FCC chief Brendan Carr urged the CEOs of Google and Apple to remove TikTok from their stores, arguing that Chinese “data harvesting” poses an “unacceptable national security risk.”


Stem cells in human urine have the potential to regenerate tissue.

Summary: Stem cells in human urine have the potential to regenerate tissue.
Source: wake forest baptist medical center.
The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) researchers who were the first to identify that stem cells in human urine have potential for tissue regenerative effects, continue their investigation into the power of these cells.

LeviPrint is a system that uses acoustic manipulation for assembling objects without physical contact. It generates acoustic fields that trap small particles, glue droplets and elongated stick-like elements that can be manipulated and reoriented as they are levitated. It is a fully functional system for manufacturing 3D structures using contactless manipulation.
It was developed by researchers from the UPNA/NUP-Public University of Navarre Asier Marzo and Iñigo Ezcurdia, who together with Rafael Morales (Ultraleap Ltd, UK) and Marco Andrade (University of São Paulo, Brazil) are authors of the paper “LeviPrint: Contactless Fabrication using Full Acoustic Trapping of Elongated Parts.”
This research is due to be presented in August in Vancouver (Canada) at SIGGRAPH, a conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques where companies such as Nvidia, Disney Research and Facebook Reality Labs present their work.
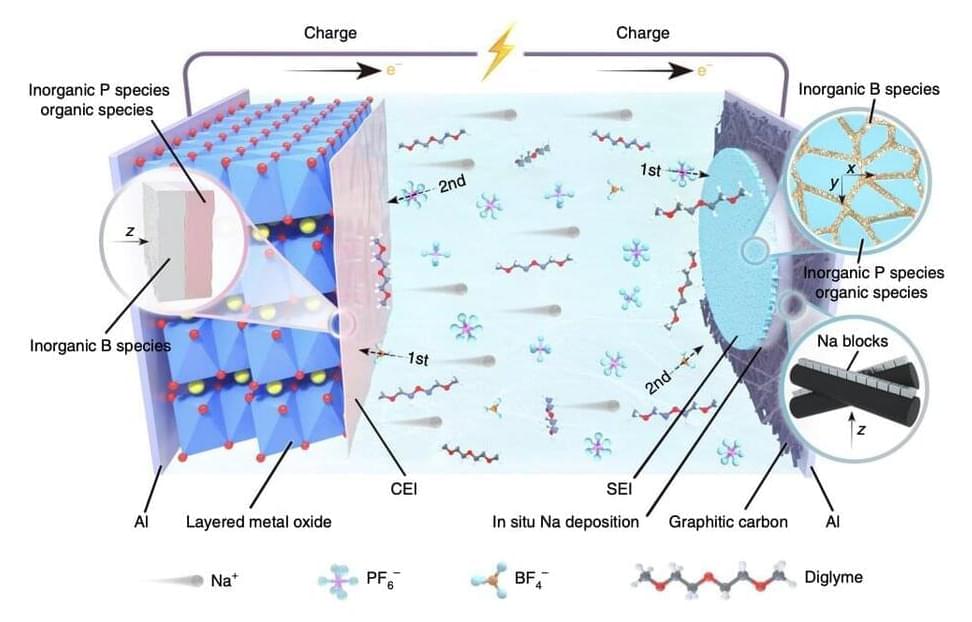
In recent years, engineers worldwide have been trying to devise new battery and energy storage technologies that are more sustainable and cost-effective. One of the solutions attracting particular interest is sodium-based battery technology.
Sodium-ion batteries could have numerous advantages over conventional and widely used lithium-based batteries. Most notably, as sodium is abundant on our planet and can be easily sourced, they could be affordable and easy to produce on a large-scale.
Despite their possible advantages, most sodium-ion batteries developed so far exhibited low energy densities, due to the relatively large atomic size of sodium and its considerable weight. Typically, these batteries exhibit energy densities below 160 Wh kg-1, which is significantly lower than that of lithium-ion batteries.

Extrusion-based 3D printing/bioprinting is a promising approach to generating patient-specific, tissue-engineered grafts. However, a major challenge in extrusion-based 3D printing and bioprinting is that most currently used materials lack the versatility to be used in a wide range of applications.
New nanotechnology has been developed by a team of researchers from Texas A&M University that leverages colloidal interactions of nanoparticles to print complex geometries that can mimic tissue and organ structure. The team, led by Dr. Akhilesh Gaharwar, associate professor and Presidential Impact Fellow in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, has introduced colloidal solutions of 2D nanosilicates as a platform technology to print complex structures.
2D nanosilicates are disc-shaped inorganic nanoparticles 20 to 50 nanometers in diameter and 1 to 2 nanometers in thickness. These nanosilicates form a “house-of-cards” structure above a certain concentration in water, known as a colloidal solution.

Mitochondria are the power plants of cells, and they contain their own genetic material and RNA molecules. Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ) have now discovered that certain modifications in mitochondrial RNA boost the invasive spread of cancer cells by supporting protein synthesis in mitochondria. They have established that a specific gene expression signature correlating with high levels of mitochondrial RNA modifications is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with head and neck cancer. When the researchers blocked the responsible RNA modifying enzyme in cancer cells, the number of metastases was reduced. Certain antibiotics that suppress protein synthesis in mitochondria were also able to prevent the invasive spread of cancer cells in laboratory experiments. The results have now been published in the journal Nature.
Cancer cells in aggressive tumors invade the surrounding tissue in an attempt to form a new tumor in other organs. During this journey, cancer cells have to survive unfavorable conditions such as shortage of oxygen or shortage in nutrients. To overcome these stress factors, cancer cells adapt their energy production accordingly. The molecular mechanisms allowing this flexibility were poorly understood until now. “However, we suspected that this metabolic plasticity must be a key to the successful spread of the cancer cells,” says Michaela Frye; cell biologist at the German Cancer Research Center.
Mitochondria are tiny, membrane-enveloped structures known as the powerhouse of every cell in our body. For energy production, they use the so-called respiratory chain present in the mitochondrial membrane. Because mitochondria contain their own genetic material, they themselves produce key components of the respiratory chain.

The production of wild and farm-raised fish, shellfish and algae reached record levels in 2020, and future increases could be vital to fighting world hunger, the Food and Agriculture Organization said Wednesday.
Driven by sustained growth in aquaculture, global fisheries and aquatic farming together hauled in 214 million tonnes, the UN agency said in a report.
The total first-sale value of 2020 production topped $400 million, with $265 million coming from aquaculture, a sector poised for further expansion.