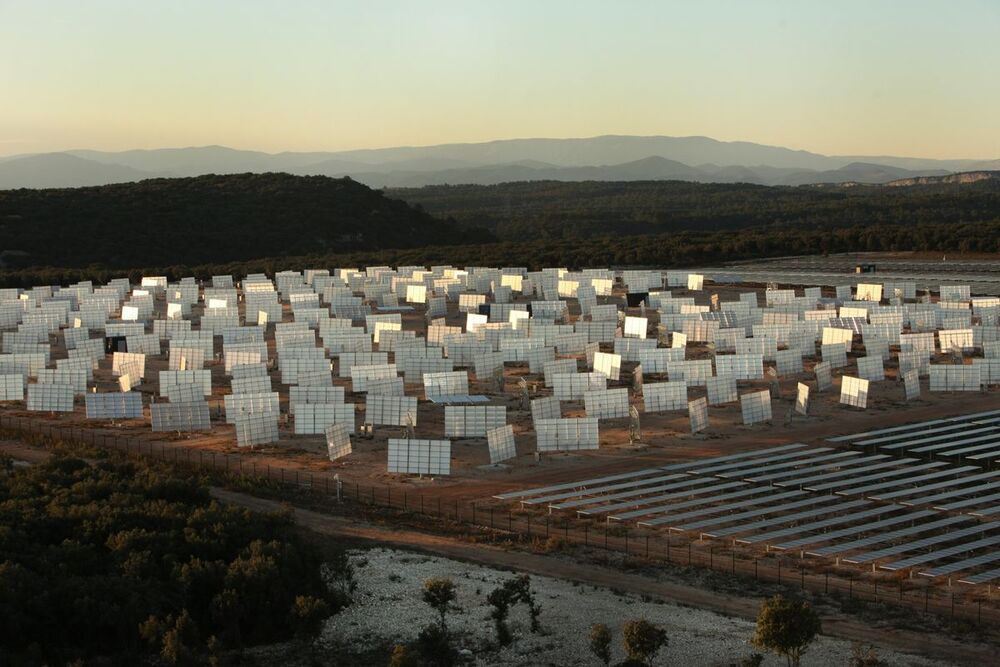
After focusing for decades on cutting costs, the solar industry is shifting attention to making new advances in technology.
Team develops simulator with 256 qubits, largest of its kind ever created.
A team of physicists from the Harvard-MIT Center for Ultracold Atoms and other universities has developed a special type of quantum computer known as a programmable quantum simulator capable of operating with 256 quantum bits, or “qubits.”
The system marks a major step toward building large-scale quantum machines that could be used to shed light on a host of complex quantum processes and eventually help bring about real-world breakthroughs in material science, communication technologies, finance, and many other fields, overcoming research hurdles that are beyond the capabilities of even the fastest supercomputers today. Qubits are the fundamental building blocks on which quantum computers run and the source of their massive processing power.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is able to recognize the biological activity of natural products in a targeted manner, as researchers at ETH Zurich have demonstrated. Moreover, AI helps to find molecules that have the same effect as a natural substance but are easier to manufacture. This opens up huge possibilities for drug discovery, which also has potential to rewrite the rulebook for pharmaceutical research.
Nature has a vast store of medicinal substances. “Over 50 percent of all drugs today are inspired by nature,” says Gisbert Schneider, Professor of Computer-Assisted Drug Design at ETH Zurich. Nevertheless, he is convinced that we have tapped only a fraction of the potential of natural products. Together with his team, he has successfully demonstrated how artificial intelligence (AI) methods can be used in a targeted manner to find new pharmaceutical applications for natural products. Furthermore, AI methods are capable of helping to find alternatives to these compounds that have the same effect but are much easier and therefore cheaper to manufacture.
And so the ETH researchers are paving the way for an important medical advance: we currently have only about 4000 basically different medicines in total. In contrast, estimates of the number of human proteins reach up to 400000, each of which could be a target for a drug. There are good reasons for Schneider’s focus on nature in the search for new pharmaceutical agents. “Most natural products are by definition potential active ingredients that have been selected via evolutionary mechanisms,” he says.
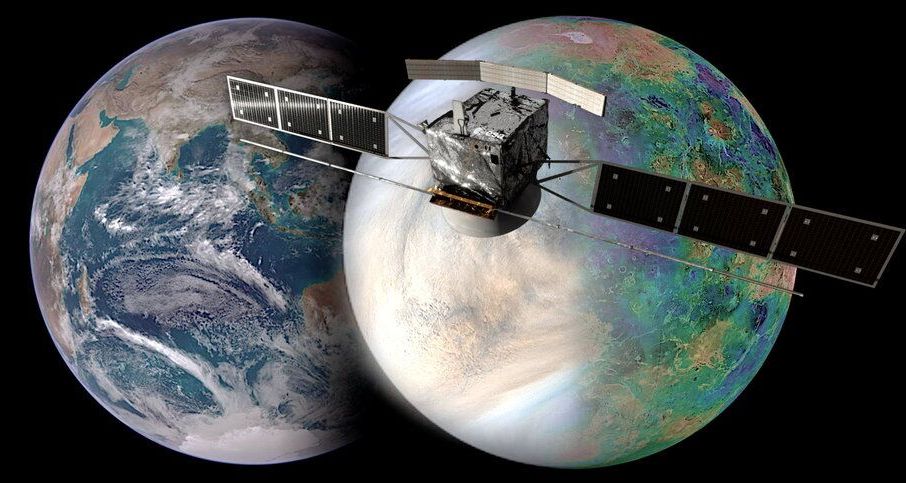
What will ESA’s EnVision mission to Venus add to the growing number of spacecraft investigating our sister planet?
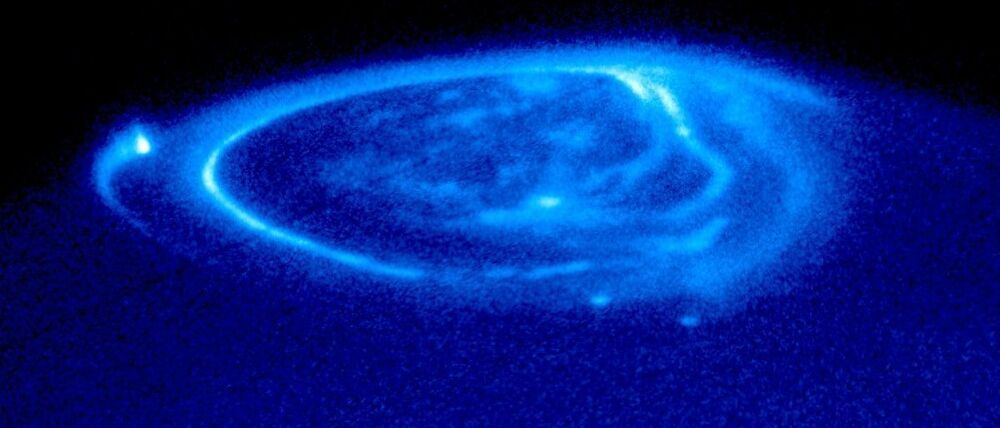
“Jupiter does this really weird thing where it pulses with a regular beat like clockwork.”
Using data from the Juno spacecraft, scientists traced the chain of events that lead to Jupiter’s mysterious auroras.
Can we explain dark matter
Posted in cosmology
Dark matter could be even weirder than anyone thought, say cosmologists who are suggesting this mysterious substance that accounts for more than 80% of the universe’s mass could interact with itself.
“We live in an ocean of dark matter, yet we know very little about what it could be,” Flip Tanedo, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy at the University of California Riverside, said in a statement.
It makes an Olympic swimming pool look like a puddle.
As if Dubai wasn’t filled with enough record-breaking attractions, the United Arab Emirates metropolis is now home to the world’s deepest pool, complete with an underwater city, caves and more.
“An entire world awaits you at Deep Dive Dubai, the world’s deepest pool,” wrote crown prince of Dubai Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, on Instagram. He was one of the first to visit the engineering marvel on July 7.
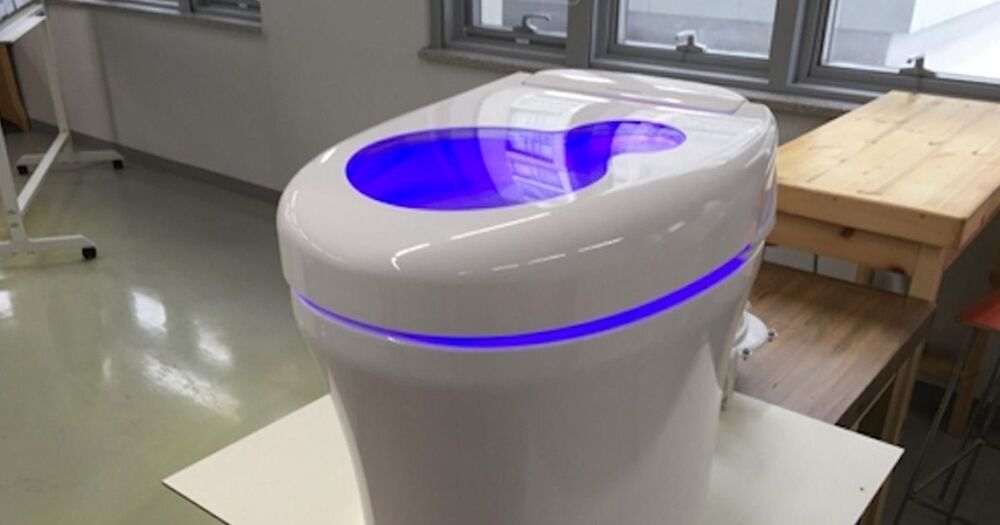
The toilet could turn roughly a pound of solid human waste, the average amount a human poops in a day, into an impressive 50 liters of methane gas, according to Cho. That means it can generate half a kilowatt hour of electricity, enough to drive an electric car for three quarters of a mile.
And because its 2021 — a day and age in which nothing is safe from the world of cryptocurrencies — Cho came up with a virtual currency called Ggool, or “honey” in Korean. Every use of the toilet scores you 10 Ggool per day, which can be used to buy stuff on the university’s campus.
“I had only ever thought that feces are dirty, but now it is a treasure of great value to me,” a postgraduate student Heo Hui-jin who’s both earned and spent Ggool, told Reuters. “I even talk about feces during mealtimes to think about buying any book I want.”
They found that insulin sensitivity can be restored within days of reducing excess production of the neurotransmitter GABA in the liver and that long-term treatment may lead to decreased appetite and weight loss.
New research suggests that reducing the production of a neurotransmitter in the liver could help normalize blood sugar and treat type 2 diabetes.
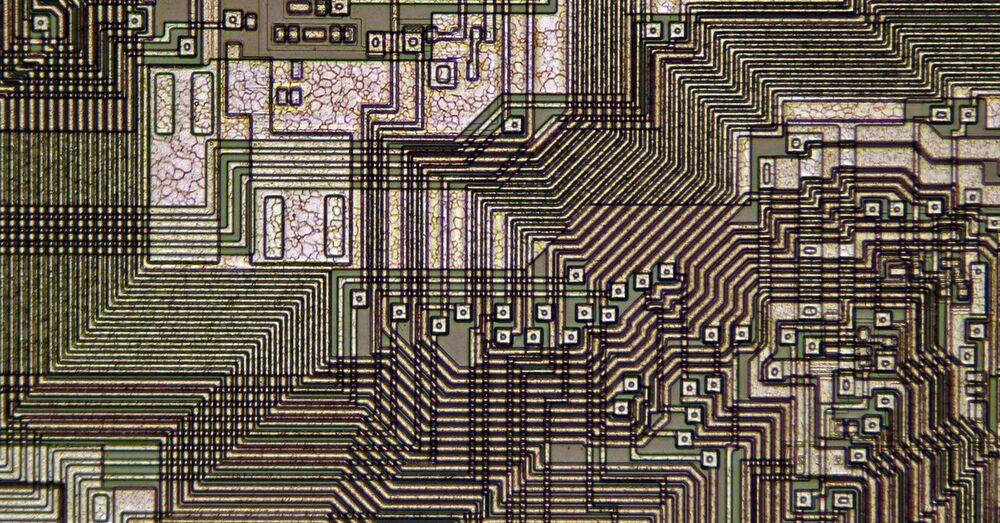
Google, Nvidia, and others are training algorithms in the dark arts of designing semiconductors—some of which will be used to run artificial intelligence programs.