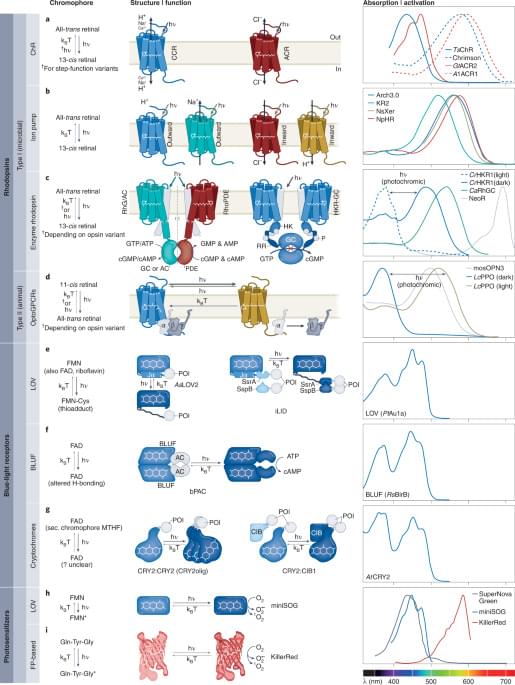
This Review provides a comprehensive overview of presynaptic applications of optogenetic tools, including the associated challenges, current limitations and future directions for this approach.

Several traditional medicines commonly used in South Asia, are effective in maintaining blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to a new study led by experts at the University of Nottingham.
Many South Asian countries, including India and Nepal, have been using the Ayurvedic natural medical system for thousands of years. Some of the herbs included in this traditional medical system are also used in other parts of the world including Iran, China, and Mexico – to name a few.
It features a multi-pronged and individualized approach to managing health conditions that can include lifestyle modification (including diet), Ayurvedic detoxifying and purifying therapies (e.g. Panchakarma), and Ayurvedic medicines (containing plant, animal, or mineral-origin ingredients – single or in combination).



Microsoft on Wednesday shed light on a now patched security vulnerability affecting Apple’s operating systems that, if successfully exploited, could allow attackers to escalate device privileges and deploy malware.
“An attacker could take advantage of this sandbox escape vulnerability to gain elevated privileges on the affected device or execute malicious commands like installing additional payloads,” Jonathan Bar Or of the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team said in a write-up.
Tracked as CVE-2022–26706 (CVSS score: 5.5), the security vulnerability impacts iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS, and watchOS and was fixed by Apple in May 2022.
Before quantum computers and quantum networks can fulfil their huge potential, scientists have got several difficult problems to overcome – but a new study outlines a potential solution to one of these problems.
As we’ve seen in recent research, the silicon material that our existing classical computing components are made out of has shown potential for storing quantum bits, too.
These quantum bits – or qubits – are key to next-level quantum computing performance, and they come in a variety of types.


Two weeks before his death, famed scientist Stephen Hawking published a research article predicting parallel universes and along with the end of our own.
Hawking and co-author Thomas Hertog published their results in “A Smooth Exit from Eternal Inflation,” outlining how scientists may also be able to discover other universes using spaceships. According to Hertog, Hawking completed the work on his deathbed, leaving a legacy worthy of the Nobel Prize.
