Working with the Navajo Nation NASA is naming landmarks and discoveries by the Perseverance rover using the Native American language.
The idea of using light for computation is far from new, dating back to the 1950s. But electronic computing proved more practical to develop and commercialize. In the 1980s, Bell Labs tried to create a general purpose light-based chip, but it failed due to the difficulty of building a working optical transistor.
Lightmatter says its chips can be dropped into an existing data center and work with most major AI software. Later this year the company plans to launch a new technology for connecting chips, including those made by other companies, using its photonic technology. Light is widely used to shuttle information between computers, using fiber-optic cables.
Harris argues that AI will hit a wall in the next few years because of rising costs and energy use, and because of engineering constraints on the horizon. As engineers try to cram more transistors into a chip to speed up performance, chips may get too hot to manage.
WASHINGTON — Stefanie Tompkins on March 15 assumed the top post at the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
Tompkins is DARPA’s 23rd director.
She is a former military intelligence officer in the U.S. Army and previously worked at DARPA for nearly a decade. From 2007 until 2017 Tompkins served as program manager and deputy director of the agency’s Strategic Technology Office, DARPA chief of staff, as director of the Defense Sciences Office and as the acting deputy director of the agency.
The cryptomining protections have been bypassed using Nvidia’s own drivers.
Nvidia’s latest beta drivers unlock RTX 3060 Ethereum cryptocurrency mining. This is likely a mistake from Nvidia, as the company was trying to nerf mining performance with the RTX 3060.
A team of researchers has created software to detect illegal mining of cryptocurrency on computers.
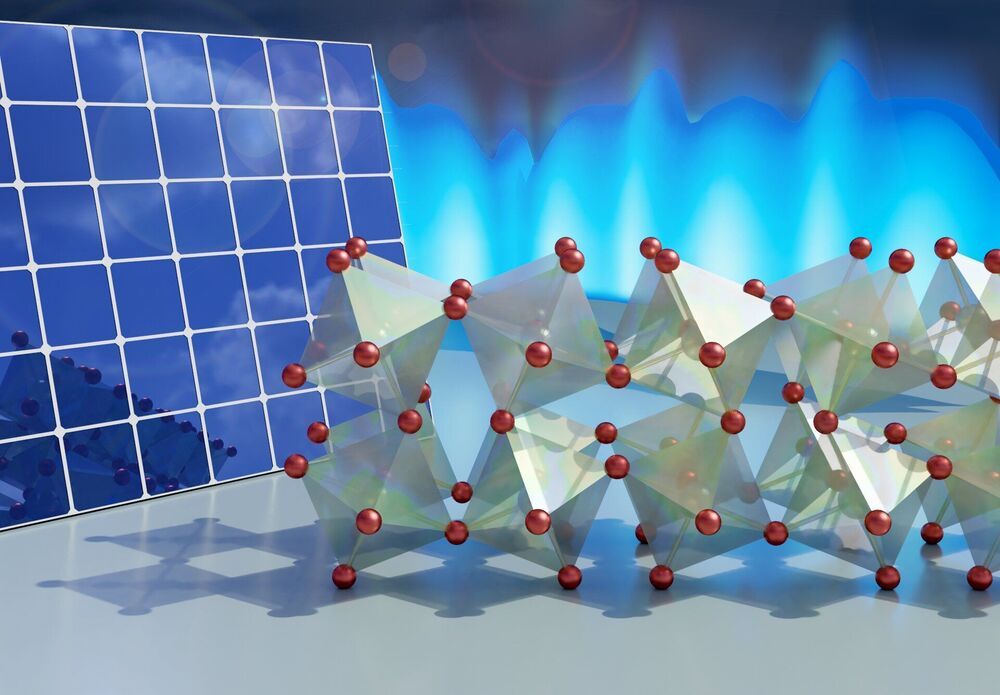
Researchers at Duke University have revealed long-hidden molecular dynamics that provide desirable properties for solar energy and heat energy applications to an exciting class of materials called halide perovskites.
A key contributor to how these materials create and transport electricity literally hinges on the way their atomic lattice twists and turns in a hinge-like fashion. The results will help materials scientists in their quest to tailor the chemical recipes of these materials for a wide range of applications in an environmentally friendly way.
The results appear online March 15 in the journal Nature Materials.
Cybersecurity researchers have unwrapped an “interesting email campaign” undertaken by a threat actor that has taken to distributing a new malware written in Nim programming language.
Dubbed “NimzaLoader” by Proofpoint researchers, the development marks one of the rare instances of Nim malware discovered in the threat landscape.
“Malware developers may choose to use a rare programming language to avoid detection, as reverse engineers may not be familiar with Nim’s implementation, or focused on developing detection for it, and therefore tools and sandboxes may struggle to analyze samples of it,” the researchers said.
In a world-first, a tattoo artist remotely needled a tattoo into a person in real-time using a 5G-powered robotic arm. Read it here.
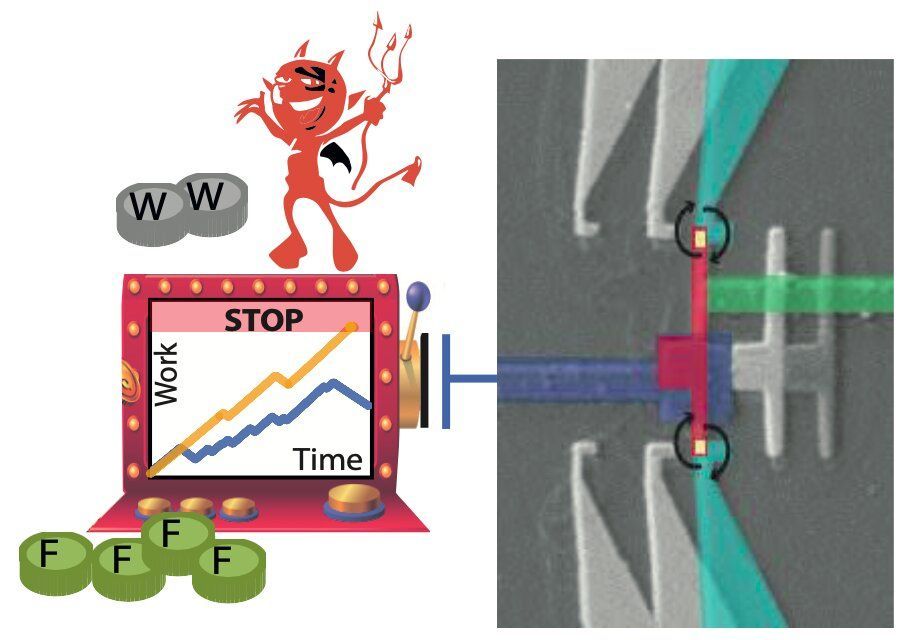
Researchers at the International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) in Italy and the PICO group at Aalto University in Finland have introduced the idea of an information demon that follows a customary gambling strategy to stop non-equilibrium processes at stochastic times. The new demons they realized, which differ from the renowned Maxwell’s demon, were presented in a paper published in Physical Review Letters.
“Our research was driven by curiosity,” Gonzalo Manzano, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “We asked ourselves about the implications of processes whose fluctuations fulfill (or break) some strong properties of stochastic processes on the link between thermodynamics and information.”
The recent study by Gonzalo Manzano, Edgar Roldan and their colleagues is based on previous works investigating the link between information and thermodynamics at the stochastic level. It also draws inspiration from recent research that explored the properties of a unique family of stochastic processes known as martingales in the context of thermodynamics.