They could be “critical in the fight against climate change.”
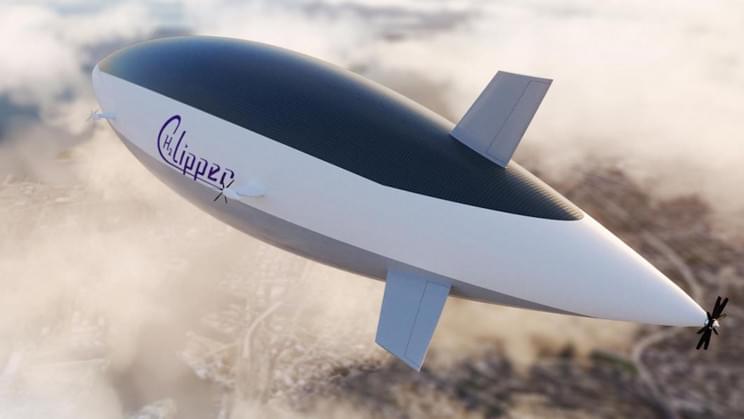
A California-based startup called H2 Clipper wants to resurrect the hydrogen-filled airship as a form of mass transport. The key difference is that it won’t be transporting people, it will be transporting cargo, a press statement reveals.
The company aims to kickstart a green global cargo network by leveraging the world’s renewed willingness to try alternative forms of transport following the IPCC’s dire climate change report for 2021.
H2 Clipper claims its cargo airships can carry 8–10 times the payload of the best cargo plane over 6,000 miles (9,656 km), and it can do so at a quarter of the price. They will have a payload capacity of approximately 340,000 lb (150,000 kg) sitting in up to 265,000 cubic feet (7,530 cubic meters) of cargo space.
As for speed, the H2 Clipper would travel at a cruising speed of 175 mph (282 km/h), meaning it would move close to ten times faster than a cargo ship — though it would obviously lag behind a cargo plane in that department. The main advantage over today’s cargo planes is that the H2 Clipper produces zero carbon emissions.
Full Story: