After a heart transplant, a patient recalled memories that weren’t her own. And she isn’t the only one.
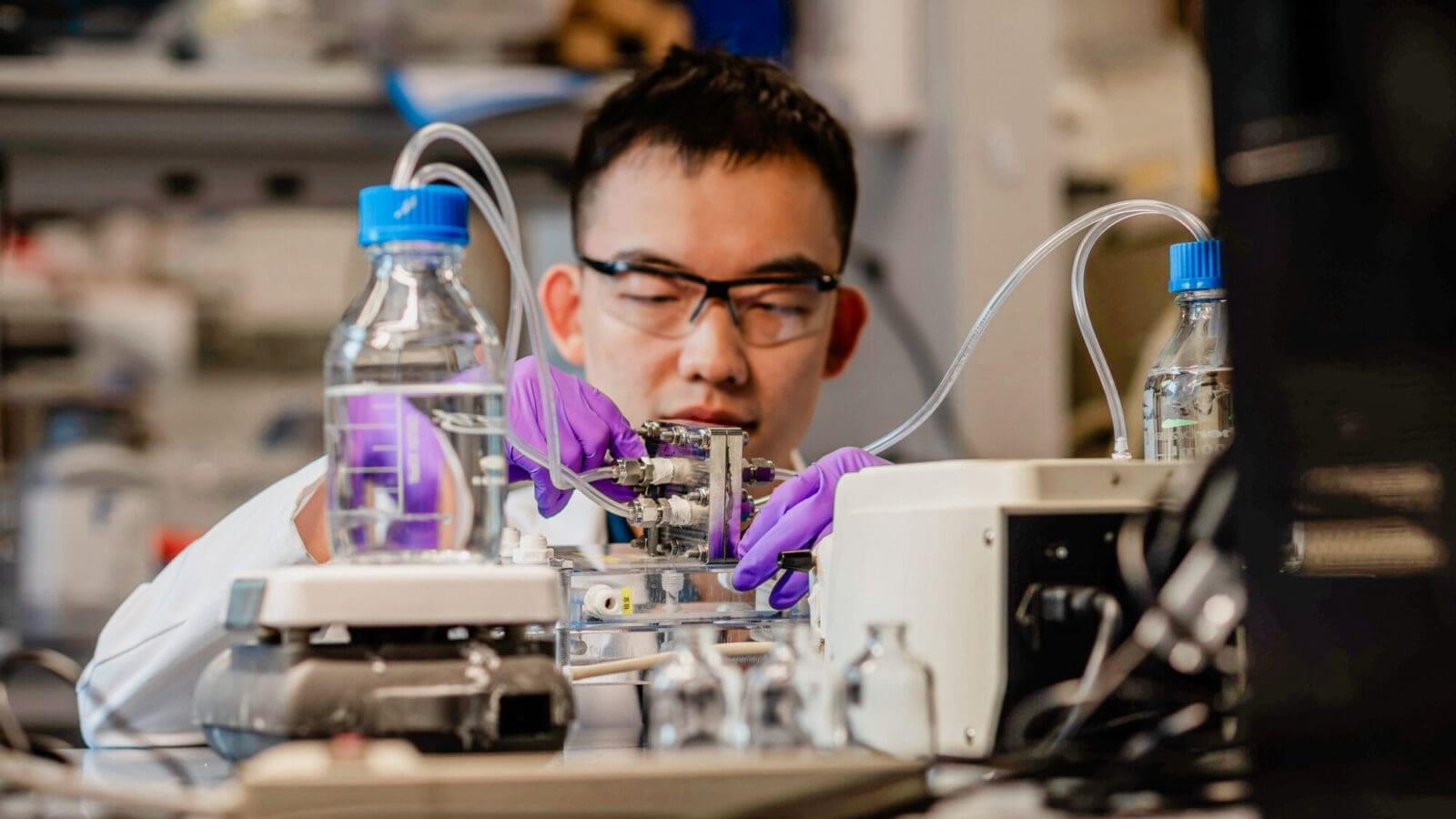




Wastewater can replace clean water as a source for hydrogen, eliminating a major drawback to hydrogen fuel and reducing water treatment costs of hydrogen production by up to 47%, according to new research from Princeton Engineering.
The findings, reported Sept. 24 in the journal Water Research, are a step toward making hydrogen a practical pathway to decarbonize industries that are difficult to electrify, such as steel and fertilizer production.
Z. Jason Ren, the senior study author, said that current electrolytic hydrogen production requires a large amount of clean water, increasing costs and straining local water supplies. His research team wanted to find out whether treated water processed by wastewater plants could be substituted.

“No one has showcased that ammonia can be used to power things at the scale of ships and trucks like us,” said CEO Seonghoon Woo, who founded the company with Hyunho Kim, Jongwon Choi, and Young Suk Jo. “We’ve demonstrated this approach works and is scalable.”
The company is targeting power-hungry industries like maritime shipping, power generation, construction, and mining for its early systems as the power density advantages of ammonia over renewables and batteries.
With a manufacturing contract secured with Samsung Heavy Industries, Amogy is set to start delivering more of its systems to customers next year. The company will deploy a 1-megawatt ammonia-to-power pilot project with the South Korean city of Pohang in 2026, with plans to scale up to 40 megawatts at that site by 2028 or 2029, according to a press release.
An investigation into why blood doesn’t always behave as doctors expect has revealed a super-rare mutation in an extremely uncommon variation of blood.
Testing more than 544,000 blood samples in a hospital in Thailand revealed three people carrying a never-before-seen version of the B(A) phenotype – a genetic quirk estimated to occur in about 0.00055 percent of people, or roughly one in 180,000.
This discovery, says a team led by hematologist Janejira Kittivorapart of Mahidol University in Thailand, suggests that there may be more rare blood variants out there, too subtle for standard testing to detect.
Researchers at MIT and other institutions have identified compounds that can fight off viral infection by activating a defense pathway inside host cells. These compounds, they believe, could be used as antiviral drugs that work against not just one but any kind of virus.
The researchers identified these compounds, which activate a host cell defense system known as the integrated stress response pathway, in a screen of nearly 400,000 molecules. In tests in human cells, the researchers showed that the compounds help cells fend off infection from RSV, herpes virus, and Zika virus. They also proved effective in combating herpes infection in a mouse model.
The research team now plans to test the compounds against additional viruses, in hopes of developing them for eventual clinical trials.

Early signs of Alzheimer’s disease may be hidden in the way a person speaks, but it’s not yet clear which details of our diction are most critical for diagnosis.
A study from 2023 suggests that as we age, how we say something may matter more than what we say. Researchers at the University of Toronto think the pace of everyday speech may be a better indicator of cognitive decline than difficulty finding a word.
“Our results indicate that changes in general talking speed may reflect changes in the brain,” said cognitive neuroscientist Jed Meltzer when the research was published.