Pushing the boundaries of math requires great minds to pose fascinating problems. What if a machine could do it? Now, scientists created one that can.


A rogue wave measuring 58 feet (17.6 meters) tall was recorded off the coast of Vancouver Island, breaking the record for proportionality at three times the size of surrounding waves.
“Only a few rogue waves in high sea states have been observed directly, and nothing of this magnitude. The probability of such an event occurring is one in 1,300 years,” said Johannes Gemmrich, one of the lead researchers on rogue waves at the University of Victoria.
The wave made a splash in the scientific community for being proportionally the most extreme rogue wave ever recorded. Although it occurred in November 2020, the study confirming it was just released February 2 of this year.
Discussion and demos about synchronizing the asynchronous robustly in computing systems.
The T2 Tile Project:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC1M91QuLZfCzHjBMEKvIc-A
https://t2tile.com/
Software:
https://github.com/DaveAckley/T2Demos.
Living Computation Foundation:
https://livingcomputation.org/
0:00 Introduction.
0:45 Sync of Computers Past.
3:05 Sync of Computers Present.
4:34 Sync of Computers Future.
5:58 Sync over Asynchronous Cellular Automata.
8:25 Demo 1: Waiting for the neighbors.
10:56 Simulating synchronous updating.
12:30 Demo 2: Conway’s Game of Life.
15:00 It’s the end of the universe.
18:30 Bottom Line: Global sync fails.
19:14 Local programmed sync is different.
21:28 Demo 3: The jerk and the empath.
24:25 Related work: Ring Oscillators.
27:50 Demo 4: Generalized Software Ring Oscillator.
34:13 Discussion: Against object-orientation.
36:53 Conclusion: Fight the master of the universe.

Circa 2021
Nissan and Waseda University in Tokyo have been working together since 2017, and today, they announced that they are starting the testing of a recycling process that recovers high-purity, rare-earth compounds from electric vehicle motor magnets.
First, they heat a used motor to 2,552F (1,400C) to melt it down. Then iron oxide is added to oxidize the rare-earth elements (REEs).
Next, a small amount of borate-based flux, which can dissolve rare-earth oxides and recover REEs efficiently, is added to the molten mixture.
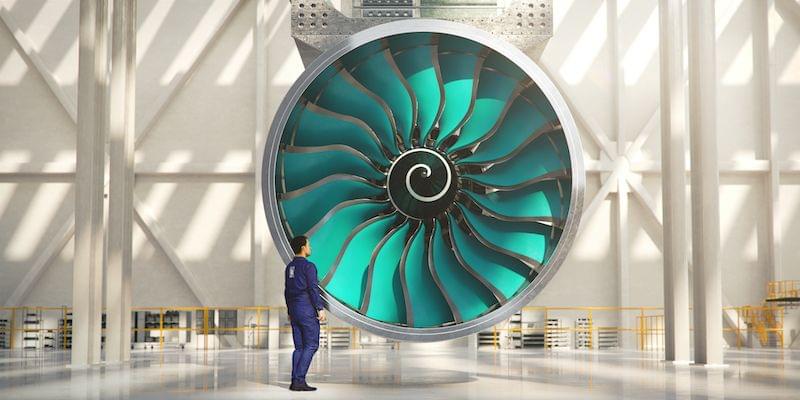

We’re big fans of this big fan.
There’s a new, more fuel-efficient airliner engine on the scene, as Rolls-Royce has started work on its UltraFan aero engine. The gigantic fan engine gets 25 percent better mileage compared with its predecessor, and Rolls-Royce says it will revolutionize passenger and cargo flight around the world.
The first demonstrator engine will be finished by the end of 2021. Rolls-Royce revealed more details in a statement:
“As engine build starts, other key parts are already coming together for delivery to Derby. Work is underway on UltraFan’s carbon titanium fan system in Bristol, UK, and its 50MW Power Gearbox, which is powerful enough to run 500 family cars, in Dahlewitz, Germany.”


According to a new job posting, Intel is setting up a GPU development center in the UK. The company is looking for experienced hardware design engineers to develop low-power GPU architectures for portable computing devices.
“We are building a brand-new team in the UK to focus solely on class-leading low power GPU architectures and designs to enable the next generation of portable computing,” reads the job description posted by Intel’s Xe Architecture and IP Engineering (XAE) Low Power Group. “This requires proven skills in a range of engineering disciplines from architecture, hardware design, software driver design all with low power as the key focus.”


The production issues could impact SSD pricing.
Western Digital says it has lost at least 6.5 exabytes (6.5 billion gigabytes) of flash storage due to contamination issues at its NAND production facilities. The contamination could see the price of NAND — the main component of SSDs — spike up to 10 percent, according to market research firm TrendForce. Any potential NAND shortages or price fluctuations could affect the PC market over the next few months, which had another big year in 2021 despite global chip shortages and demand for GPUs.
The contamination of materials used in the manufacturing processes appears to have been detected in late January at two plants in Japan, with Western Digital’s joint venture partner, Kioxia (previously Toshiba), revealing it has affected BiCS 3D NAND flash memory.
Western Digital and Kioxia’s partnership amounts to around 30 percent of the NAND flash market, according to TrendForce. Both Western Digital and Kioxia primarily supply SSD and eMMC storage drives for PCs, and Western Digital is one of the leading suppliers in the industry.