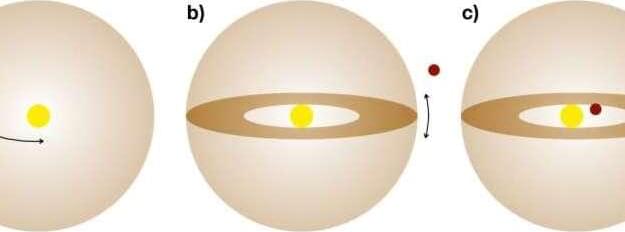
Stars die and vanish from sight all the time, but astronomers were puzzled when one that had been stable for more than a decade almost disappeared for eight months.
Between late 2024 and early 2025, one star in our galaxy, dubbed ASASSN-24fw, dimmed in brightness by about 97%, before brightening again. Since then, scientists have been swapping theories about what was behind this rare, exciting event.
Now, an international team led by scientists at The Ohio State University may have come up with an answer to the mystery. In a new study recently published in The Open Journal of Astrophysics, astronomers suggest that because the color of the star’s light remained unchanged during its dimming, the event wasn’t caused by the star evolving in some way, but by a large cloud of dust and gas around the star that occluded Earth’s view of it.