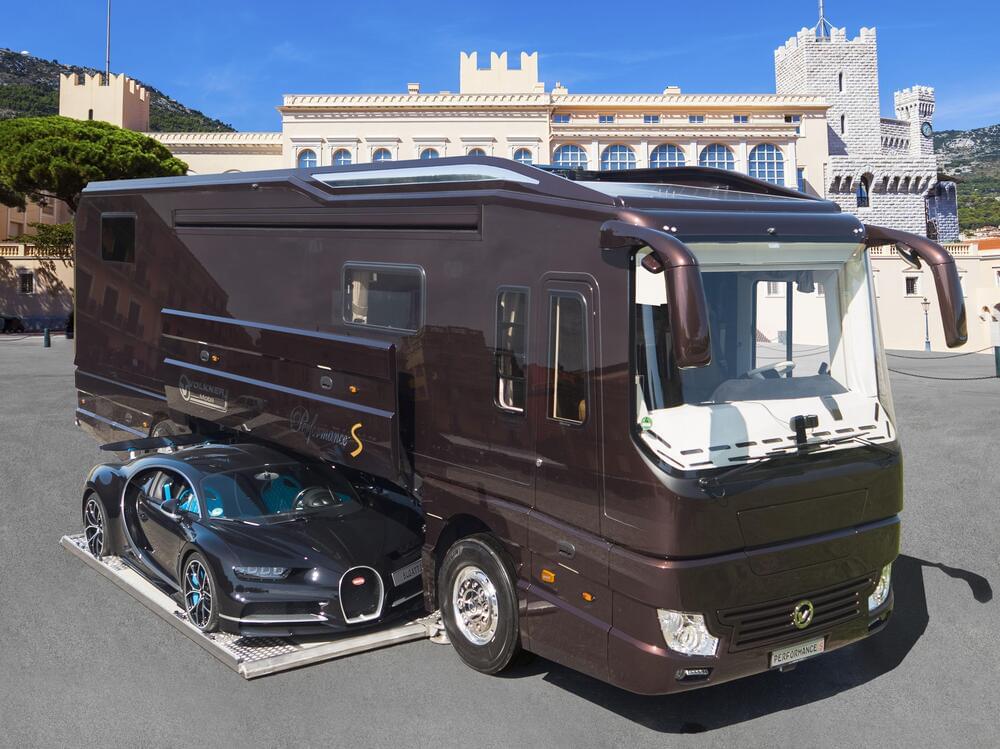
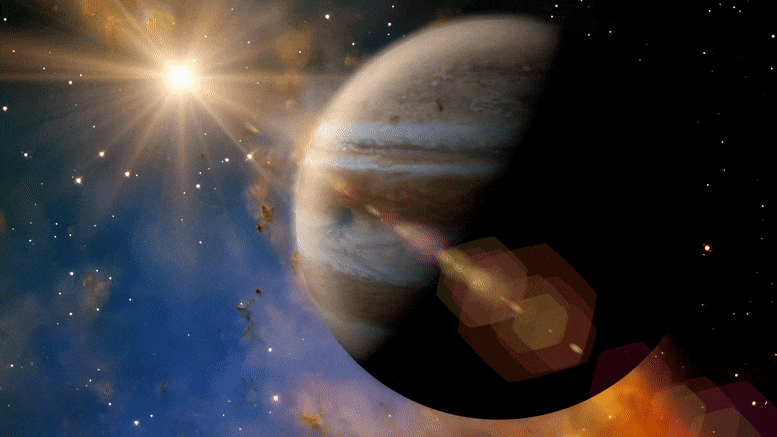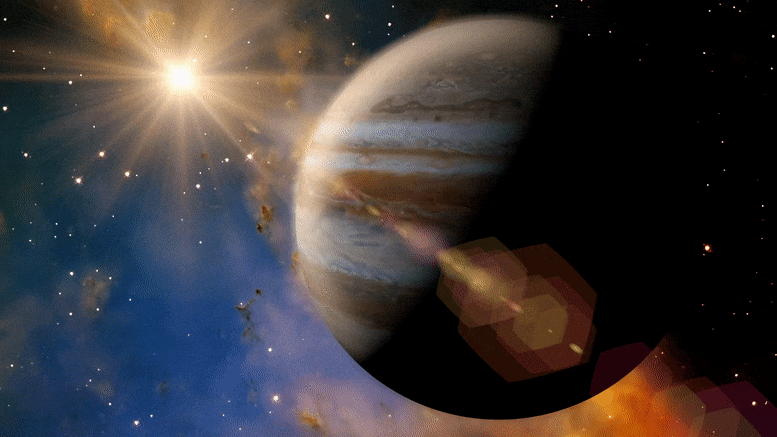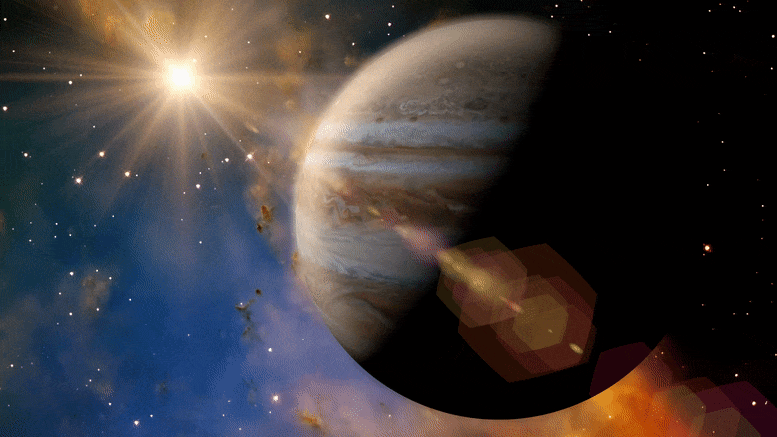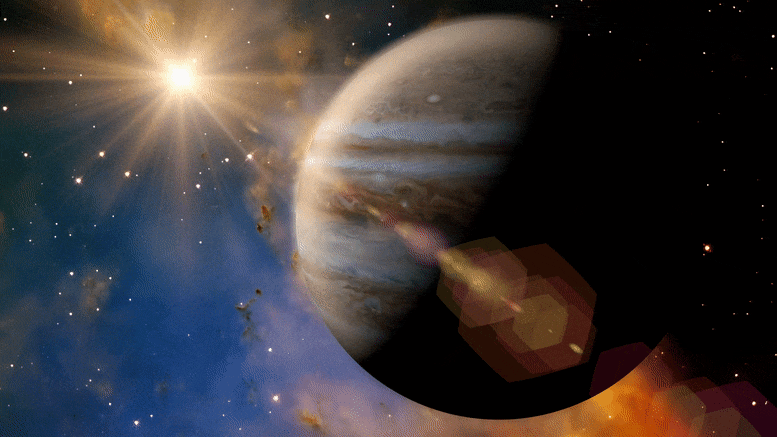
Volkner’s over-the-top motorhome package slides a 1,480-hp Bugatti Chiron aboard its $2.4-million Performance S motorhome and treats owners of the elaborate ultra-luxury/hypercar vehicle experience.
In the past, we’ve seen Volkner edge out its few competitors for “most expensive motorhome of the Düsseldorf Caravan Salon” honors with stretched luxury homes as “modestly” priced as $1.7 million. This year, it leaves the competition in the dust, going all out on the priciest, most over-the-top motorhome package on the show floor. It slides a 1,480-hp Bugatti Chiron aboard its $2.4-million Performance S motorhome and treats owners of the elaborate ultra-luxury/hypercar vehicle experience to a lavishly appointed abode complete with custom Burmester audio system carefully tailored to the mobile space.
For more than a decade, Volkner has been wowing the Düsseldorf crowds with the sporty roadsters and supercars it manages to squeeze between the axles of its huge motorhomes. This year, it’s really upped its own game.
The $3-million Bugatti Chiron actually costs more than the Performance S motorhome itself and packs more than triple the horsepower of Volkner’s 430-hp 18-ton 39-footer. We preferred the Porsche 911 GT2 Volkner brought to the 2018 Caravan Salon not a full year after the car’s Nürburgring record, but there’s no denying that the Chiron and Performance S team is an absolutely stunning package, a pairing of extreme, over-the-top motorized engineering like few we’ll ever see.