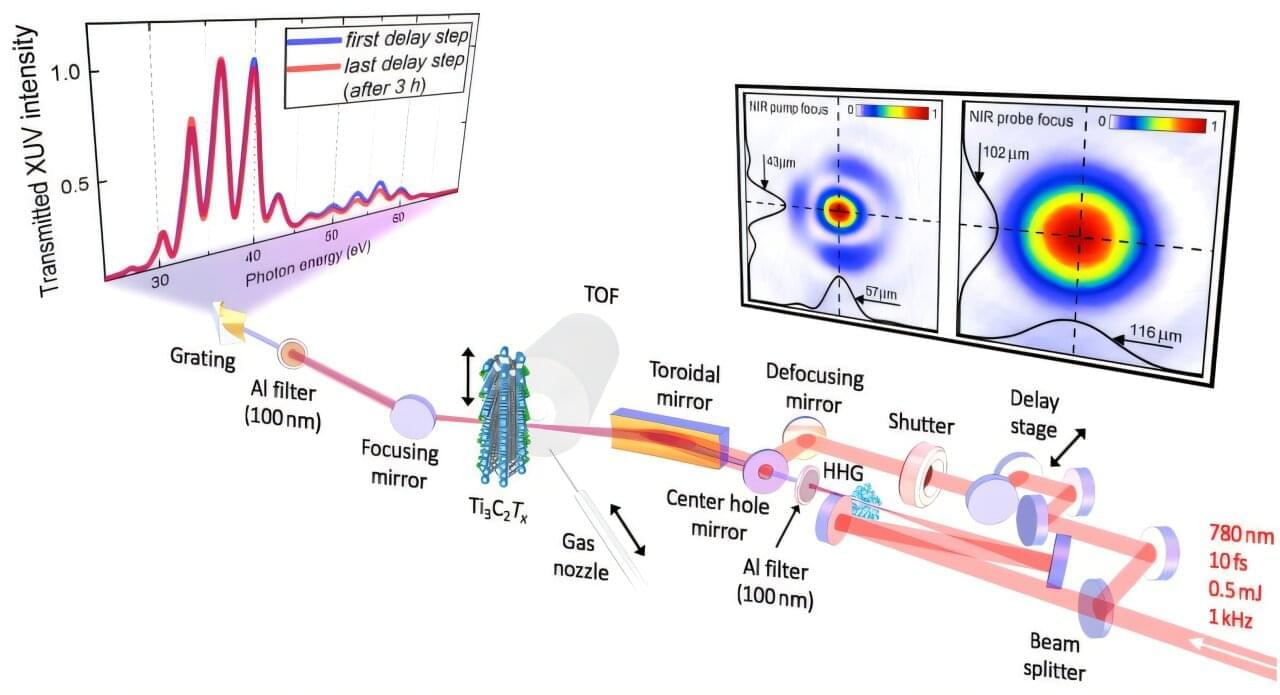
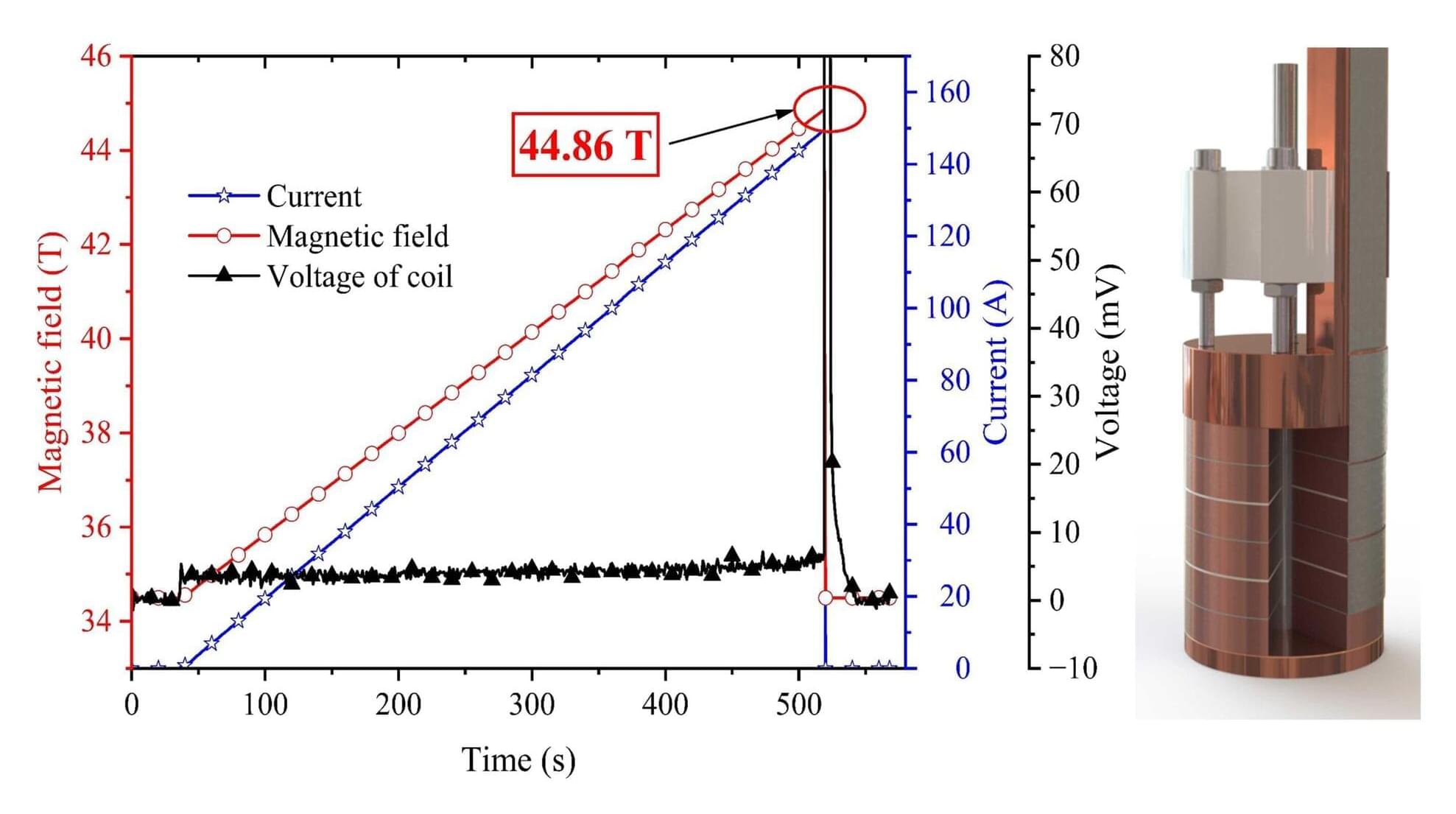
One of the great successes of 20th-century physics was the quantum mechanical description of solids. This allowed scientists to understand for the first time how and why certain materials conduct electric current and how these properties could be purposefully modified. For instance, semiconductors such as silicon could be used to produce transistors, which revolutionized electronics and made modern computers possible.
To be able to mathematically capture the complex interplay between electrons and atomic nuclei and their motions in a solid, physicists had to make some simplifications. They assumed, for example, that the light electrons in an atom follow the motion of the much heavier atomic nuclei in a crystal lattice without any delay. For several decades, this Born-Oppenheimer approximation worked well.