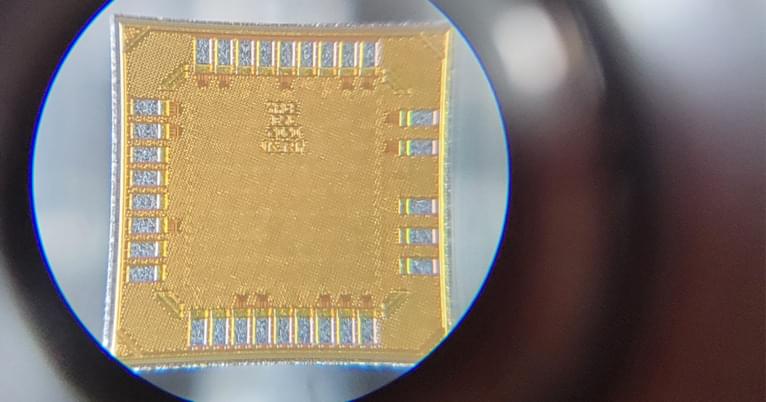
𝙎𝙞𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙮 𝙘𝙖𝙢𝙚 𝙞𝙣𝙩𝙤 𝙪𝙨𝙚 𝙗𝙮 𝙥𝙝𝙮𝙨𝙞𝙘𝙞𝙖𝙣𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙘𝙝𝙚𝙧𝙨, 𝘽𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣-𝘾𝙤𝙢𝙥𝙪𝙩𝙚𝙧 𝙄𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙧𝙛𝙖𝙘𝙚𝙨 (𝘽𝘾𝙄𝙨) 𝙤𝙧 𝘽𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣-𝙈𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙣𝙚 𝙄𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙧𝙛𝙖𝙘𝙚𝙨 (𝘽𝙈𝙄𝙨) 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙫𝙞𝙙𝙚𝙙 𝙬𝙖𝙮𝙨 𝙩𝙤 𝙩𝙧𝙚𝙖𝙩 𝙣𝙚𝙪𝙧𝙤𝙡𝙤𝙜𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙡 𝙙𝙞𝙨𝙤𝙧𝙙𝙚𝙧𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙨𝙝𝙚𝙙 𝙡𝙞𝙜𝙝𝙩 𝙤𝙣 𝙝𝙤𝙬 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣 𝙛𝙪𝙣𝙘𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣𝙨. 𝘼𝙨 𝙗𝙚𝙣𝙚𝙛𝙞𝙘𝙞𝙖𝙡 𝙖𝙨 𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙮’𝙫𝙚 𝙗𝙚𝙚𝙣, 𝘽𝘾𝙄𝙨 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙥𝙤𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙖𝙡 𝙩𝙤 𝙜𝙤 𝙛𝙖𝙧 𝙗𝙚𝙮𝙤𝙣𝙙 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙩𝙚𝙘𝙝𝙣𝙤𝙡𝙤𝙜𝙮’𝙨 𝙘𝙪𝙧𝙧𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙘𝙖𝙥𝙖𝙗𝙞𝙡𝙞𝙩𝙞𝙚𝙨. 𝙄𝙣 𝙖 𝙘𝙤𝙡𝙡𝙖𝙗𝙤𝙧𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙗𝙚𝙩𝙬𝙚𝙚𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙔𝙖𝙡𝙚 𝙎𝙘𝙝𝙤𝙤𝙡 𝙤𝙛 𝙀𝙣𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜 & 𝘼𝙥𝙥𝙡𝙞𝙚𝙙 𝙎𝙘𝙞𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚 (𝙎𝙀𝘼𝙎) 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙔𝙖𝙡𝙚 𝙎𝙘𝙝… See more.
The Neuro-Network.
𝐘𝐚𝐥𝐞 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐌𝐚𝐠𝐚𝐳𝐢𝐧𝐞:
𝐋𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞, 𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐩𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐫
Yale SEAS teams with the Medical School to deliver a faster, more capable brain-implanted device to treat multiple disorders.