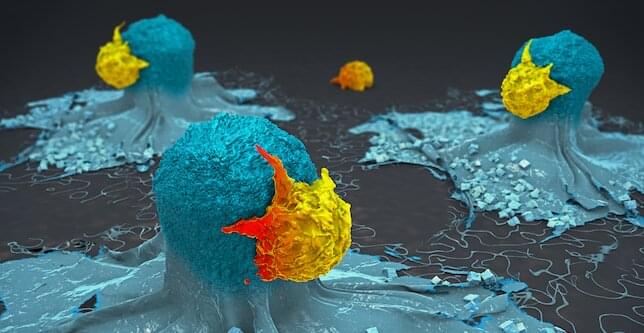
It’s not often that a failed clinical trial leads to a scientific breakthrough.
When patients in the UK started showing adverse side effects during a cancer immunotherapy trial, researchers at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) Center for Cancer Immunotherapy and University of Liverpool went back through the data and worked with patient samples to see what went wrong.
Their findings, published recently in Nature, provide critical clues to why many immunotherapies trigger dangerous side effects—and point to a better strategy for treating patients with solid tumors.