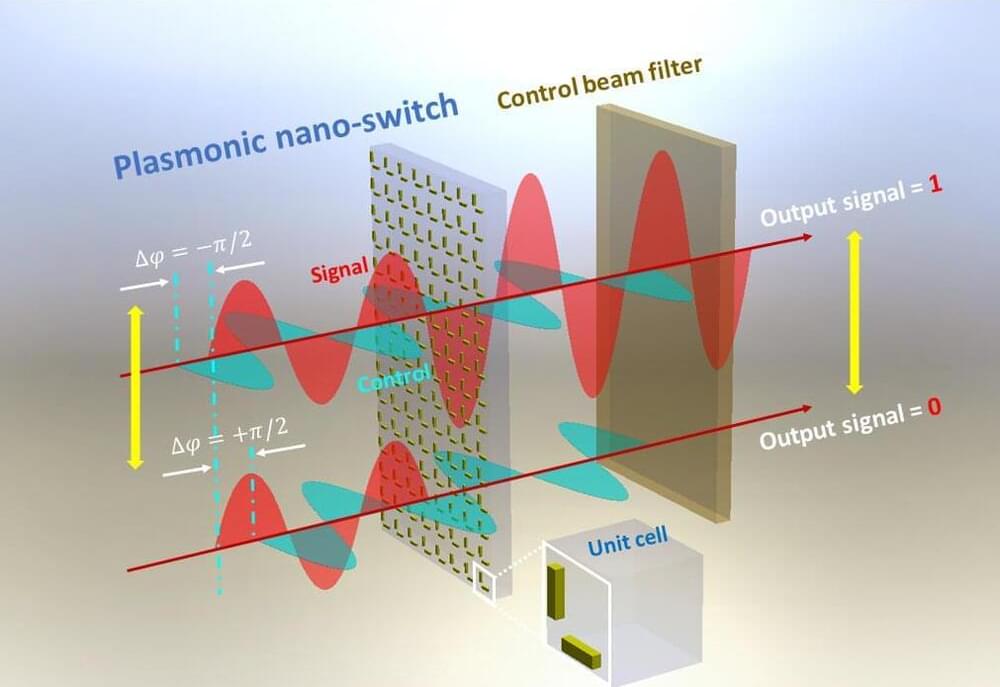
A group of photonics researchers at Tampere University have introduced a novel method to control a light beam with another beam through a unique plasmonic metasurface in a linear medium at ultra-low power. This simple linear switching method makes nanophotonic devices such as optical computing and communication systems more sustainable, requiring low intensity of light.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
A novel all-optical switching method makes optical computing and communication systems more power-efficient
A group of photonics researchers at Tampere University have introduced a novel method to control a light beam with another beam through a unique plasmonic metasurface in a linear medium at ultra-low power. This simple linear switching method makes nanophotonic devices such as optical computing and communication systems more sustainable, requiring low intensity of light.
All–optical switching is the modulation of signal light due to control light in such a way that it possesses the on/off conversion function. In general, a light beam can be modulated with another intense laser beam in the presence of a nonlinear medium.
The switching method developed by the researchers is fundamentally based on the quantum optical phenomenon known as Enhancement of Index of Refraction (EIR).


Musk accuses Twitter of ‘resisting and thwarting’ his right to information on fake accounts
Elon Musk accused Twitter of “resisting and thwarting” his right to information about fake accounts on the platform, calling it in a letter to the company on Monday a “clear material breach” of the terms of their merger agreement.
“Mr. Musk reserves all rights resulting therefrom, including his right not to consummate the transaction and his right to terminate the merger agreement,” the letter, signed by Skadden Arps attorney Mike Ringler, says.
Twitter shares were down 5% on Monday morning.
Drug combination shows promise against cancer’s ‘death star’ protein
A drug combination targeting multiple mutant versions of cancer’s “death star” protein has shown promise in a small, early-phase clinical trial for some patients with advanced lung, ovarian and thyroid cancer.
The two–drug combination was effective against advanced cancers with a range of mutations to the KRAS gene—dubbed the “death star” because its protein drives one in four cancers and has a largely impenetrable, drug-resistant surface.
The phase I trial tested the drugs VS-6766 and everolimus in 30 patients with a range of mutations to KRAS—including 11 with highly advanced, non-small cell lung cancer.

Automatic debugging of software
Circa 2016
Computer programs often contain defects, or bugs, that need to be found and repaired. This manual “debugging” usually requires valuable time and resources. To help developers debug more efficiently, automated debugging solutions have been proposed. One approach goes through information available in bug reports. Another goes through information collected by running a set of test cases. Until now, explains David Lo from Singapore Management University’s (SMU) School of Information Systems, there has been a “missing link” that prevents these information gathering threads from being combined.
Dr Lo, together with colleagues from SMU, has developed an automated debugging approach called Adaptive Multimodal Bug Localisation (AML). AML gleans debugging hints from both bug reports and test cases, and then performs a statistical analysis to pinpoint program elements that are likely to contain bugs.
“While most past studies only demonstrate the applicability of similar solutions for small programs and ‘artificial bugs’ [bugs that are intentionally inserted into a program for testing purposes], our approach can automate the debugging process for many real bugs that impact large programs,” Dr Lo explains. AML has been successfully evaluated on programs with more than 300,000 lines of code. By automatically identifying buggy code, developers can save time and redirect their debugging effort to designing new software features for clients.

Monkeypox treatment: Smallpox antiviral shows promise
Although the researchers cannot say for sure whether this was a direct result of tecovirimattreatment, the results suggest tecovirimat could help to prevent progression to severe disease and shorten the time spent in hospital. They recommend a 2-week course of treatment in order to fully clear the virus.
Speaking to Medical News Today, Dr. Stephen Morse, professor of epidemiology at the Columbia University Medical Center, and director of the Infectious Disease Epidemiology Certificate Program, noted that “tecovirimat is the most effective known antiviral for the orthopoxviruses, which includes smallpox — now officially eradicated — monkeypox, and others.”
“The mechanism of action of the drug, and the relatedness of these viruses, suggests that tecovirimat should be equally effective for other orthopoxviruses, but rigorous comparisons have not been possible because of small case numbers,” he added.
Quantum information was teleported over a network for the first time
When Heroes (now streaming on Peacock!) hit the airwaves in September of 2006, few characters were as immediately beloved as the appropriately named Hiro Nakamura. Granted the ability to manipulate space-time, Hiro could not only slow down, speed up, and stop time, he could also teleport from one place to another. That’s a useful skill if you need to get to a specific point in time and space to fight an evil brain surgeon or prevent the end of the world. It’s also useful if you want to build the quantum internet.
Researchers at QuTech — a collaboration between Delft University of Technology and the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research — recently took a big step toward making that a reality. For the first time, they succeeded in sending quantum information between non-adjacent qubits on a rudimentary network. Their findings were published in the journal Nature.
While modern computers use bits, zeroes, and ones, to encode information, quantum computers us quantum bits or qubits. A qubit works in much the same way as a bit, except it’s able to hold both a 0 and a 1 at the same time, allowing for faster and more powerful computation. The trouble begins when you want to transmit that information to another location. Quantum computing has a communications problem.