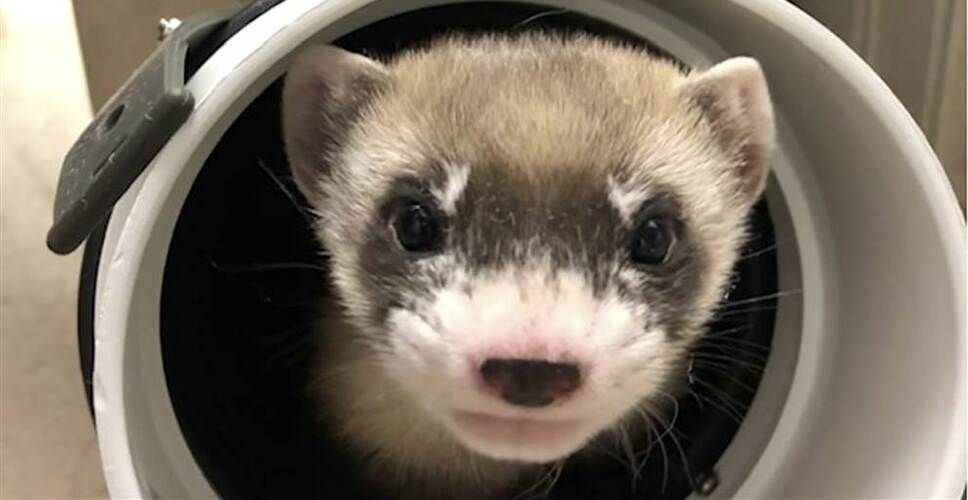
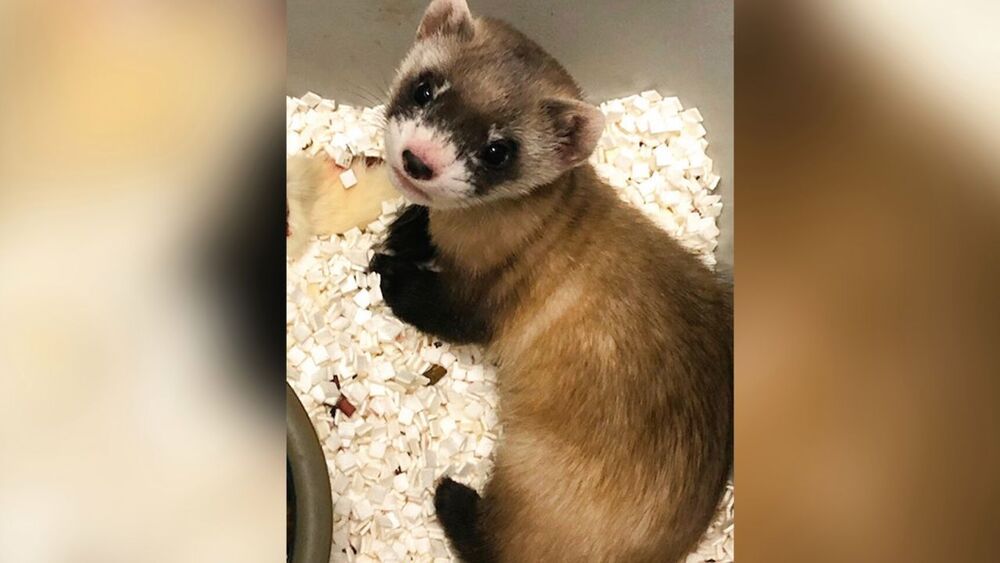
Scientists have cloned the first U.S. endangered species, a black-footed ferret duplicated from the genes of an animal that died over 30 years ago.
Samsung’s find my mobile app will work without a network connection.
Lost your phone and your connection? Samsung’s Find My Mobile App is promising a solution for that.
No fuel. No electricity. Just the power of nature! This pump harnesses the flow of rivers to bring water to farmers over a mile away! It’s an affordable and sust… See More.
NASA Perseverance Lands on Mars!!
Posted in space
HOW CUTE 🥰 Meet Elizabeth Ann, the first-ever cloned U.S. endangered species. She’s a black-footed ferret duplicated from the genes of an animal that died in 1988.
“You might have been handling a black-footed ferret kit and then they try to take your finger off the next day,” U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service black-footed ferret recovery coordinator Pete Gober said Thursday. “She’s holding her own.”
Elizabeth Ann was born and is being raised at a Fish and Wildlife Service black-footed ferret breeding facility in Fort Collins, Colorado. She’s a genetic copy of a ferret named Willa who died in 1988 and whose remains were frozen in the early days of DNA technology.
Cloning eventually could bring back extinct species such as the passenger pigeon. For now, the technique holds promise for helping endangered species including a Mongolian wild horse that was cloned and last summer born at a Texas facility.
This is the most important thing in the universe now.
Good.is | By GOOD
Put your flippers together for a six-pack that even seabirds can support.
International scientists have unlocked a new and exciting avenue to explore the world of dreams.
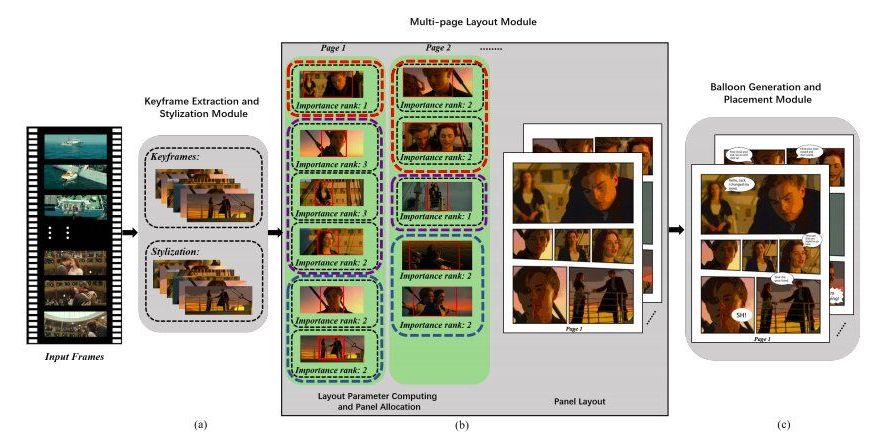
Over the past few years, computer scientists have created numerous computational techniques that can automatically generate texts, images and other types of data. These models are highly advantageous, particularly for creating data or creative works that are demanding and time-consuming for humans to produce manually.
Samsung Electronics has announced on its Newsroom webpage the development of a new kind of memory chip architecture called high-bandwidth memory, processing-in-memory—HBM-PIM. The architecture adds artificial intelligence processing to high-bandwidth memory chips. The new chips will be marketed as a way to speed up data centers, boost speed in high performance computers and to further enable AI applications.