SpaceX is gearing up to launch the Starship into orbit, the biggest test yet for the ship designed to send humans to Mars and beyond.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
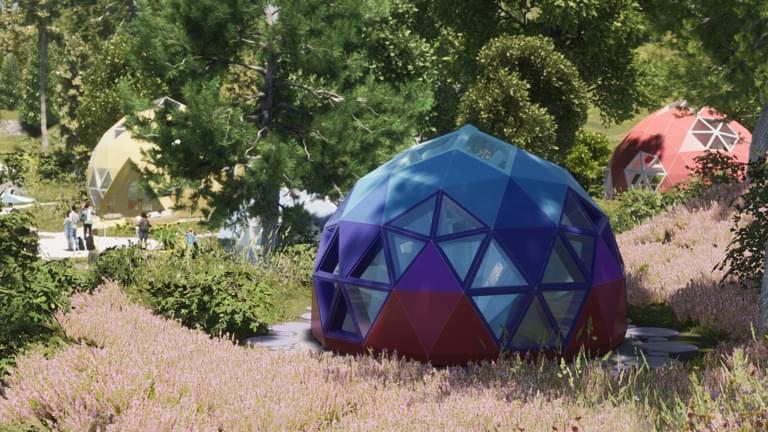


Carbon-neutral geodesic domes built to withstand natural disasters
U.S. startup Geoship have created ‘dome homes’ which last up to 500 years and are resistant to fire, floods, earthquakes and hurricanes.
Made of earth-friendly bioceramic, Geoship’s geodesic domes envision a new future for humanity.
Although no images of the built domes have been released yet, Geoship has shared these renders of what the dwellings could look like.
Mark Cuban Reveals Two of His Largest Altcoin Investments, Says First Viral Crypto App Is Coming
Billionaire entrepreneur and shark tank star Mark Cuban says he’s heavily invested in two popular altcoins while waiting for the first viral crypto app to emerge.
In a new interview with Crypto Banter, Cuban says that he owns “a lot” of Ethereum (ETH) and Polygon (MATIC) due to their strong use cases.

China to test the latest version of the world’s largest amphibious aircraft
Boeing 737 sized aircraft can “ski” on water.
China is set to test the latest prototype of its amphibious aircraft, the AG600, that will increase its maritime coverage to the entire South China Sea. The previous iterations of the aircraft have conducted separate trials on the land and sea in 2017 and 2020 respectively, South China Morning Post (SCMP) reported.
The South China Sea has become a contentious issue after China has claimed sovereignty over the region. Apart from untapped reserves of oil and natural gas, the region is also home to a third of the world’s maritime trade routes and fisheries that could impact the food security of millions in the region. The U.S. and its allies are keen on protecting the rights of other island nations even as China flexes its muscle in the region. sovereignty over the South China Sea, China needs to strengthen its maritime reach in the region and the AG600 will give it just that.