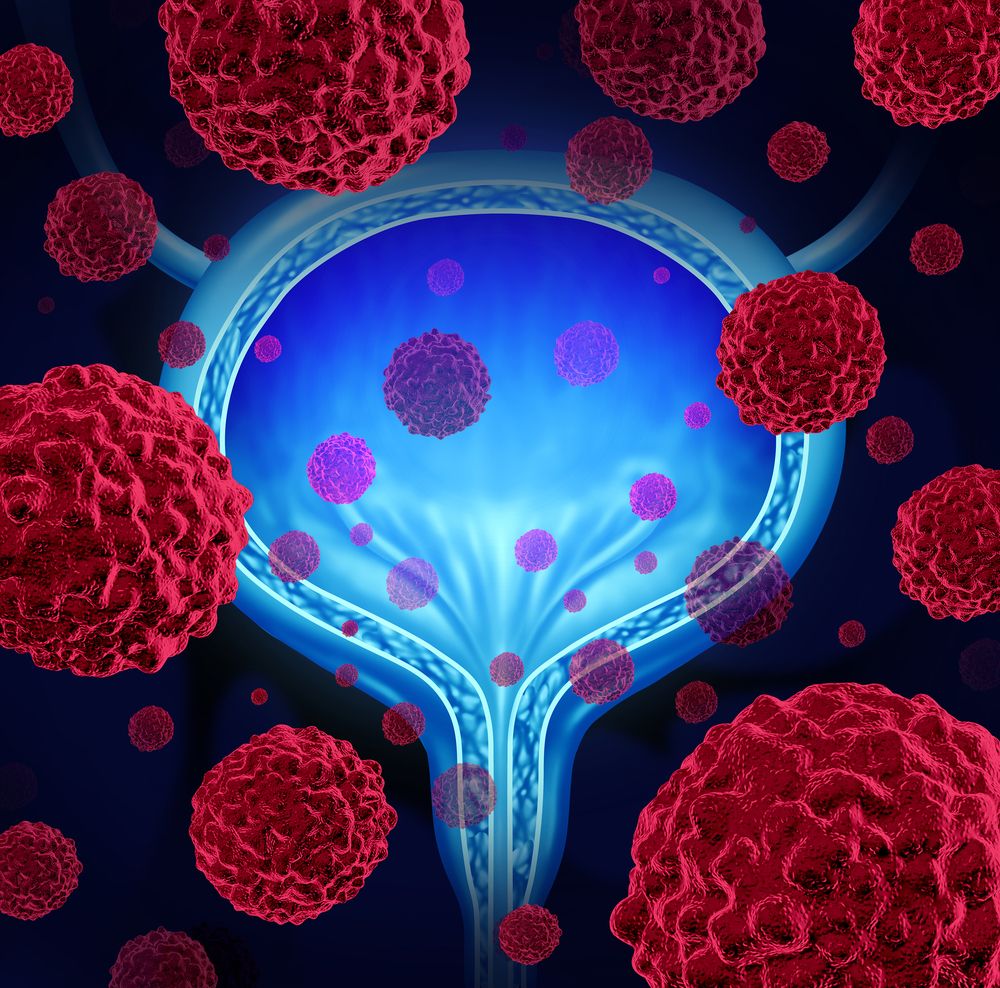
A new treatment for advanced urothelial cancer was effective with tolerable side effects in an international, multi-center phase 2 clinical trial led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
The trial results prompted a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated approval of the treatment on April 13, giving patients with this very aggressive type of cancer a new therapeutic option.
In the study, published online April 30 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, the researchers gave the treatment, sacituzumab govitecan (SG), previously known as IMMU-132 and now by the trade name Trodelvy, to 113 patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma, the most common type of bladder cancer. The trial population had progressed despite treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy and immune-boosting checkpoint inhibitors, and overall had a median of 3 prior lines of therapy. Treatment with SG was followed by sustained reductions in tumor size for 31 patients (27 percent), including complete tumor disappearance in six patients. The most common severe side effects included very low white blood cell count in 34 percent (with fever in 10 percent) and severe diarrhea in 9 percent, which were managed with dose adjustment and best supportive care.
“We have really enjoyed working with General Fusion and their team of scientists on the design of the Fusion Demonstration Plant, and are particularly excited that the first of its kind will be built in the UK,” the studio told Dezeen.
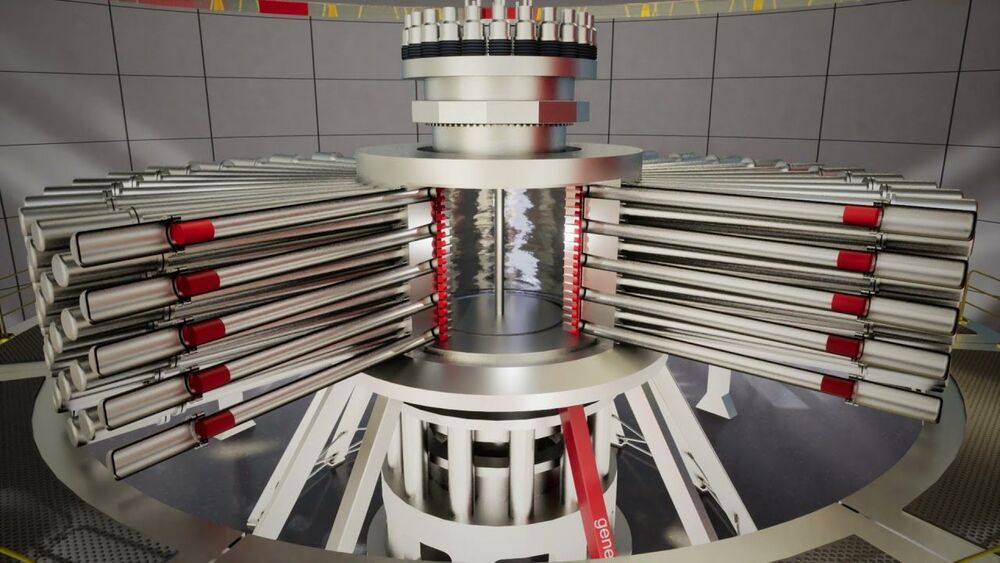
A prototype power plant with a nuclear fusion reactor is set to be built in Oxfordshire, England, by Amanda Levete’s firm AL_A for the Canadian energy company General Fusion.
Located on the UK Atomic Energy Authority’s (UKAEA) campus in Culham, the Fusion Demonstration Plant will be used to prove the viability of General Fusion’s nuclear fusion technology as a carbon-free energy source.
A_LA said it will be the world’s first nuclear power plant of its kind upon completion in 2025.
Alcohol and Life Expectancy
Posted in life extension
I know some epidemiological studies have promoted moderate alcohol intake as better for longevity than not drinking at all, but I thought that sounded kinda suspicious, so I dug into all the research to see for myself.
Turns out, there’s actually some in vivo studies showing life extension effects of low amounts of alcohol on animals.
What’s the effect of moderate alcohol on life expectancy? The science is confusing so we did a deep dive to find if a little booze is healthy.
The US military’s AI experiments are growing particularly ambitious. The Drive reports that US Northern Command recently completed a string of tests for Global Information Dominance Experiments (GIDE), a combination of AI, cloud computing and sensors that could give the Pentagon the ability to predict events “days in advance,” according to Command leader General Glen VanHerck. It’s not as mystical as it sounds, but it could lead to a major change in military and government operations.
The machine learning-based system observes changes in raw, real-time data that hint at possible trouble. If satellite imagery shows signs that a rival nation’s submarine is preparing to leave port, for instance, the AI could flag that mobilization knowing the vessel will likely leave soon. Military analysts can take hours or even days to comb through this information — GIDE technology could send an alert within “seconds,” VanHerck said.
The most recent dry run, GIDE 3, was the most expansive yet. It saw all 11 US commands and the broader Defense Department use a mix of military and civilian sensors to address scenarios where “contested logistics” (such as communications in the Panama Canal) might pose a problem. The technology involved wasn’t strictly new, the General said, but the military “stitched everything together.”
Last week, a young woman with sickle cell anemia became the first person in the United States to have her cells altered with CRISPR gene editing technology. Here’s what that means for the future treatment of genetic diseases.
Harvard professor Avi Loeb launches new project to search for extraterrestrial life.
An effort announced Monday called the Galileo Project aims to search for and investigate physical objects that could be the result of an intelligent extraterrestrial civilization.
It’s helmed by Avi Loeb, a professor at Harvard University’s department of astronomy, who was recently the subject of scrutiny for claiming that interstellar comet ‘Oumuamua was in fact a piece of annihilated alien technology.
The project will continue Loeb’s efforts to pin down the origin of ‘Oumuamua, as well as look for other similar objects that Loeb believes are indicative of alien life. It was founded in light of the recently released UAP government report.
Right now, protection against Covid-19 comes via an injection. But in future, those vaccines could come from inhalers or even pills.
In a white, airy laboratory in Medicon Village, one of southern Sweden’s largest science parks, chemist Ingemo Andersson holds up a thin, plastic inhaler, half the size of a matchbox.
Her team is hoping this tiny product could play a big role in the global fight against coronavirus allowing people to take powdered versions of future vaccines at home.
Researchers are looking at easier ways for people to get the vaccine, including via inhalers and tablets.
The paper’s authors said they’ve created an endlessly challenging virtual playground for AI. The world, called XLand, is a vibrant video game managed by an AI overlord and populated by algorithms that must learn the skills to navigate it.
The game-managing AI keeps an eye on what the game-playing algorithms are learning and automatically generates new worlds, games, and tasks to continuously confront them with new experiences.
The team said some veteran algorithms faced 3.4 million unique tasks while playing around 700000 games in 4000 XLand worlds. But most notably, they developed a general skillset not related to any one game, but useful in all of them.