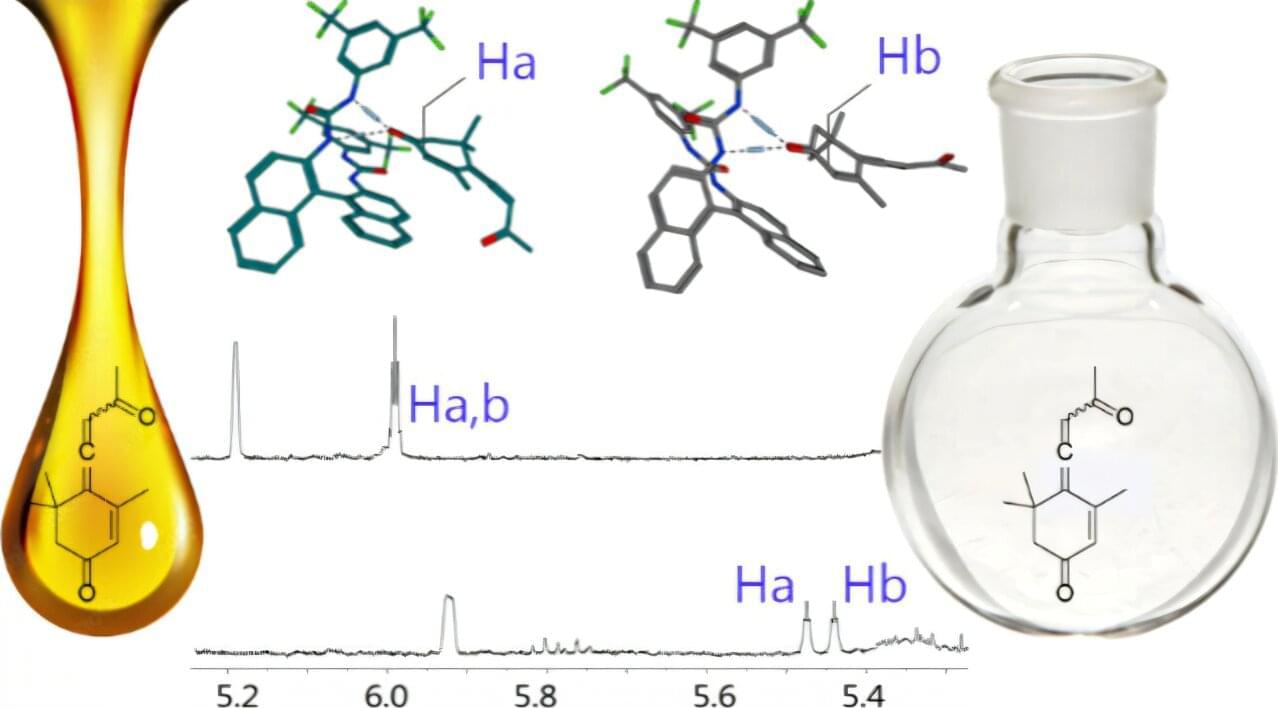
Researchers at the University of Chemistry and Technology, Prague have successfully developed a method to chemically synthesize callunene, a natural compound that protects bumblebees from a deadly gut parasite. In a recent discovery, the team also determined that the naturally occurring compound is a 50/50 mixture of its mirror-image forms, meaning the synthetic version can be used directly to safeguard vital pollinator colonies.
The study, published in the Journal of Natural Products, addresses the threat posed by the parasite Crithidia bombi. This protozoan infects bumblebees, impairing their ability to find nectar-rich flowers, which ultimately leads to starvation, reduced colony fitness, and death. The problem is especially acute in commercial indoor farming operations that rely on healthy pollinator colonies. Not only because of the farming effectiveness, but also because parasites might be spread from indoor pollinators to wild colonies.
Nature provides a defense in the form of callunene, a compound found in the nectar of heather (Calluna vulgaris). Bumblebees that forage on heather are prophylactically protected from Crithidia infection. However, the loss of heathland habitats and the difficulty of isolating the compound from natural sources have made this solution impractical on a large scale.