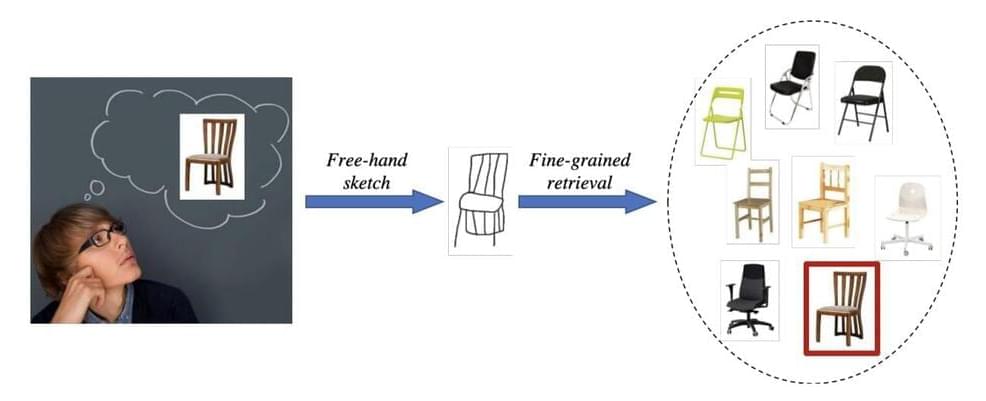
Researchers at the SketchX, University of Surrey have recently developed a meta learning-based model that allows users to retrieve images of specific items simply by sketching them on a tablet, smartphone, or on other smart devices. This framework was outlined in a paper set to be presented at the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), one of the top three flagship computer vision conferences along with CVPR and ICCV.
“This is the latest along the line of work on ‘fine-grained image retrieval,’ a problem that my research lab (SketchX, which I direct and founded back in 2012) pioneered back in 2015, with a paper published in CVPR 2015 titled ‘Sketch Me That Shoe,’” Yi-Zhe Song, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “The idea behind our paper is that it is often hard or impossible to conduct image retrieval at a fine-grained level, (e.g., finding a particular type of shoe at Christmas, but not any shoe).”
In the past, some researchers tried to devise models that can retrieve images based on text or voice descriptions. Text might be easier for users to produce, yet it was found only to work at a coarse level. In other words, it can become ambiguous and ineffective when trying to describe details.