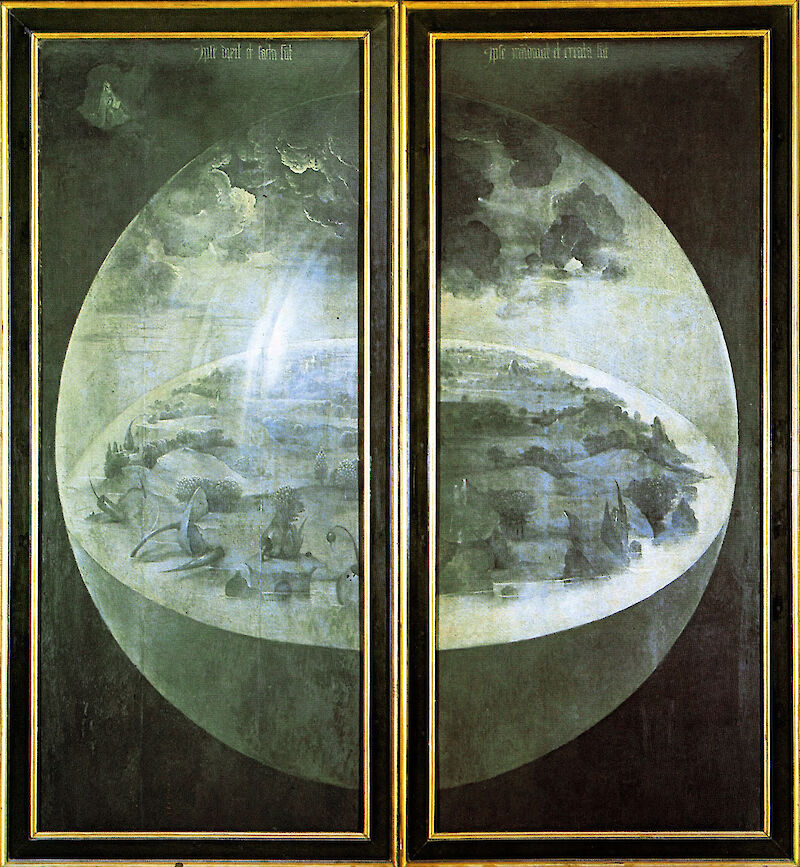
Right after the Big Bang, in the Planck epoch, the Universe occupied a space region with a radius of 1.4 × 10-13 cm – remarkably, equal to the fundamental length characterizing elementary particles. Analogue to the way nearly all cells contain the DNA information required to build the entire organism, every region the size of an elementary particle had then the energy necessary for the Universe’s creation.
As the Universe cooled down, electrons and quarks were the first to appear, the latter forming protons and neutrons, combining into nuclei in a mere matter of minutes. During its expansion, processes started happening slower and slower: it took 380,000 years for electrons to start orbiting around the nuclei, and 100 million years for hydrogen and helium to form the first stars. Even more, it wasn’t until 4.5 billion years ago that our young Earth was born, with its oceans emerging shortly after, and the first microbes to call them home for the first time. Life took over our planet in what seems, on the scale of the Universe, a sheer instant, and turned this world into its playground. There came butterflies and tricked the non-existence of natural blue pigment by creating Christmas tree-shaped nanometric structures in their wings to reflect blue’s wavelength only; fireflies and lanternfish which use the chemical reaction between oxygen and luciferin for bioluminescence; and it all goes all the way up to the butterfly effect leading to the unpredictability of the weather forecasts, commonly known as the reason why a pair of wings flapping in Brazil can lead to a typhoon in Texas. The world as we know it now developed slowly, and with the help of continuous evolution and natural selection, the first humans came to life.
Without any doubt, we are the earthly species never ceasing to surprise. We developed rationality, logic, strategic and critical thinking, yet human nature cannot be essentially defined without bringing into the equation our remarkable appetite for art and beauty. In the intricate puzzle human existence represents, this particular piece has given it valences no other known being possesses. Not all beauty is art, but many artworks both in the past, as well as today, embody some understanding of beauty.
To define is to limit, as Oscar Wilde stated, and even though we cannot establish clear definitions of art and beauty. Yet, great works of art manage to establish a strong thread between the creator and receptor. In contrast to this byproduct of human self-expression that encapsulates unique creative behaviour, beauty has existed long before our emergence as a species and isn’t bound to it in any way. It is omnipresent, a metaphorical Higgs field that can be observed by the ones who wish to open their eyes thoroughly. From the formation of Earth’s oceans and butterflies’ blue wings to Euler’s identity and rococo architecture, beauty is a subjective ubiquity. Though a question remains – why does it evoke such pleasure in our minds? What happens in our brains when we see something beautiful? The question is the subject of an entire field, named neuroaesthetics, which identified an intricate whole-brain response to artistic stimuli. As such, our puzzling reactions to art can be explained by these responses similar to “mind wandering”, involving “thoughts about the self, memory, and future”– in other words, art seems to evoke our past experiences, present conscious self, and imagination about the future. There needs to be noted that critics of the field draw attention to the superficiality and oversimplification that may characterize our attempts to view art through the lenses of neuroscience.