Science is always looking for more computing power and more efficient tools capable of answering its questions. Quantum computers are the new frontier in data processing, as they use the quantum properties of matter, such as the superposition of states and entanglement, to perform very complex operations.
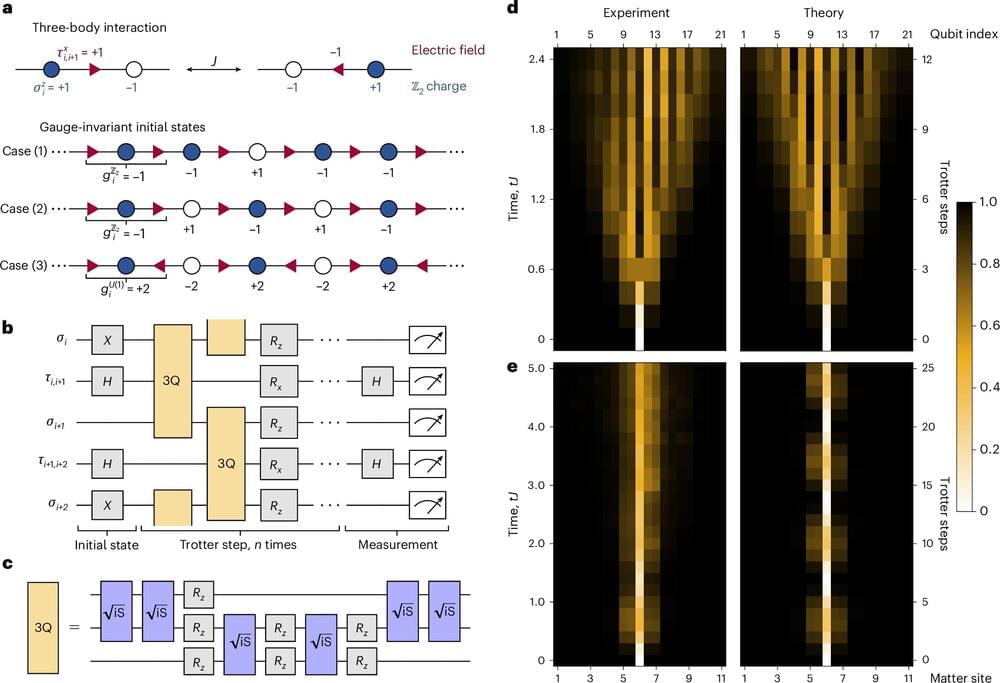
A research team coordinated by the Department of Physics of the University of Trento had the opportunity to test some hypotheses on confinement in Z2 lattice gauge theory on the quantum computers of Google’s Quantum Artificial Intelligence Lab, in California. Their work was published in Nature Physics.
Gauge theories describe the fundamental forces in the standard model of particle physics and play an important role in condensed matter physics. The constituents of gauge theories, such as charged matter and electric gauge field, are governed by local gauge constraints, which lead to key phenomena that are not yet fully understood. In this context, quantum simulators may offer solutions that cannot be reached using conventional computers.