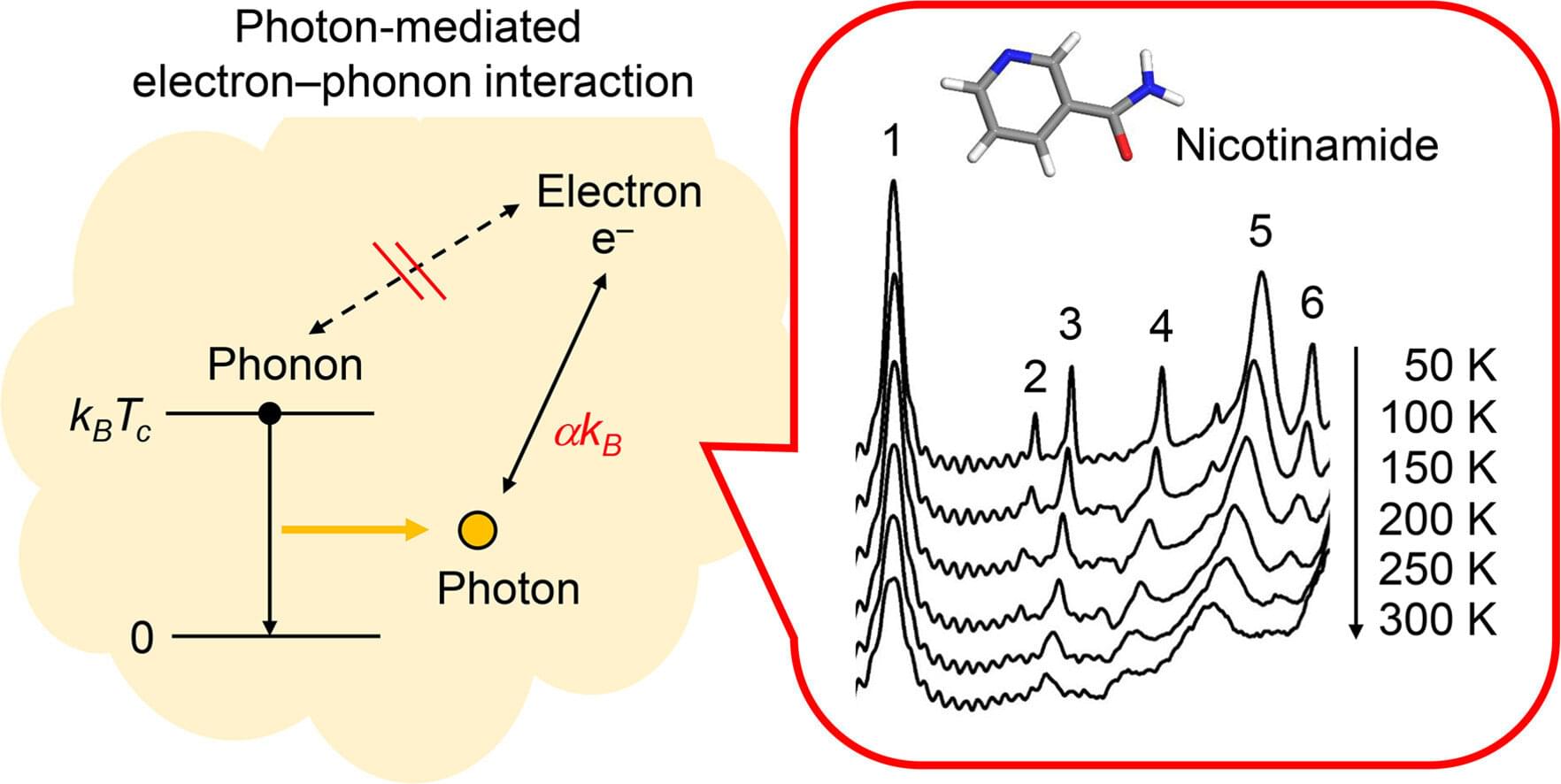
Tiny cavities in energy storage devices form small vortices that help with charging, according to a research team led by TU Darmstadt. This previously unknown phenomenon could advance the development of faster storage devices.
Solar and wind are the energy sources of the future, but they are subject to significant natural fluctuations. Storage solutions are therefore particularly important for a successful energy transition. Rechargeable batteries achieve very high energy densities by storing energy chemically. However, this high energy density comes at the price of long charging times and a dependence on precious raw materials such as cobalt.
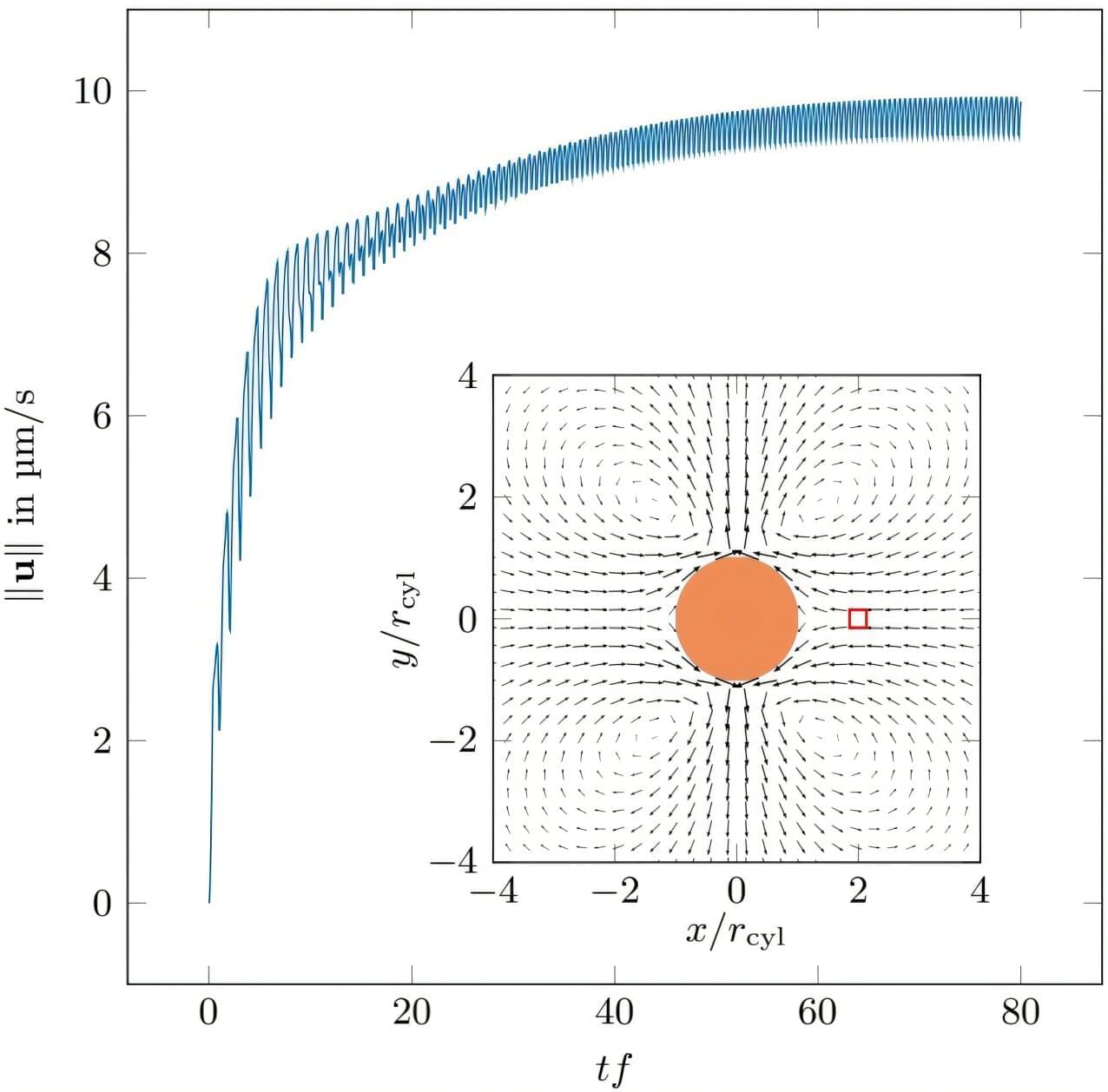
In contrast to rechargeable batteries, so-called supercapacitors store energy in electric double layers: a voltage is applied between two electrodes. They are immersed in a liquid in which tiny charged particles, ions, float. The positive and negative ions move in opposite directions and accumulate in charged, nanometer-thick layers, the electric double layers, on the surfaces of the electrodes. In order to provide as much surface area as possible for the accumulation of ions, supercapacitors use porous electrodes that have many tiny pores, like a sponge.