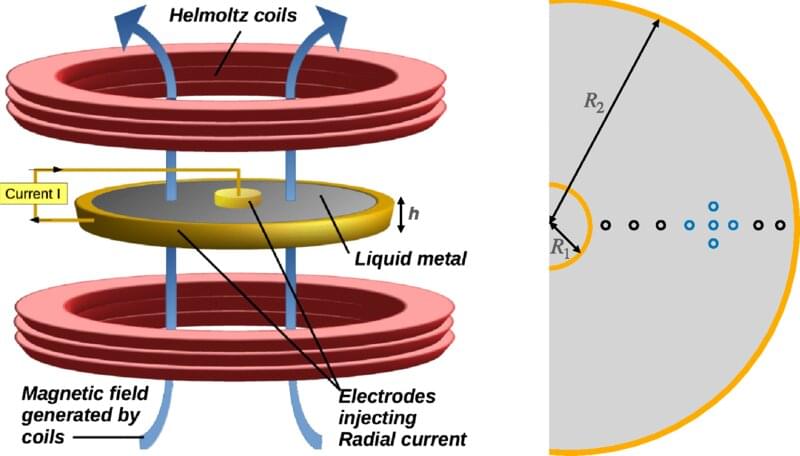
A team of researchers at the Sorbonne University of Paris reports a new way to emulate black hole and stellar accretion disks. In their paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the group describes using magnetic and electric fields to create a rotating disk made of liquid metal to emulate the behavior of material surrounding black holes and stars, which leads to the development of accretion disks.
Prior research has shown that massive objects have a gravitational reach that pulls in gas, dust and other material. And since such massive objects tend to spin, the material they pull in tends to swirl around the object as it moves closer. When that happens, gravity exerted by materials in the swirling mass tends to coalesce, resulting in an accretion disk. Astrophysicists have been studying the dynamics of accretion disks for many years but have not been able to figure out how angular momentum is transferred from the inner parts of a given accretion disk to its outer parts as material in the disk moves ever closer to the central object.
Methods used to study accretion disks have involved the development of math formulas, computer simulations and real-world models using liquids that swirl like eddies. None of the approaches has proven suitable, however, which has led researchers to look for new models. In this new effort, the researchers developed a method to generate an accretion disk made of liquid metal bits spinning in the air.