It is the latest major economy to announce its own virtual currency, as China trials the digital yuan.


Everywhere you want to go in deep space is far! For example, Elon Musk wants to put humans on Mars permanently while NASA wants to send astronauts there.
However, any traveler going to Mars has to endure a grueling trip through harsh space that lasts not less than five months, even with the most powerful rocket in history! If only we could find a faster way to travel through space! Also, the next star to us is about 4.5 light-years away, making it impossible to visit with the current space technologies!
However, an accidental discovery promises to fix that problem by enabling faster than the speed of light travel! What is the discovery, how does it affect space travel, and how does it affect you personally?

A report by Business Insider says Microsoft has scrapped plans for its own HoloLens 3 and has instead partnered with Samsung—but that no one really knows what’s going on.
Microsoft has reportedly scrapped its third-generation HoloLens, leaving the company’s “metaverse” plans in disarray.
According to a report from Business Insider, Microsoft killed off the HoloLens 3 in 2021, shifting to a planned device with Samsung instead. The problem? According to the publication, the company’s mixed-reality/augmented reality/virtual-reality division isn’t sure what it plans to do. That’s resulted in employees leaving for Meta and other companies instead.
The company told BI that it remains committed to HoloLens and future HoloLens development. It said the same to PCWorld in a statement. “Microsoft HoloLens remains a critical part of our plans for emerging categories like mixed reality and the metaverse,” the company said. “We remain committed to HoloLens and future HoloLens development.”


By studying the risk of re-identification more thoroughly, researchers were able to better articulate the fundamental requirements for information to be anonymous. They realized that a robust definition of anonymous should not rely on what side information may be available to an attacker. This led to the definition of Differential Privacy in 2006 by Cynthia Dwork, then a researcher at Microsoft. It quickly became the gold standard for privacy and has been used in global technology products like Chrome, the iPhone, and Linkedin. Even the US Census used it for the 2020 census.
Differential privacy solves the problem of side information by looking at the most powerful attacker possible: an attacker who knows everything about everyone in a population except for a single individual. Let’s call her Alice. When releasing information to such an attacker, how can you protect Alice’s privacy? If you release exact aggregate information for the whole population (e.g., the average age of the population), the attacker can compute the difference between what you shared and the expected value of the aggregate with everyone but Alice. You just revealed something personal about Alice.
The only way out is to not share the exact aggregate information but add a bit of random noise to it and only share the slightly noisy aggregate information. Even for the most well-informed of attackers, differential privacy makes it impossible to deduce what value Alice contributed. Also, note that we have talked about simple insights like aggregations and averages but the same possibilities for re-identification apply to more sophisticated insights like machine learning or AI models, and the same differential privacy techniques can be used to protect privacy by adding noise when training models. Now, we have the right tools to find the optimal tradeoff: adding more noise makes it harder for a would-be attacker to re-identify Alice’s information, but at a greater loss of data fidelity for the data analyst. Fortunately, in practice, there is a natural alignment between differential privacy and statistical significance.
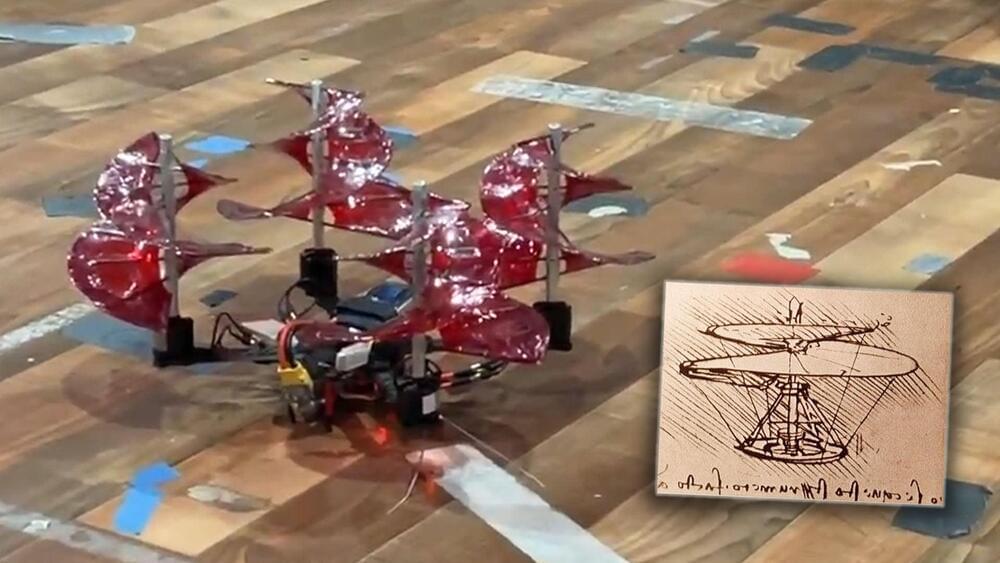


DaVinci penned the aerial screw design in the 1400s, way before air travel was a thing. Now, it’s being put to action with this student-built drone.
Drones aren’t anything new —multi-rotor aircraft are becoming a bigger part of people’s lives every day. From the latest batch of up-and-coming urban air mobility companies to hobby applications, electric aircraft with four or more motors are commonplace, and generally, they use conventional multi-bladed propellers to keep themselves aloft. That’s not what’s going on with this particular drone developed by engineering students at the University of Maryland, though.
Assembled for a student design competition hosted by the Vertical Flight Society, it’s a mixture of old and new. With rotors reminiscent of Leonardo DaVinci’s aerial screw illustrations from the late 1490s, it flies like any other drone would, all while looking extremely bizarre and having interesting flight characteristics.

WASHINGTON, Feb 1 (Reuters) — Tesla Inc (TSLA.O) will recall 53,822 U.S. vehicles with the company’s Full Self-Driving (Beta) software that may allow some models to conduct “rolling stops” and not come to a complete stop at some intersections posing a safety risk.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) said the recall covers some 2016–2022 Model S and Model X, 2017–2022 Model 3, and 2020–2022 Model Y vehicles. NHTSA said the feature also known as FSD Beta may allow vehicles to travel through an all-way stop intersection without first coming to a stop.
Tesla will perform an over-the-air software update that disables the “rolling stop” functionality, NHTSA said. The agency added it “maintains regular discussions with all manufacturers to discuss potential safety concerns of these types of systems.”
