The chip also comes with improved AI performance.
“We have a much deeper sense of what actions make a difference for the safety of our restaurant teams and crew,” McDonald’s USA President Joe Erlinger said during a Wednesday meeting, according to the materials.
In Wednesday’s conference call, McDonald’s executives recommended franchisees consider closing indoor seating in counties where Covid cases exceed 250 per 100,000 people on a rolling three-week average.
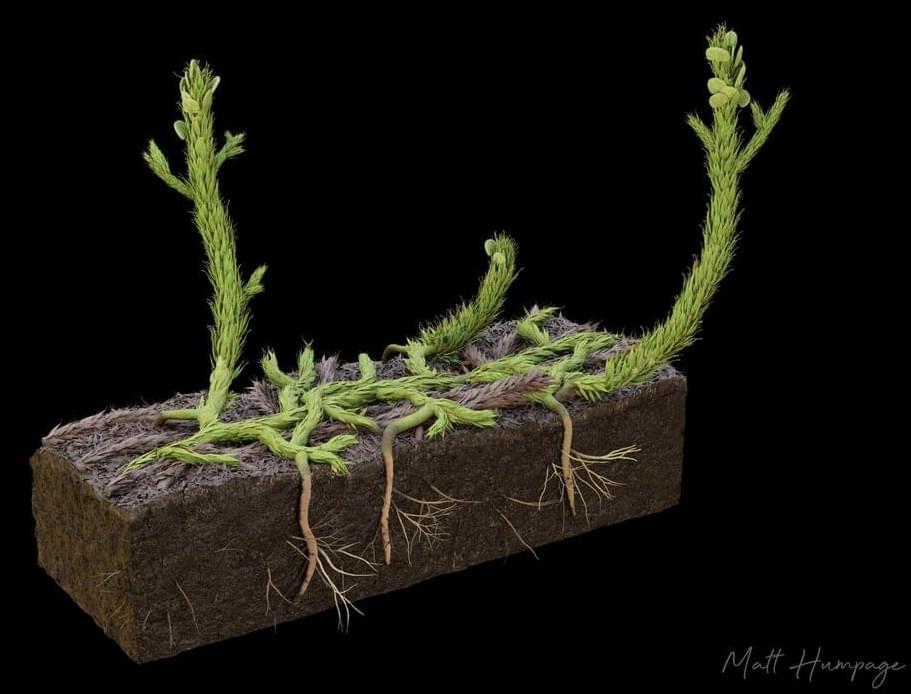
A plant fossil from a geological formation in Scotland sheds light on the development of the earliest known form of roots. A team led by researchers at GMI – the Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the University of Edinburgh, and the University of Oxford realize the first 3D reconstruction of a Devonian plant based exclusively on fossil evidence. The findings demonstrate that the appearance of different axis types at branching points resulted in the evolution complexity soon after land plants evolved sometime before 400 million years ago. The results are published in eLife.
New research demonstrates how the oldest known root axed developed more than 400 million years ago. The evolution of roots at this time was a dramatic event that impacted our planet and atmosphere and resulted in transformative ecological and climate change.
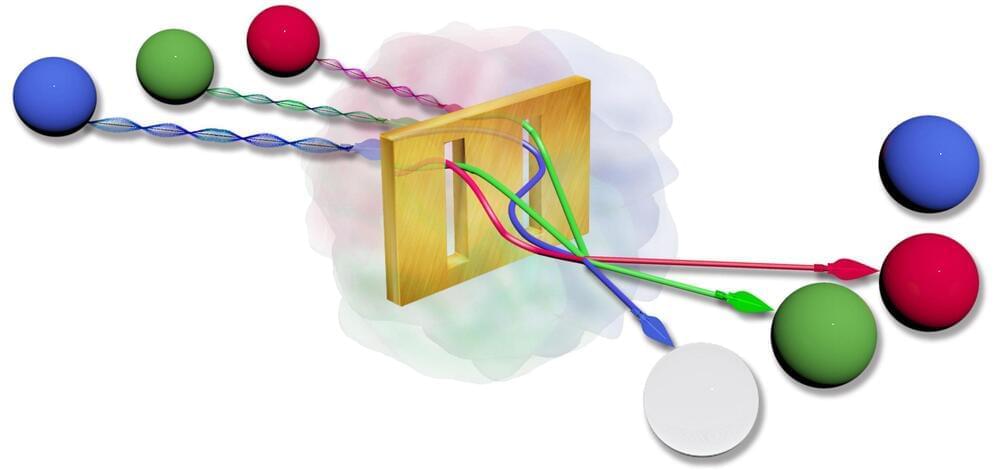
LSU Quantum researchers rearrange photon distribution to create different light sources.
For decades, scholars have believed that the quantum statistical properties of bosons are preserved in plasmonic systems, and therefore will not create different form of light.
This rapidly growing field of research focuses on quantum properties of light and its interaction with matter at the nanoscale level. Stimulated by experimental work in the possibility of preserving nonclassical correlations in light-matter interactions mediated by scattering of photons and plasmons, it has been assumed that similar dynamics underlie the conservation of the quantum fluctuations that define the nature of light sources. The possibility of using nanoscale system to create exotic forms of light could pave the way for next-generation quantum devices. It could also constitute a novel platform for exploring novel quantum phenomena.
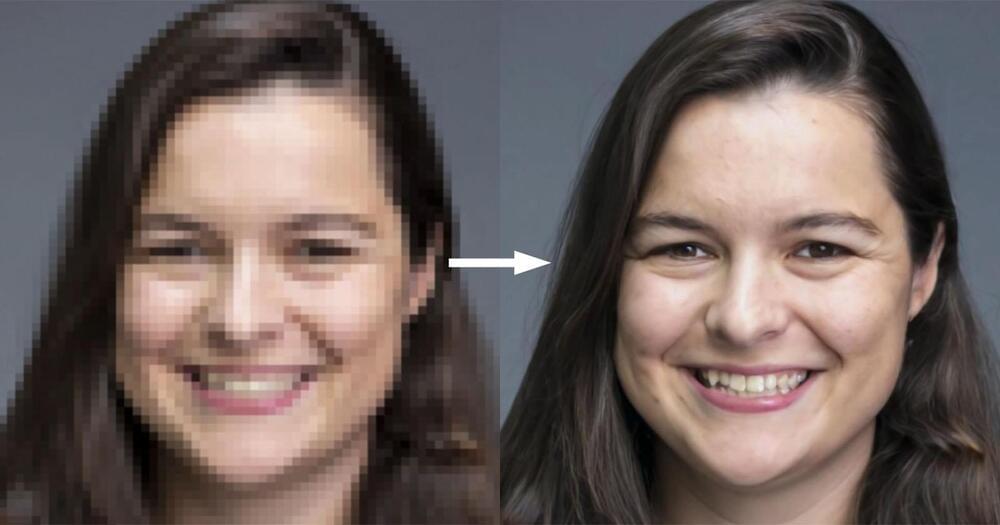
Google shares its latest breakthroughs in the area of using artificial intelligence to upscale low-res photos, and the results are amazing.
New research by Surrey’s Nuclear Physics Group has shown that it’s possible to mimic excited quantum states with exotic nuclei, opening up a host of opportunities for next generation radioactive beam facilities, such as the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB).
The results of the project – which was a collaboration between the University of Surrey and Michigan State University, USA – were published in Physical Review Letters in January 2021. The lead author was Surrey PhD student Samuel Hallam, who also studied for his undergraduate physics degree at Surrey.
One of the biggest challenges in nuclear physics is measuring reactions that occur on excited quantum states, such as are found in exploding stars due to extreme temperature and density. Until now, physicists have had to determine the rates at which nuclear reactions occur in these conditions through theoretical estimates.
“Enormous clouds of gas are pulled into galaxies and used in the process of making stars,” said co-lead author Deanne Fisher, associate professor at the Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing at Swinburne University in Australia.
On its way in it is made of hydrogen and helium. By using a new piece of equipment called the Keck Cosmic Web Imager, we were able to confirm that stars made from this fresh gas eventually drive a huge amount of material back out of the system, mainly through supernovas.
But this stuff is no longer nice and clean – it contains lots of other elements, including oxygen, carbon, and iron.
Stanford University scientists experimenting with a decades-old, single-use battery architecture have developed of a new version that is not only rechargeable, but offers around six times the capacity of today’s lithium-ion solutions. The breakthrough hinges on the stabilization of volatile chlorine reactions within the device, and could one day provide the basis for high-performance batteries that power smartphones for a week at a time.
The new battery is described as an alkali metal-chlorine battery, and is based on chemistry that first emerged in the 1970s called lithium-thionyl chloride. These batteries are highly regarded for their high energy density, but rely on highly reactive chlorine that makes them unsuitable for anything other than a single use.
In a regular rechargeable battery, the electrons travel from one side to the other during discharging and then are reverted back to their original form as the battery is recharged. In this case, however, the sodium chloride or lithium chloride is converted to chlorine, which is too reactive to be converted back to chloride with any great efficiency.
Firms that make chips for cars are set to see big benefits if electric car sales continue rise. Here are some of Goldman, UBS and Morgan Stanley’s stock picks.